Q1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
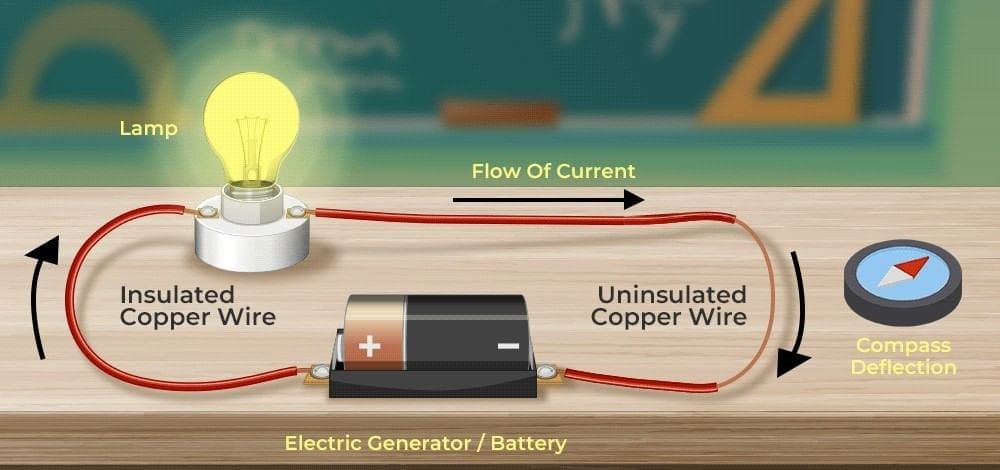 What did Oersted discover in 1820?
What did Oersted discover in 1820?
a) Heating effect of current
b) Electric charge of Earth
c) Magnetic effect of electric current
d) Structure of dry cell- Which instrument can detect the magnetic field around a current-carrying wire?
a) Vernier caliper
b) Magnetic compass
c) Thermometer
d) Barometer - An electromagnet is:
a) A permanent magnet made of steel
b) A coil with an iron core that becomes a magnet when current flows
c) A bar magnet with fixed poles
d) A coil without any core - Which change will increase the strength of an electromagnet?
a) Using fewer turns of wire
b) Reducing current
c) Inserting a soft iron core
d) Removing the battery - Lifting electromagnets are used mainly to:
a) Measure current
b) Lift and move heavy steel in scrap yards
c) Store electrical energy
d) Heat metals - When current passes through a nichrome wire, it becomes hot due to:
a) Absence of resistance
b) Magnetic shielding
c) Cooling effect of current
d) Heating effect of electric current - Which factor increases heat in a wire for the same time?
a) Thicker wire and less current
b) Shorter wire and less current
c) Longer, thinner wire with more current
d) No resistance in wire 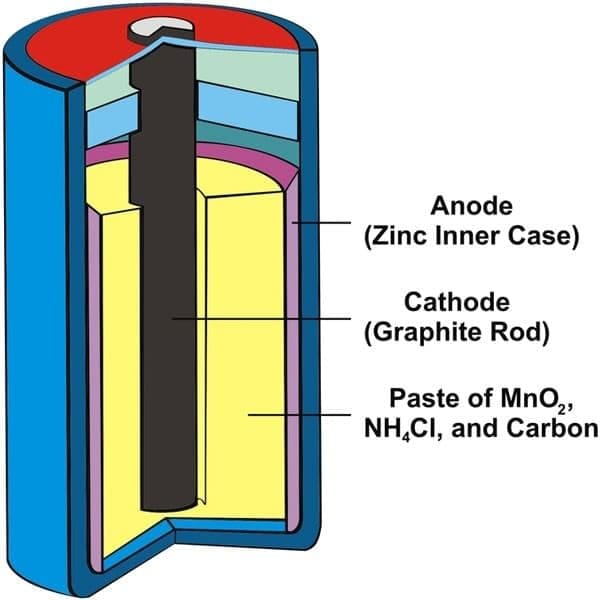 In a simple voltaic (galvanic) cell, electricity is produced by:
In a simple voltaic (galvanic) cell, electricity is produced by:
a) Chemical reactions between metals and electrolyte
b) Friction
c) Magnetic induction
d) Solar energy
Dry Cell- In a dry cell, the negative terminal is the:
a) Zinc container
b) Carbon rod
c) Electrolyte paste
d) Air gap - Lithium-ion batteries are:
a) Single-use only
b) Not suitable for recharging
c) Only for torches and clocks
d) Rechargeable and used in phones/laptops
Q2. Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
- A current-carrying conductor produces a __________ field around it.
- The deflection of a __________ needle shows the presence of current nearby.
- An iron nail wrapped with a current-carrying coil becomes an __________.
- Reversing the direction of current reverses the __________ of an electromagnet.
- The heating of a wire due to current is called the __________ effect of electric current.
- __________ wire is used as a heating element because it has high resistance.
- A device that produces electricity by a chemical reaction is called an electric __________.
- In a dry cell, the electrolyte is a moist __________.
- In the lemon battery, the lemon juice acts as an __________.
- Multiple cells connected together form a __________.
Q3. Very Short Answer Questions (1 line)
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
- What simple observation shows the magnetic effect of current?
- Name any one factor that increases the strength of an electromagnet.
- What happens to an electromagnet when the current is switched off?
- What is resistance?
- Which terminal is at the center of a dry cell?
Q4. Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
- State Oersted’s finding and its importance.
- How can you make a simple electromagnet at home?
- Mention two ways to increase the heat produced in a wire.
- What is the basic structure of a dry cell?
- How can you light an LED with lemons?
Q5. Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.
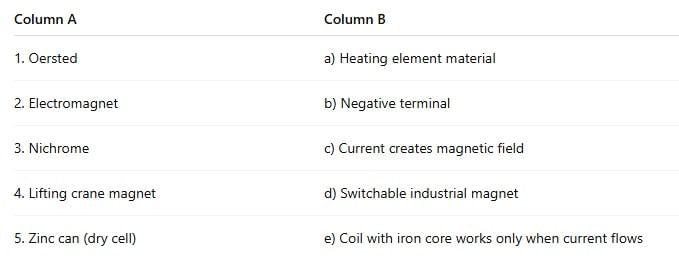
Ans:
- Oersted — c) Current creates magnetic field
He discovered the magnetic effect of electric current. - Electromagnet — e) Coil with iron core works only when current flows
It becomes magnetic only when powered. - Nichrome — a) Heating element material
Nichrome’s high resistance makes it ideal for heaters. - Lifting crane magnet — d) Switchable industrial magnet
Used to lift/drop heavy steel by switching current ON/OFF. - Zinc can (dry cell) — b) Negative terminal
In a dry cell, the zinc container acts as the negative electrode.