Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: If the area of an object is less than the pressure acting on that object will be
(a) Less
(b) More
(c) Independent of area
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Pressure is defined as force divided by area (P = F / A). For a given force, if the area decreases the value of P increases. Therefore, when the area is smaller, the pressure on the object is greater.
Q2: Even though stone also attracts earth towards itself, earth does not move
(a) Because of greater mass of earth
(b) Because of lesser mass of stone
(c) Force exerted by stone is less
(d) Force exerted earth is large
Ans: (a)
Explanation: The stone and Earth attract each other with equal forces (Newton’s third law). However, acceleration = force/mass. Because the Earth has a very large mass, the acceleration produced in Earth by the stone’s pull is extremely small and thus not noticeable.
Q3: Which of the statements is correct?
(a) Mass is constant and weight is variable
(b) Mass is variable and weight is constant.
(c) Both Mass and weight are variable
(d) Both Mass and weight are constant.
Ans: (a)
Explanation: Mass is an intrinsic property of matter and does not change with location. Weight is the force due to gravity on that mass (W = mg) and depends on the local gravitational acceleration g, so weight can change with place (for example, on the Moon or at different heights).
Q4: Weight of the object is:
(a) More at the equator and less at poles
(b) More at poles and less at equator
(c) Same at poles and equator
(d) Depend on Mass of the object
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Effective weight depends on local gravitational acceleration. Two factors make weight slightly greater at the poles than at the equator: (i) centrifugal effect of Earth’s rotation reduces apparent gravity at the equator, and (ii) Earth is slightly flattened at the poles which affects g. Hence weight is more at the poles and less at the equator for the same mass.
Q5: An object is put one by one in three liquids having different densities. The object floats with 1/9, 2/11 and 3/7 parts of their volumes outside the liquid surface in liquids of densities d1, d2 and d3respectively. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) d1 > d2 > d3
(b) d1 > d2 < d3
(c) d1 < d2 > d3
(d) d1 < d2 < d3
Ans: (a)
Explanation: If a fraction fout of volume is outside, the submerged fraction is 1 – fout. The submerged fraction is proportional to the liquid’s density (for the same object). Submerged fractions here are 8/9 (≈0.889), 9/11 (≈0.818), and 4/7 (≈0.571). These numbers show d1 > d2 > d3, so option (a) is correct.
Q6: In the relation F = GM mld2, the quantity G
(a) depends on the value ofg at the place of observation
(b) is used only when the Earth is one of the two masses
(c) is greatest at the surface of the Earth
(d) is universal constant of nature
Ans: (d)
Explanation: G is the universal gravitational constant. Its value does not depend on location, nor on the masses involved. It is the same for all pairs of masses anywhere in the universe.
Q7: Law of gravitation gives the gravitational force between
(a) the Earth and a point mass only
(b) the Earth and Sun only
(c) any two bodies having some mass
(d) two charged bodies only
Ans: (c)
Explanation: Newton’s law of universal gravitation applies to any two masses anywhere: it gives the mutual gravitational force between any pair of masses, not only Earth-related pairs.
Q8: The value of quantity G in the law of gravitation
(a) depends on mass of Earth only
(b) depends on radius of Earth only
(c) depends on both mass and radius of Earth
(d) is independent of mass and radius of the Earth
Ans: (d)
Explanation: The universal constant G is independent of the properties of Earth or any other body. It is a fundamental constant of nature and has the same value everywhere.
Q9: Two particles are placed at some distance. If the mass of each of the two particles is doubled, keeping the distance between them unchanged, the value of gravitational force between them will be
(a) 1/4 times
(b) 4 times
(c) 1/2 times
(d) unchanged
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Gravitational force 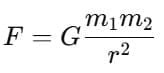 If both masses are doubled, the product m1 × m2 becomes 4 times larger, so the force becomes 4 times the original.
If both masses are doubled, the product m1 × m2 becomes 4 times larger, so the force becomes 4 times the original.
Q10: The atmosphere is held to the Earth by
(a) gravity
(b) wind
(c) clouds
(d) Earth’s magnetic field
Ans: (a)
Explanation: The atmosphere is retained around the Earth because of Earth’s gravitational attraction on air molecules. Wind or clouds do not hold the atmosphere; Earth’s magnetic field affects charged particles but not the neutral gases of the atmosphere.
Fill in the blank
(i) The value of g on the earth is about Six times of that on the moon.
(ii) In fluids (liquids and gases), pressure acts in All directions, and pressure increases as the depth increases.
