IntroductionImagine you’re exploring a world full of shapes, patterns, and fun designs.
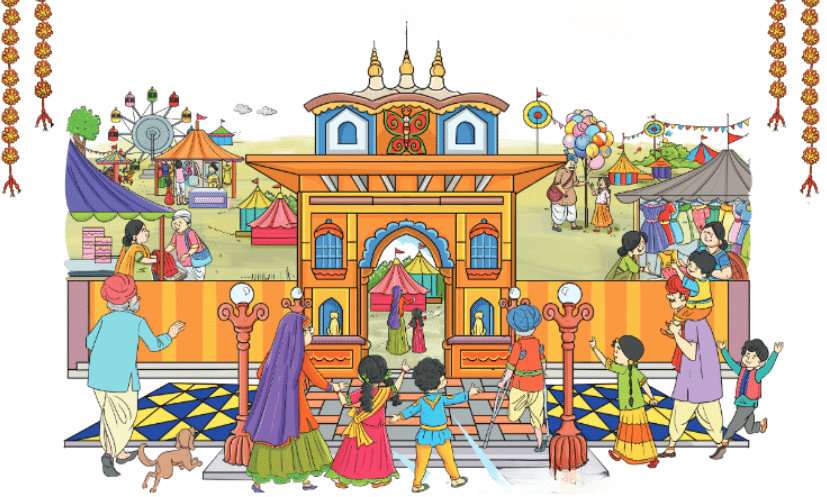
Soni and Avi are going to the famous Surajkund fair in Faridabad with their grandparents, where the fair is filled with exciting stalls, games, and activities. In this chapter, we will learn about the things they see at the fair, like symmetrical objects, patterns, and making malas, while also discovering the magic of shapes and directions that make everything more organised and exciting!
In this chapter, we will learn about symmetry, patterns, and how to read maps—just like Soni and Avi!

Understanding Symmetry
Soni: “Dadaji, look at that butterfly! Its wings look exactly the same!”
Dadaji: “That’s because it is symmetrical, Soni! If you draw a line down the middle, both sides will match like a mirror image.”
Now, let’s understand What is Symmetry?Symmetry means that a shape can be divided into two identical parts, like a mirror image.
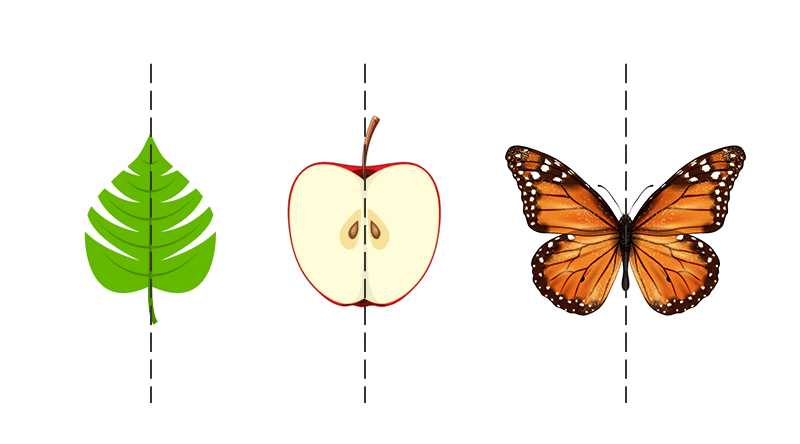
Example:
- A butterfly – If you draw a line down the middle, both wings look the same.
- An apple – If you cut an apple, both halves look the same.
Try out yourself:
Look at the shape of a heart. If you draw a line down the middle, what do you notice? Do both sides of the heart look the same?
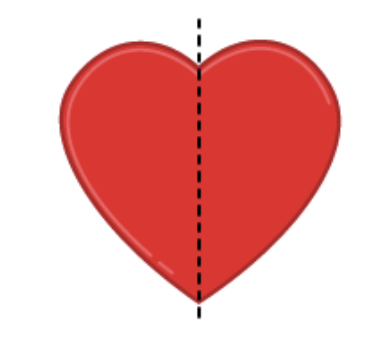
Solution:
When you draw a line down the middle of the heart, you’ll see that both sides of the heart look identical. This shows symmetry, as the two halves are mirror images of each other!
