Short Answer Questions
Q1: Why is India called a subcontinent?
Ans: India is called a subcontinent because it has distinct geographical features like mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus, and coasts. It is also culturally and historically different from its neighbors.
Q2: How do natural boundaries affect India’s geography?
Ans: Natural boundaries like the Himalayas, deserts, and oceans protect India and influence its climate and biodiversity. They also help shape regional cultures and lifestyles.

Himalayas
Q3: What are the main features of the Himachal range?
Ans: The Himachal range has moderate height, rich biodiversity, and human settlements. It is home to popular hill stations like Shimla and Mussoorie.
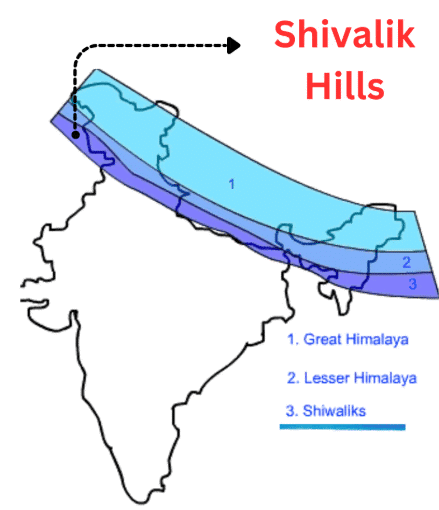
Q4: What role do the Shivalik Hills play in India’s geography?
Ans: The Shivalik Hills are the outermost part of the Himalayas and are covered with forests. They form the transition between the mountains and the Gangetic plains.
Q5: Describe the climate and terrain of Ladakh.
Ans: Ladakh is a cold desert with freezing winters and little rainfall. It has rocky terrain, high valleys, and lakes like Pangong Tso.
Q6: How do people in Ladakh adapt to their environment?
Ans: People in Ladakh use yaks for transport, wool, and milk. They celebrate local festivals and live simply due to harsh weather conditions.
Q7: What is the importance of rivers in the Gangetic Plains?
Ans: Rivers like the Ganga and Brahmaputra provide water for farming and daily use. They also carry minerals from the Himalayas that enrich the soil.
Q8: Why is the Thar Desert known for its unique lifestyle?
Ans: People in the Thar Desert use camels, store rainwater, and clean utensils with sand. These adaptations help them survive in the hot, dry climate.

Thar Desert
Q9: What is the historical importance of forts in the Aravalli Hills?
Ans: Forts like Chittorgarh and Ranthambore were built in the Aravalli Hills for defense. They show India’s rich historical and architectural heritage.
Q10: How is the Peninsular Plateau different from the Northern Plains?
Ans: The Peninsular Plateau is elevated and made of hard rocks, while the Northern Plains are flat and fertile. The plateau is rich in minerals and forests.
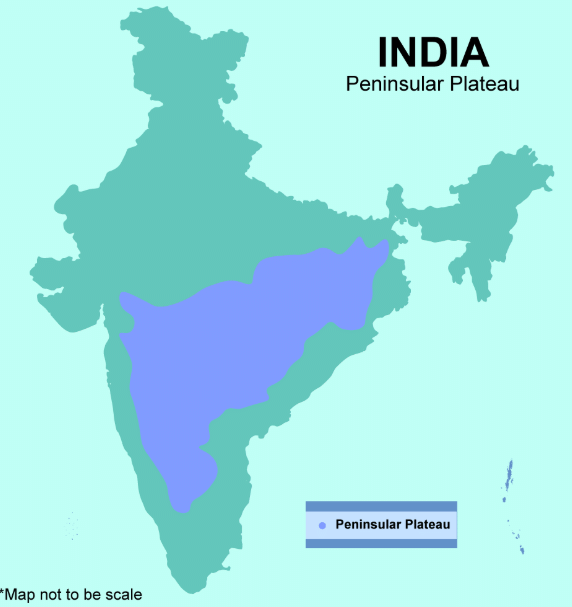
Peninsular Plateau
Long Answer Questions
Q1: How do India’s diverse physical features influence the way people live across the country?
