Introduction Do you know, what is the shape of a rock? Can you change its shape or see through it? When we look around, we see objects with various properties: some are shiny, while others are dull; some are hard, while others are soft.
These properties depend on the materials they are made from. Let’s explore the different materials and understand how their properties determine their use in everyday life.

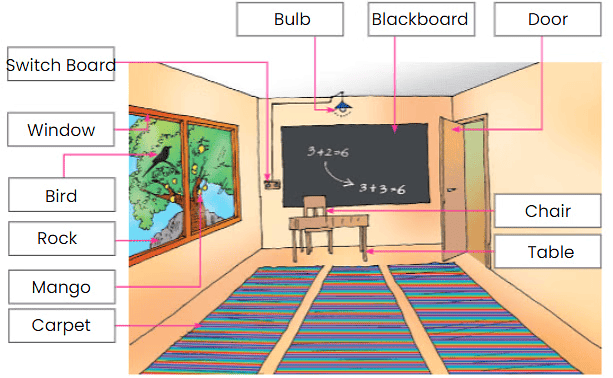
Explanation Let’s Take a Look Around Us!
- Khushi notices her classroom is filled with various objects made of different materials.
- She wonders where they come from and what they are made of.
- Tables and chairs are made of wood, while door hinges, nails, and latches are made of metals.
- Metals are extracted from the Earth.
- Glass is mostly made of sand!
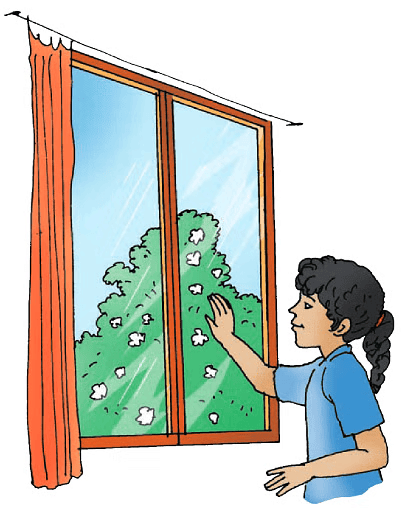
See-through Materials!
Khushi saw the tree and beautiful flowers. She tried to touch them but her hand touched the glass. She realised that she can see through the glass. She understands that there are two types of objects. i.e
1. See-Through: Objects that let light pass through them, so you can see what’s on the other side.
2. Clear: These objects are clear and don’t block your view.
Types of Materials
1. Transparent: These materials allow light to pass through them clearly, so you can see through them easily. Example: Glass windows, Spectacles.

2. Translucent: These materials are those that let some light through but not enough to see through them. Example: Frosted glass, thin plastic.

3. Opaque: These materials do not allow light to pass through, making it impossible to see through them. Example: Wood, Book.
What is it made of? Different things are made of different materials. They also sound different when they are hit by an object.

Does it Bend? Khushi’s table is made of wood. And the table is strong and cannot bend. Bending happens when you push or pull on something, and it bends like a piece of rubber or a paperclip. If it can bend without snapping, it’s flexible.
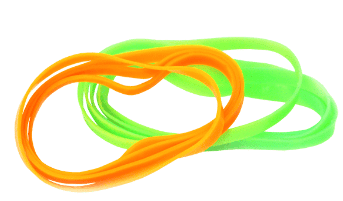
1. Flexible (Can Bend): These materials can be bent easily without breaking. Example: Fabric, rubber.
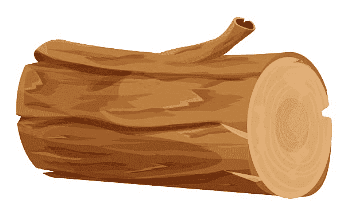
2. Rigid (Cannot Bend): These materials are hard and do not bend easily. Example: Glass, Wood, metal.
Try yourself:Which type of material allows light to pass through them clearly, so you can see through them easily?
- A.Transparent
- B.Translucent
- C.Opaque
- D.Rigid
View Solution
In Khushi’s classroom, she looks at different materials, like wood for tables. She wonders if fabric or rubber could be used to make tables, showing the real-world uses of material properties. For example:
- Wood: Hard and rigid.
- Fabric: Soft and flexible.

This flexibility makes fabric better for making clothes and curtains, think what it would be like if clothes were made of wood?
Does it Flow?
Flow tells how liquids, gases, and other things move. It means moving smoothly without stopping.
1. Solids (Do Not Flow): Solids don’t flow like liquids or gases. They keep their shape and don’t move to fit a container. Example: Wood, metal.

2. Liquids (Flow): Liquids can flow easily. When you pour water into a cup, it moves smoothly and takes the shape of the cup. This is because liquids don’t have a fixed shape and can flow to fit their container. Example: Water, milk.

3. Gases (Flow Freely): Gases flow around us, filling any space it can find. It doesn’t stay in one place like a liquid; instead, it moves freely and can spread out quickly. Example: Air, helium.
Natural – Artificial
- Natural materials are found in nature without any human involvement.
- They can be living (like plants and animals) or non-living (like rocks, water, and air).
- Examples include wood (from trees) and metals (taken from ores).

- Artificial materials are made by humans, often from natural resources.
- Examples include plastic (from petroleum), fabrics (like nylon and polyester), and metal alloys (like steel and brass).
- Materials like petrol and rubber create non-biodegradable waste.
- These materials are used to create many everyday items.
Try yourself:Which type of material takes the shape of its container and flows?
- A.Solids
- B.Liquids
- C.Gases
- D.Artificial materials
View Solution
Points To Remember
1. Metals come from ores extracted from the Earth. ie. iron, copper, gold, and silver are different materials.
2. Materials can be classified as transparent, opaque, or translucent based on how much light passes through them.
3. Solid materials hold their shape, liquids flow, and gases spread out to fill their container.
4. Natural materials exist in nature, while artificial materials are created by humans.
5. Some materials, like rubber and wax, can be both natural and artificial.
6. Understanding the properties of materials helps us know what they can be used for.
Difficult Words
1. Transparent: A material that you can see through clearly, like glass.
2. Opaque: A material that you cannot see through, like wood.
3. Translucent: A material that you can partially see through, like frosted glass.
4. Materials: The substances used to make things, like wood or plastic.
5. Alloys: Mixtures of two or more metals, like steel. –
6. Biodegradable: Materials that can break down naturally in the environment.