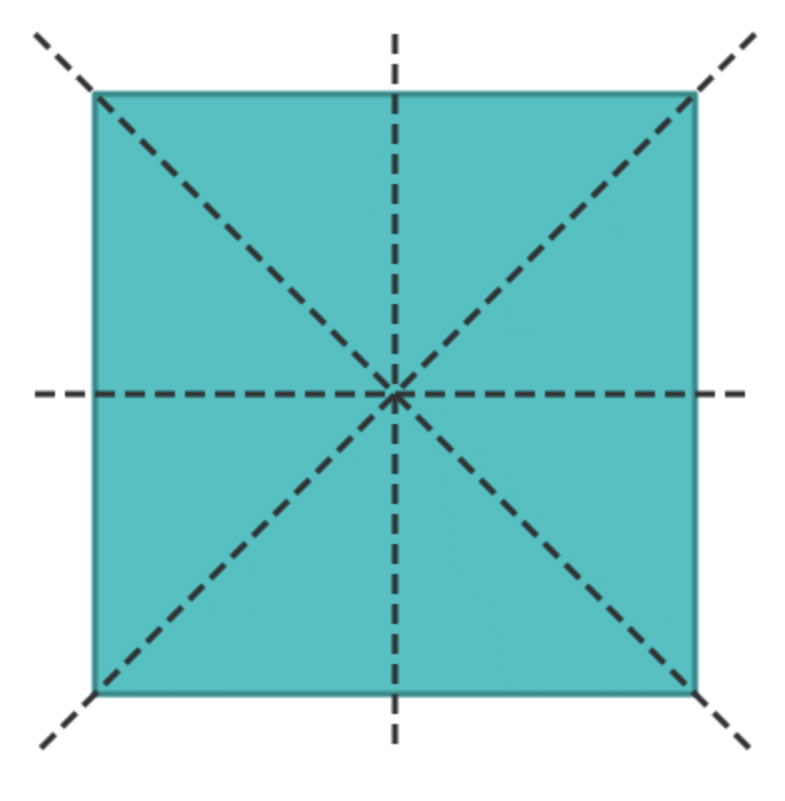
Line of Symmetry:A line of symmetry is an invisible line that splits a shape into two equal halves.
Fun Fact: Some shapes have more than one line of symmetry!
For Example:
- Square: Has four lines of symmetry.
- Heart: Has one line of symmetry.
- Butterfly: Has one line of symmetry.
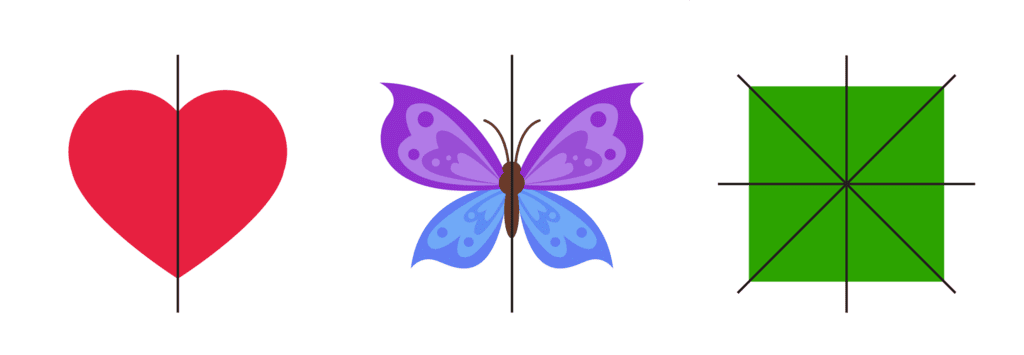
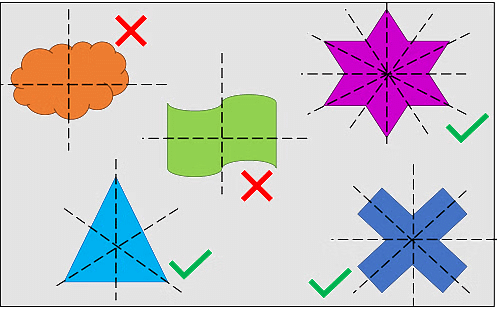
Let’s explore more objects and understand their symmetry.
- So, the three figures in the images above are symmetric, meaning that if cut along the dotted line, both halves will match when folded.
- While two figures when cut along the dotted line and the parts do not align when folded so they are asymmetric.
Try yourself:Which of the following shapes has three lines of symmetry?
- A.Square
- B.Rectangle
- C.Equilateral Triangle
- D.Circle
View Solution
Mirror Images
When we look into a mirror, we see our reflection! The right side of our body appears on the left, and the left side appears on the right.
Try This: Stand in front of a mirror and raise your right hand. What happens? The mirror shows it as your left hand!
