Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What was the main problem with the barter system?
a) Lack of variety of goods
b) Double coincidence of wants
c) Lack of trust between traders
d) Inability to measure value
Ans: b) Double coincidence of wants
In the barter system, both parties had to have what the other wanted, which made trade difficult and rare.

Barter System
Q2: What is money primarily used for?
a) To save for future use
b) To measure value
c) To buy and sell goods and services
d) To store commodities
Ans: c) To buy and sell goods and services
Money is primarily used as a medium of exchange, allowing goods and services to be bought and sold easily.
Q3: Which of these is an example of modern digital money?
a) Cowrie shells
b) Wheat
c) UPI
d) Paper notes
Ans: c) UPI
UPI (Unified Payments Interface) is a form of digital money used for instant bank transactions.
Q4: What is the main reason why money is more efficient than the barter system?
a) Money can be saved and used later
b) Money is harder to carry
c) Money only works with coins
d) Money has no value
Ans: a) Money can be saved and used later
Money allows for transactions over time, as it can be stored and used for future purchases, unlike goods in barter.
Q5: Which of the following was one of the earliest forms of money?
a) Digital currency
b) Cowrie shells
c) Coins with currency symbols
d) Banknotes
Ans: b) Cowrie shells
Cowrie shells were used in ancient times as a form of money for trade.
Q6: What does the term “medium of exchange” refer to?
a) A tool used to measure trade
b) A method to store wealth
c) Something that is accepted for buying and selling
d) A product for trade
Ans: c) Something that is accepted for buying and selling
A medium of exchange is something widely accepted for buying and selling goods and services.
Q7: Which item was commonly used as money in ancient India?
a) Cattle
b) Paper notes
c) Digital codes
d) Credit cards
Ans: a) Cattle
In the barter system, cattle were commonly used as a form of trade for goods and services.

