Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What was the main reason for the formation of new kingdoms after the Maurya Empire?
a) Rise of new empires
b) Internal conflicts and invasions
c) Religious conversion
d) Peace treaties
Ans: b) Internal conflicts and invasions
After the Maurya Empire collapsed, internal conflicts and foreign invasions led to the rise of new kingdoms.

Maurya Empire
Q2: Who started the Śhunga dynasty?
a) Ashoka
b) Chandragupta Maurya
c) Puṣhyamitra Śhunga
d) Dhanananda
Ans: c) Puṣhyamitra Śhunga
Puṣhyamitra Śhunga, a Mauryan commander, killed the last Maurya emperor and started the Śhunga dynasty.
Q3: What was the primary feature of the Śhunga Empire?
a) Large expansion across the subcontinent
b) Promotion of Buddhism
c) Revival of Vedic rituals
d) Invasion of the south
Ans: c) Revival of Vedic rituals
The Śhunga Empire revived Vedic rituals, such as the Ashvamedha yajña, and supported art and architecture.
King Rama Performing Ashwamedha Yajna
Q4: Which ancient city was the capital of the Sātavāhana dynasty?
a) Ujjain
b) Pataliputra
c) Amrāvatī
d) Kausambi
Ans: c) Amrāvatī
Amrāvatī was one of the capitals of the Sātavāhana dynasty, located in present-day Andhra Pradesh.
Q5: What was the primary trade item for the Sātavāhanas?
a) Spices
b) Gold
c) Pearls
d) Textiles
Ans: a) Spices
The Sātavāhanas traded spices, textiles, gold-plated pearls, and ivory, especially with the Roman Empire.
Q6: Which ruler of the Chedi dynasty was a supporter of Jainism?
a) Khāravela
b) Dhanananda
c) Chandragupta Maurya
d) Ashoka
Ans: a) Khāravela
King Khāravela of the Chedi dynasty was a follower of Jainism, known for his patronage of Jain culture.
Q7: What was the contribution of the Sātavāhanas to literature?
a) Development of Sanskrit literature
b) Promotion of Tamil poetry
c) Support for Sangam literature
d) Spread of Vedic texts
Ans: c) Support for Sangam literature
The Sātavāhanas supported Tamil literature, particularly the Sangam poems, which focused on love and heroism.
Q8: What role did the Indo-Greeks play in India?
a) They formed the first Indian empire.
b) They blended Greek and Indian cultures.
c) They conquered all of India.
d) They promoted Hinduism.
Ans: b) They blended Greek and Indian cultures.
The Indo-Greeks adopted Indian culture while introducing Greek styles in art, architecture, and governance.
Q9: Which famous art styles did the Kuṣhāṇas contribute to?
a) Gandhara and Mathura
b) Ajanta and Ellora
c) Mughal art
d) Rajasthani miniature painting
Ans: a) Gandhara and Mathura
The Kuṣhāṇas influenced the Gandhara and Mathura art styles, blending Indian and Greek elements.
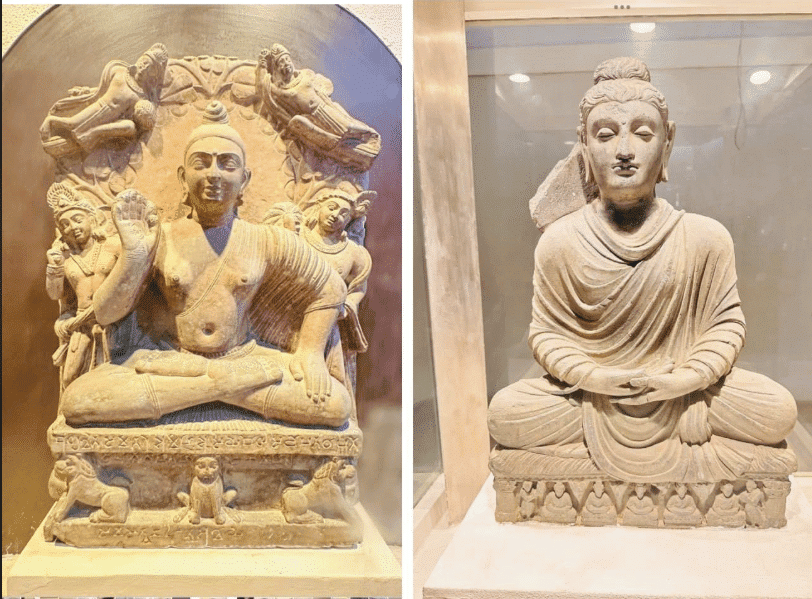
Gandhara and Mathura Art Styles
Q10: Which dynasty ruled parts of south India during the period of reorganisation?
a) Mauryas
b) Cholas
c) Guptas
d) Cheras, Cholas, and Pāṇḍyas
Ans: d) Cheras, Cholas, and Pāṇḍyas
The Cheras, Cholas, and Pāṇḍyas ruled parts of south India, boosting trade and culture.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The Śhunga dynasty was started by __________, a Mauryan commander.
Ans: Puṣhyamitra Śhunga
Puṣhyamitra Śhunga killed the last Maurya emperor and founded the Śhunga dynasty.
Q2: The Sātavāhanas ruled the __________ region.
Ans: Deccan
The Sātavāhanas controlled the Deccan region, which includes present-day Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Maharashtra)