(iii) If the area of a snow shoe is five times Bigger than the area of an ordinary shoe, then the pressure of a snow shoe on the snow is five times smaller.
(iv) Force acting on a unit area is called Pressure.
(v) The weight of an object on the earth is about Six times of its weight on the moon.
Crossword
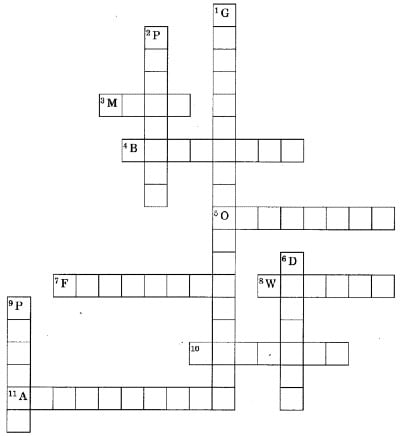
Across
3. Quantity of matter contained in a body
4. The property due to which a body immersed in fluid experiences upward force.
5. Acceleration due to gravity of moon is how much time that of Earth
7. Whenever objects fall towards the Earth under gravitational force alone, we say that objects are in
8. The force with which a body is attracted towards the Earth
10. Force of gravitation due to Earth is called
11. Nature of gravitational force is always
Down
1. Force between two bodies due to their masses
2. Thrust on unit area
6. Mass per unit volume
9. SI unit of pressure
Ans:
Across:
3. Mass
4. Buoyancy
5. One sixth
7. Free fall
8. Weight
10. Gravity
11. Attractive
Down:
1. Gravitational force
2. Pressure
6. Density
9. Pascal
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: A man of mass 60 Kg is standing on the floor holding a stone weighing 40 N. What is the force with which the floor is pushing him up?
Ans: The gravitational pull on the man = Mg
= 60 × 10 = 600 N
The weight he is carrying (stone) = 40 N
Total downward force on the floor = 600 N + 40 N = 640 N
By Newton’s third law and equilibrium, the floor pushes the man upward with a force of 640 N.
Q2: State Archimedes Principle?
Ans: According to Archimedes’ principle, when a body is partially or completely immersed in a fluid, it experiences an upthrust (buoyant force) equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body.
Q3: Why does a block of plastic released under water come up to the surface of water?
Ans: The density of the plastic is less than the density of water. Therefore the buoyant force on the plastic (which depends on the fluid displaced) is greater than the weight of the plastic, and the net upward force makes the block rise to the surface and float.
Q4: Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
Ans: A flat sheet of paper has a much larger surface area facing the air, so it experiences greater air resistance (drag). This larger opposing force slows its fall. A crumpled ball has a smaller area and encounters less air resistance, so it falls faster.
Q5: Why is it difficult to hold a schoolbag having a strap made of a thin and strong string?
Ans: A thin strap concentrates the bag’s weight on a small area of the shoulder. Pressure = force / area, so a smaller contact area gives a larger pressure on the shoulder, which feels painful and makes it difficult to hold.
Q6: What makes a body to float or sink in a liquid?
Ans:
- When an object is immersed in a liquid, it experiences its weight acting downward and an upthrust (buoyant force) from the liquid acting upward.
- If the weight of the body is greater than the upthrust, the object sinks.
- If the weight of the body is less than the upthrust, the object floats.
- If the weight equals the upthrust, the object remains neutrally buoyant (suspends at that depth).
Q7: What is the importance of universal law of gravitation?
The universal law of gravitation is important due to the following:
Ans:
- This law explains why objects stay on Earth – the force that binds us to Earth.
- It describes the motion of planets around the Sun and satellites around planets.
- It accounts for the tides on Earth caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun.
- It explains why the Moon moves around the Earth under gravitational attraction.
Q8: What happens to the force between two objects, if
(i) The mass of one object is doubled?
(ii) The distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
(iii) The masses of both objects are doubled?
Ans:
(i) The force between two objects will be doubled (force ∝ product of masses).
(ii) If distance is doubled, force becomes 1/4 of the original (since force ∝ 1 / r2). If distance is tripled, force becomes 1/9 of the original.
(iii) If both masses are doubled, the force becomes 4 times the original (product of masses increases by 4).
Q9: State the universal law of gravitation.
According to Newton’s universal law of gravitation:
Ans: Every mass in the universe attracts every other mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centres.
Q10: What do you mean by buoyancy?
Ans: Buoyancy (or upthrust) is the upward force experienced by an object when it is wholly or partially immersed in a fluid. It equals the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.