Q1. What tool helps us see tiny organisms that are invisible to the naked eye?
Answer: A microscope helps us see tiny organisms that our eyes cannot see directly.
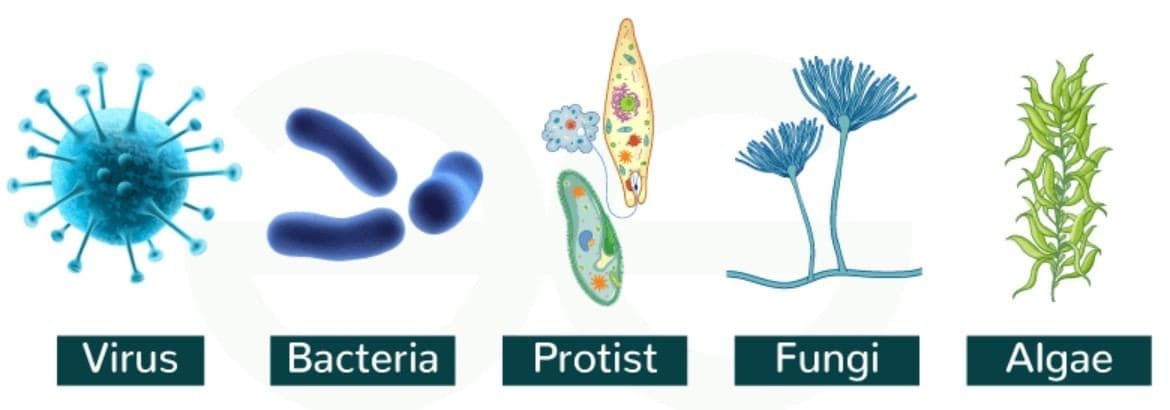
Q2. Why can’t we see most microorganisms without help?
Answer: Most microorganisms are too small to be seen with the unaided eye.
Microorganisms
Q3. What simple object filled with water can act like a magnifying glass?
Answer: A round-bottom flask filled with water can act like a magnifying glass.
Q4. Who first used the word “cell” in science?
Answer: Robert Hooke first used the word “cell” after observing cork under a microscope.
Q5. Who is called the Father of Microbiology?
Answer: Antonie van Leeuwenhoek is called the Father of Microbiology.
Q6. What is the basic unit of life?
Answer: The cell is the basic unit of life.
Q7. Which part of the cell controls all activities?
Answer: The nucleus controls all cell activities.
Q8. Which cell part is a thin, flexible boundary around the cell?
Answer: The cell membrane is the thin, flexible boundary around the cell.
Q9. Name the jelly-like substance inside the cell where life processes occur.
Answer: The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance where life processes occur.
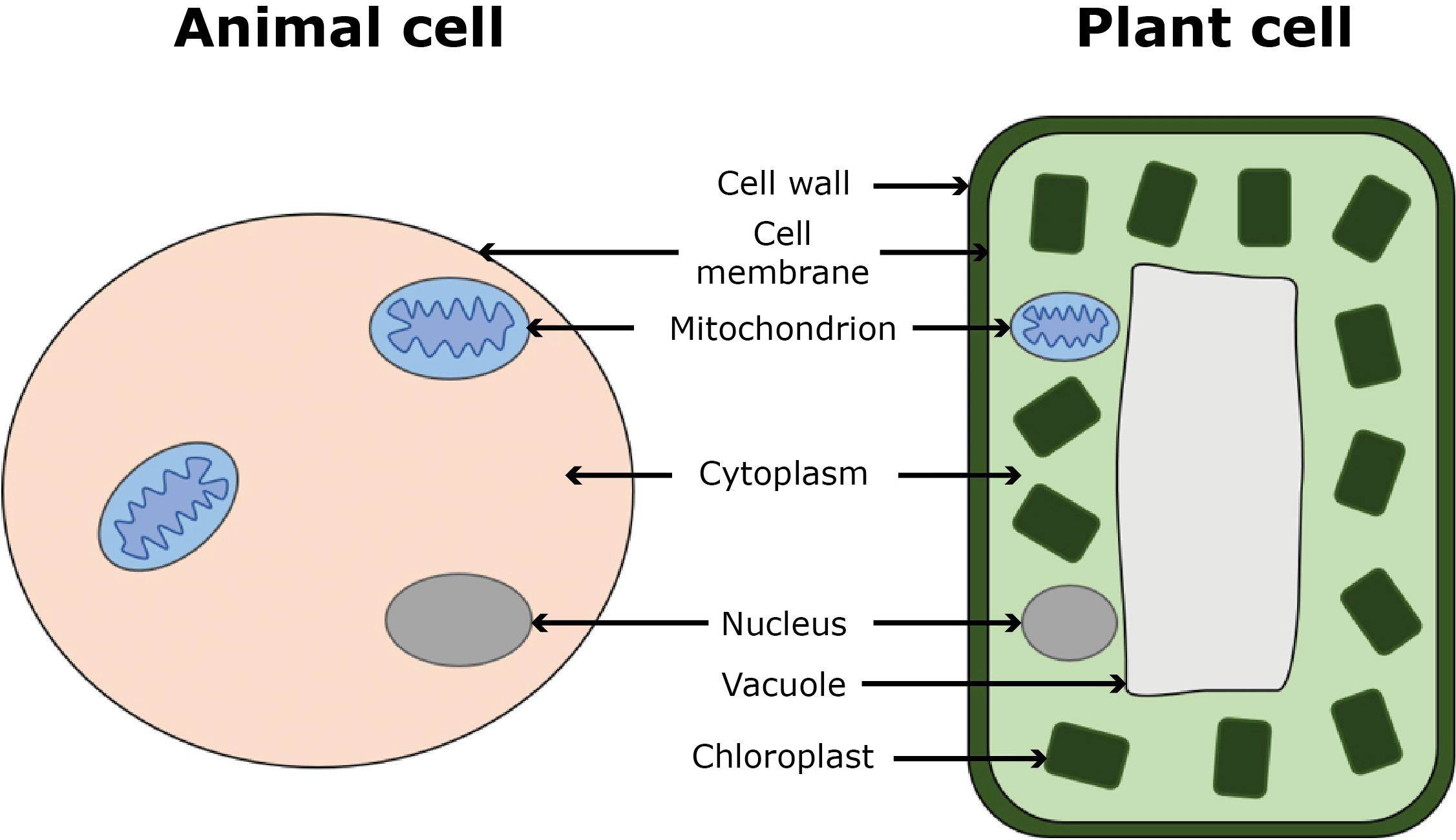
Q10. Which extra layer is present in plant cells but not in animal cells?
Answer: The cell wall is present in plant cells but not in animal cells.
Q11. Which plant cell part contains chlorophyll for photosynthesis?
Answer: Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
Q12. Which cell part stores food, water, and waste in plant cells?