Mirror Images of Capital Letters and Numbers
- Certain letters and numbers have mirror images that look exactly like their originals.
- For example, letters like A, H, M, and numbers like 0 and 8 have mirror images that are the same as their original forms.


- The key concept is that if an object will be symmetric, its two halves will be identical or mirror each other.
Examples of Non-Symmetrical Letters and Numbers
- Not all letters and numbers have symmetrical mirror images.
- For instance, letters like B, C, D and numbers like 2, 3, 5 do not have mirror images resembling their original forms.
This contrast helps clarify the idea of symmetry.
Try out yourself:
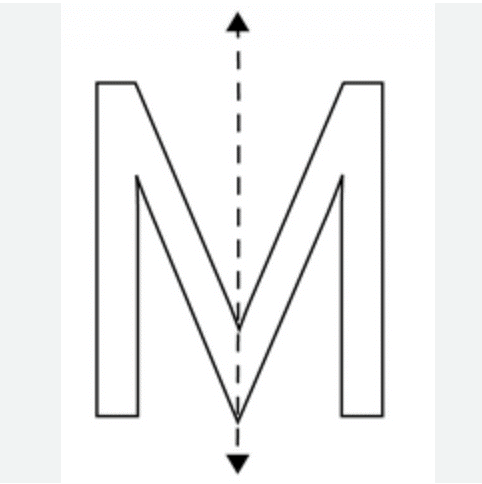
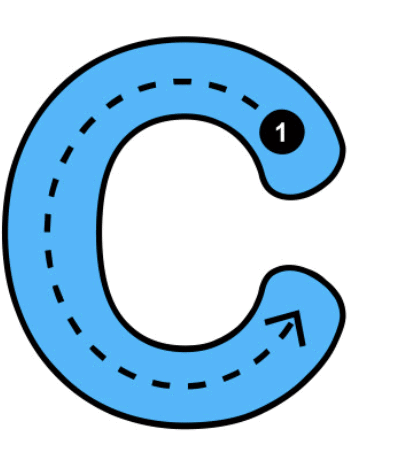
Is the letter “M” symmetrical when you look at it in the mirror? What about the letter “C”?
Solution:
The letter “M” looks the same in the mirror, as it has symmetrical mirror images. However, the letter “C” does not look the same in the mirror, showing that “C” is not symmetrical.
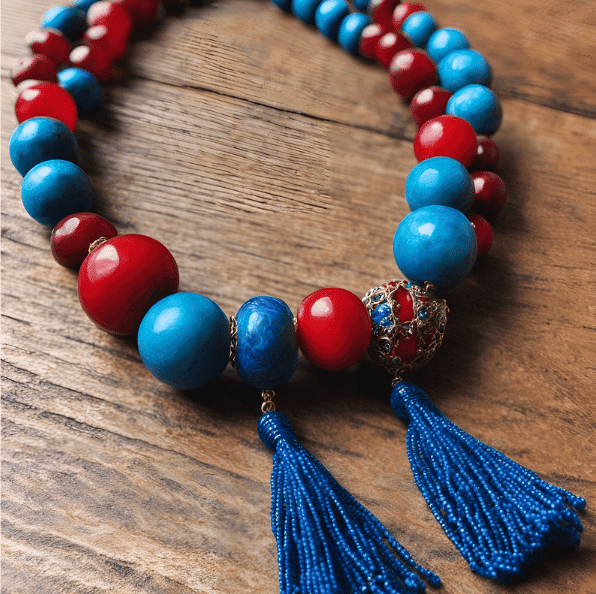
Making Malas (Bead Necklaces)
At a bead stall, Soni and Avi see a man and a woman making beautiful malas (necklaces).
Question:
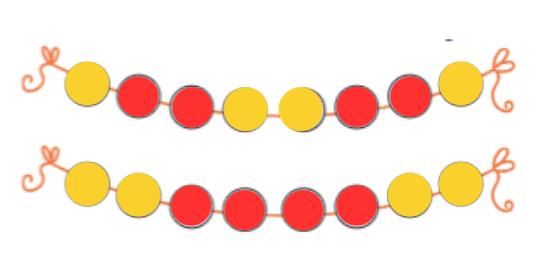
How can you make a simple mala (necklace) using 8 beads?
Solution:
To make a simple mala, take 8 beads—4 of one color and 4 of another. String them in a pattern like red-blue-red-blue, and tie a knot. Your mala is ready to wear!