Digital Currency
Q8: What is the main advantage of money over bartering goods like wheat or cattle?
a) Money is portable, divisible, and durable
b) Money can be eaten
c) Money is easier to store than goods
d) Money does not need to be traded
Ans: a) Money is portable, divisible, and durable
Money is easy to carry, can be divided into smaller units, and does not spoil or rot like perishable goods.
Q9: What did John Maynard Keynes say about money?
a) Money is only useful for buying goods
b) Money connects the present to the future
c) Money is not important for trade
d) Money should only be used in the form of coins
Ans: b) Money connects the present to the future
Keynes emphasized that money helps us save for future needs and plan for later use.
Q10: What was one problem with using cattle in the barter system?
a) Cattle were not accepted by all traders
b) Cattle could be divided into smaller parts
c) Cattle rotted quickly
d) Cattle were difficult to transport
Ans: d) Cattle were difficult to transport
Cattle were large and difficult to move over long distances, making them inefficient for trade.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The barter system was inefficient because it required a ________ of wants.
Ans: Double coincidence
In the barter system, both parties had to want what the other had, which made successful exchanges rare.
Q2: Money solves the problems of the barter system by being ________, meaning it can be carried easily.
Ans: Portable
Money is portable, unlike large goods like cattle, making it easier to carry and use in trade.
Q3: In the barter system, a farmer could not split an ________ into smaller units for trade.
Ans: Ox
Items like oxen were not divisible, which made them unsuitable for smaller trades in the barter system.
Q4: The modern form of money used in transactions is ________ currency.
Ans: Paper
Paper currency is widely used today for transactions, unlike the ancient forms of money like coins or shells.
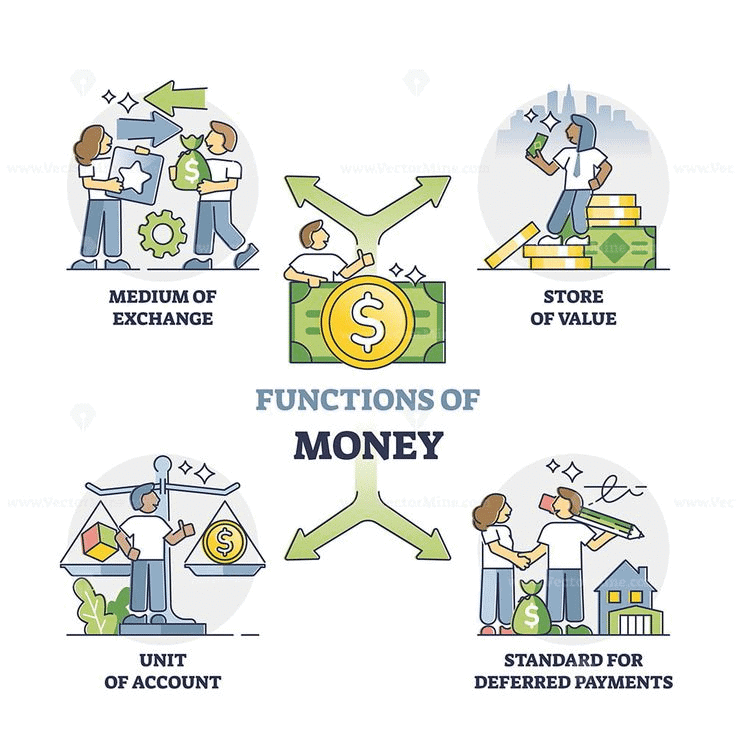
Q5: One early form of money used in ancient India was called ________ or panas.
Ans: Kārshāpanas
Ancient Indian coins, known as kārshāpanas or panas, were used in trade and often had symbols like animals and gods.
Q6: ________ is an example of digital money that allows users to transfer money between accounts.
Ans: UPI
UPI (Unified Payments Interface) is a form of digital money that allows seamless transactions between bank accounts.
Q7: The ________ is the symbol used on Indian banknotes, designed in 2010.
Ans: ₹
The ₹ symbol represents the Indian Rupee and was designed in 2010 to symbolize India’s currency.
Q8: The ________ system, introduced in ancient China, was the first use of paper money.
Ans: Paper currency
Paper currency was first introduced in China and later in India by the Bank of Bengal in the late 18th century.
Q9: A major disadvantage of using the barter system was that goods like ________ could spoil quickly.
Ans: Wheat
Perishable goods like wheat could spoil or get eaten by pests, making them unsuitable for long-term trade.
Q10: The modern form of payment involving scanning a ________ code is called digital money.
Ans: QR
QR codes are used for digital money transactions, making it easier for consumers to pay without physical money.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What was the primary problem with the barter system?
Ans: The main problem was the double coincidence of wants.
Q2: What does “money as a store of value” mean?
Ans: Money can be saved and used later, unlike perishable goods.
Q3: How did the invention of money help in trade?
Ans: Money made trade easier by solving the issues of portability, divisibility, and value measurement.
Q4: What is the modern equivalent of money used in daily transactions?
Ans: Modern money includes coins, notes, and digital payments like UPI.
Q5: What does “durability” mean in the context of money?
Ans: Money can last for a long time without spoiling, unlike perishable goods in the barter system.

Paper Currency
Short Answer Questions
Q1: Why was the barter system not effective for long-distance trade?
Ans: The barter system was ineffective for long-distance trade because goods like cattle were hard to transport, and the double coincidence of wants was difficult to find.
Q2: Explain the difference between the barter system and money.
Ans: The barter system required a mutual need for goods, while money is a common, portable, and divisible medium of exchange, making trade more efficient.
Q3: What was the first form of paper currency used in India?
Ans: Paper currency was introduced in India in the late 18th century by banks like the Bank of Bengal and Bank of Bombay.
Q4: How did money evolve from coins to digital money?
Ans: Money evolved from coins made of precious metals to paper currency and now to digital money like UPI and mobile payments for easier transactions.
Q5: How did John Maynard Keynes describe the role of money?
Ans: John Maynard Keynes described money as a means to connect the present with the future, helping people save and spend later.
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)
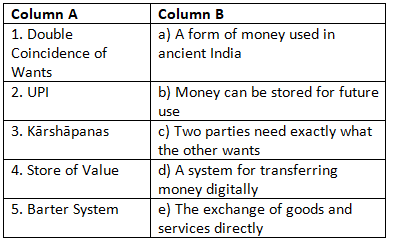
Ans: Matched Pairs and Explanations:
- 1 → c: Double Coincidence of Wants means both parties need what the other offers.
- 2 → d: UPI is a system for transferring money digitally.
- 3 → a: Kārshāpanas were coins used in ancient India for transactions.
- 4 → b: Store of value means money can be saved for future use.
- 5 → e: Barter system is the direct exchange of goods and services.