Satavahana Coin
Q3: The __________ caves in Odisha were built by King Khāravela for Jain monks.
Ans: Udayagiri-Khandagiri
These caves have intricate carvings and are significant examples of Jain rock-cut architecture.
Q4: The __________ was a Vedic ritual performed by the Śhunga kings.
Ans: Ashvamedha yajña
The Ashvamedha yajña was performed by Śhunga rulers, where a horse roamed freely to claim land or establish dominance.
Q5: The Sātavāhanas were known for their __________, showing their trade connections.
Ans: Coins
The Sātavāhanas used coins that often depicted ships, indicating their strong maritime trade.
Q6: The Indo-Greek ruler __________ built the Heliodorus pillar in Madhya Pradesh.
Ans: Antialcidas
The Heliodorus pillar praises the god Vāsudeva and represents the blending of Greek and Indian cultures.

Heliodorus Pillar Near Vidisha
Q7: The __________ dynasty had an empire that stretched from Central Asia to northern India.
Ans: Kuṣhāṇa
The Kuṣhāṇa Empire was a Central Asian dynasty that significantly influenced northern India.
Q8: The __________ art style was influenced by the Kuṣhāṇas and mixed Indian and Greek elements.
Ans: Gandhara
Gandhara art, developed under the Kuṣhāṇas, combined Greek artistic techniques with Indian religious themes.
Q9: The __________ kingdom of south India was known for trading pearls with the Romans.
Ans: Pāṇḍya
The Pāṇḍyas were known for their prosperous pearl trade, especially with the Romans.
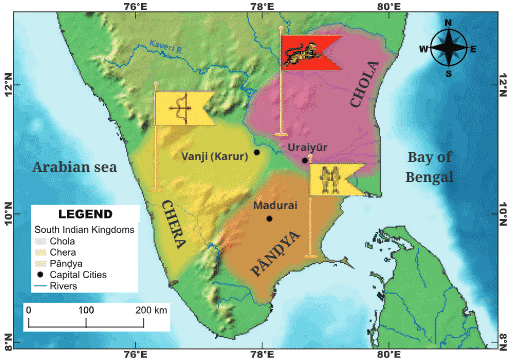
Chera, Chola, Pandya
Q10: The __________ period in south India is known for its Sangam literature.
Ans: Sangam
The Sangam Age produced Tamil poetry that described love, heroism, and social values.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: Who founded the Śhunga dynasty?
Ans: Puṣhyamitra Śhunga.
Q2: What were the Sātavāhana rulers known for in terms of trade?
Ans: They had strong maritime trade, trading spices and textiles.
Q3: Which ruler promoted Jainism in the Chedi dynasty?
Ans: Khāravela.
Q4: Where did the Indo-Greeks establish their presence in India?
Ans: Northwest India.
Q5: What was the major contribution of the Kuṣhāṇas to Indian art?
Ans: Gandhara and Mathura art styles.

Shunga Contribution to Art
Short Answer Questions
Q1: How did the Śhunga Empire influence Indian culture?
Ans: The Śhunga Empire revived Vedic rituals, promoted Sanskrit literature, and contributed to art by building the Bharhut Stūpa with beautiful carvings.
Q2: What role did trade play in the Sātavāhana Empire?
Ans: The Sātavāhanas thrived on trade, especially maritime trade, importing goods like glass and perfumes while exporting spices, textiles, and ivory.
Q3: How did the Indo-Greek rulers blend their culture with Indian traditions?
Ans: The Indo-Greeks adopted Indian culture, blending Greek and Indian artistic styles and religious practices, as seen in their coins and sculptures.
Q4: Why did the Sātavāhanas support multiple religions?
Ans: The Sātavāhanas, while supporting Vedic rituals, allowed Jains, Buddhists, and other groups to thrive by providing them with land and patronage.
Q5: What was the significance of the Kalinga War in Ashoka’s life?
Ans: The Kalinga War led Ashoka to embrace Buddhism and non-violence, promoting peace and moral governance through his edicts.
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)

Ans: Matched Pairs and Explanations:
- 1 → d: Puṣhyamitra Śhunga revived Vedic rituals and expanded the Śhunga Empire.
- 2 → b: The Sātavāhanas thrived on trade, particularly in spices and textiles with foreign countries.
- 3 → c: Khāravela built Jain rock-cut caves in Odisha and supported Jainism.
- 4 → a: The Indo-Greeks contributed to Gandhara art, blending Greek and Indian elements.
- 5 → e: The Kuṣhāṇas promoted Jainism, Buddhism, and art, blending Indian and Greek styles.