Rangolis and PatternsSoni and Avi arrive at a stall from Tamil Nadu, where they see lovely kolam designs being created. Kolam is a traditional art that involves drawing detailed patterns on the ground, often using rice flour. They notice that some of the rangolis are symmetrical, while others are not. They learn to make their own symmetrical rangolis by drawing lines that split the designs into two matching halves.
Try yourself:
Which of the following letters has a mirror image that looks the same as its original form?
- A.B
- B.D
- C.A
- D.G
View Solution
Exploring the Fair with a Map
Soni and Avi are visiting Surajkund in the Faridabad district of Haryana. This chapter teaches how to use maps effectively. Soni and Avi navigate the fair using a map, learning to interpret signs and symbols to find places like the restaurant, shops, and play area.
Let’s Understand using an example:
While enjoying the Surajkund fair, Soni and Avi realised they had lost track of their Dada and Dadi. Suddenly, they heard an announcement: “Soni and Avi’s Dada and Dadi are waiting at the Chaupal for them.”
Excited to reunite, Soni and Avi decided to follow the directions on the map to reach the Chaupal.
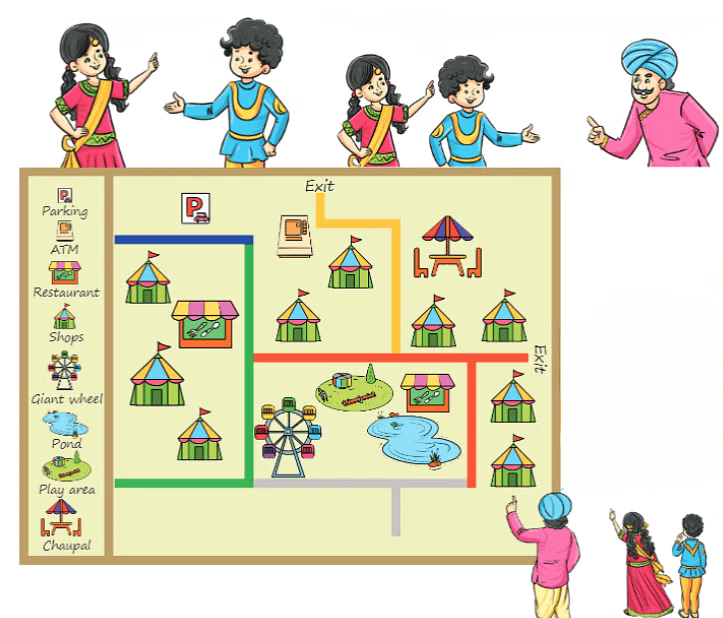
- They started by walking on the blue lane.
- Next, they turned right onto the green lane.
- Soon, they saw a restaurant on their right, but they remembered not to stop there.
- They took a left towards the red lane.
- After that, they found the golden lane and took the first left turn, passing colourful stalls selling exciting items.
- Continuing past the stalls, they aimed to find the Chaupal and meet Dada and Dadi.
Soni and Avi’s visit to the Surajkund fair was not just enjoyable but also a valuable learning experience. They explored concepts like symmetry, pattern making, and using maps for navigation. The fair was vibrant and thrilling, showcasing the beauty of symmetry in their surroundings.
Let’s Practise
1.Which of the following objects has more than one line of symmetry?
(a) Heart
(b) Butterfly
(c) Square
(d) Letter B
Answer: c) Square (A square has four lines of symmetry.)
2.What happens when you look at your reflection in a mirror?
(a) Your image flips upside down
(b) Your left side appears on the right and vice versa
(c) Your size changes
(d) The reflection looks exactly like the original without any change
Answer: b) Your left side appears on the right and vice versa (A mirror reverses left and right, not upside down.)
3.Which of these letters has a symmetrical mirror image?
(a) R
(b) M
(c) G
(d) P
Answer: b) M (Letters like A, H, M have symmetrical mirror images.)

4.What is the correct sequence to create a symmetrical bead mala?
(a) Red, Red, Blue, Blue, Red, Red, Blue, Blue
(b) Red, Blue, Red, Blue, Red, Blue, Red, Blue
(c) Red, Red, Red, Blue, Blue, Blue, Red, Blue
(d) Blue, Blue, Red, Red, Blue, Red, Blue, Red
Answer: b) Red, Blue, Red, Blue, Red, Blue, Red, Blue (This pattern is symmetrical because it repeats evenly on both sides.)

5. How did Soni and Avi find their way to the Chaupal at the fair?
(a) By asking people for directions
(b) By following a map and recognizing symbols
(c) By walking randomly until they found it
(d) By using a mobile GPS
Answer: b) By following a map and recognizing symbols (They used a map to navigate the fair.)