Answer: The vacuole stores food, water, and waste in plant cells.
Q13. How do onion peel cells appear under a microscope?
Answer: Onion peel cells look rectangular and are closely packed.
Q14. What shape are cheek cells generally?
Answer: Cheek cells are thin, flat, and irregular in shape.
Q15. Why do different cells have different shapes?
Answer: Different cells have different shapes to perform specific functions.
Q16. Arrange these levels of organization from simplest to most complex: organ, cell, tissue, organism, organ system.
Answer: Cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism.
Q17. What do microbes that decompose waste help form in soil?
Answer: They help form dark, nutrient-rich manure called compost.
Q18. Why don’t pickles spoil easily?
Answer: High salt or sugar prevents microbes from growing in pickles.
Q19. What gas is the main component of biogas made by microbes?
Answer: Methane is the main component of biogas.

Q20. Which microbe is used to make dough rise?
Answer: Yeast is used to make dough rise.
Rising Dough
Q21. Which bacteria turn milk into curd?
Answer: Lactobacillus bacteria turn milk into curd.
Q22. Which bacteria living in legume roots fix nitrogen?
Answer: Rhizobium bacteria fix nitrogen in legume roots.
Q23. What are very small, plant-like organisms in water that release much of Earth’s oxygen?
Answer: Microalgae are tiny plant-like organisms that release much oxygen.
Q24. Name a microalga known as a “superfood.”
Answer: Spirulina is a microalga known as a superfood.
Q25. What is a unicellular organism?
Answer: A unicellular organism is a living thing made of only one cell.