Ans:
- India’s physical features—mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus, coasts, and islands—shape climate, agriculture, transport, and lifestyle.
- People in the mountains rely on terrace farming and wool, while those in plains farm extensively.
- Desert communities adapt with water conservation methods.
- Coastal areas engage in fishing and trade, while islanders depend on marine life.
- These geographical conditions also influence housing, clothing, food habits, and festivals.
Q2: Explain the economic and cultural importance of the Peninsular Plateau.
Ans:
- The Peninsular Plateau is rich in minerals like iron, bauxite, and manganese, which support mining and industries.
- Rivers such as the Krishna and Godavari provide water for farming and hydroelectric power.
- The region is home to tribal communities with unique traditions.
- Forests and wildlife here promote biodiversity and tourism.
- The plateau’s waterfalls and scenic beauty attract visitors, adding to its economic value.
Q3: What makes the Andaman and Nicobar Islands ecologically and strategically important?
Ans:
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are home to coral reefs, dense forests, rare wildlife, and ancient tribes.
- Barren Island, India’s only active volcano, is located here.
- These islands also have a strategic military importance due to their location near international sea routes.
- The naval base helps protect India’s maritime interests.
- The islands are also important for environmental studies and eco-tourism.
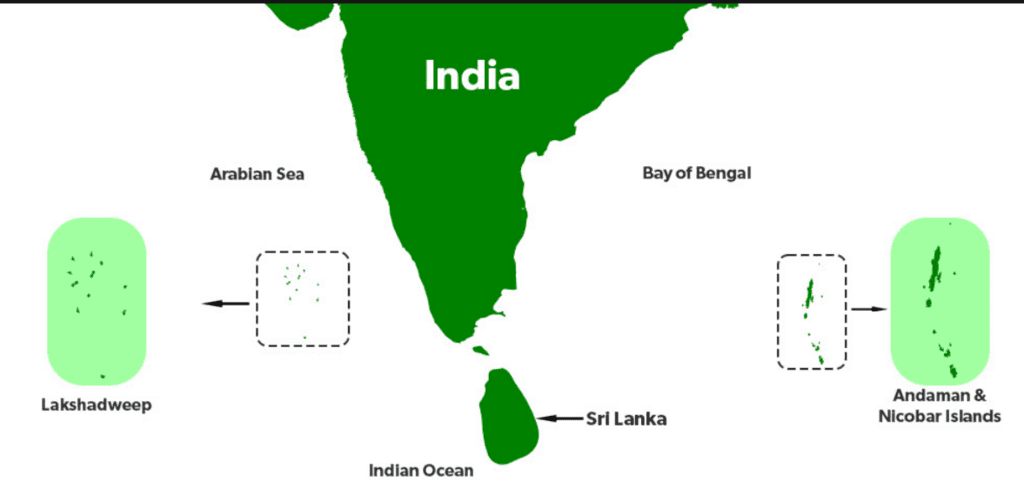
Islands of India
Q4: Describe the features and importance of India’s delta regions.
Ans:
- Deltas in India, like the Sundarbans in West Bengal and the Godavari Delta on the east coast, are formed by sediment deposits at river mouths.
- These regions are highly fertile and ideal for rice and jute cultivation.
- The Sundarbans is a UNESCO World Heritage Site with mangrove forests and the Royal Bengal Tiger.
- Deltas also protect coastal areas from storms and support fishing and farming communities.
Q5: How does high rainfall impact the lifestyle and environment of the Northeast region?
Ans:
- The Northeast receives some of the world’s highest rainfall, especially in places like Cherrapunji and Mawsynram.
- This supports thick forests, waterfalls, and a wide variety of plants and animals.
- The soil is fertile, allowing people to grow crops like rice, ginger, and pineapple.
- The heavy rainfall has led to the creation of unique features like living root bridges.
- Cultural festivals and eco-friendly lifestyles are also part of life in this region.