Q1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
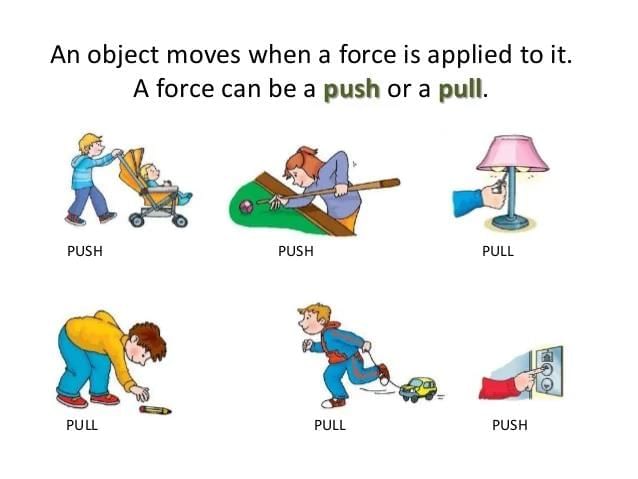 In science, a force is defined as:
In science, a force is defined as:
a) Only a push
b) Only a pull
c) A push or a pull
d) Energy of motion
Answer: c) A push or a pull
Any push or pull on an object is called a force.- Which of these is NOT an effect of force?
a) Change of shape
b) Change of direction
c) Production of light
d) Start/stop motion
Answer: c) Production of light
Force changes motion or shape; producing light is not a direct effect of force. - Forces always involve:
a) Only one object
b) Interaction between two objects
c) Only moving objects
d) Only heavy objects
Answer: b) Interaction between two objects
A force arises from interaction (e.g., hand and table). 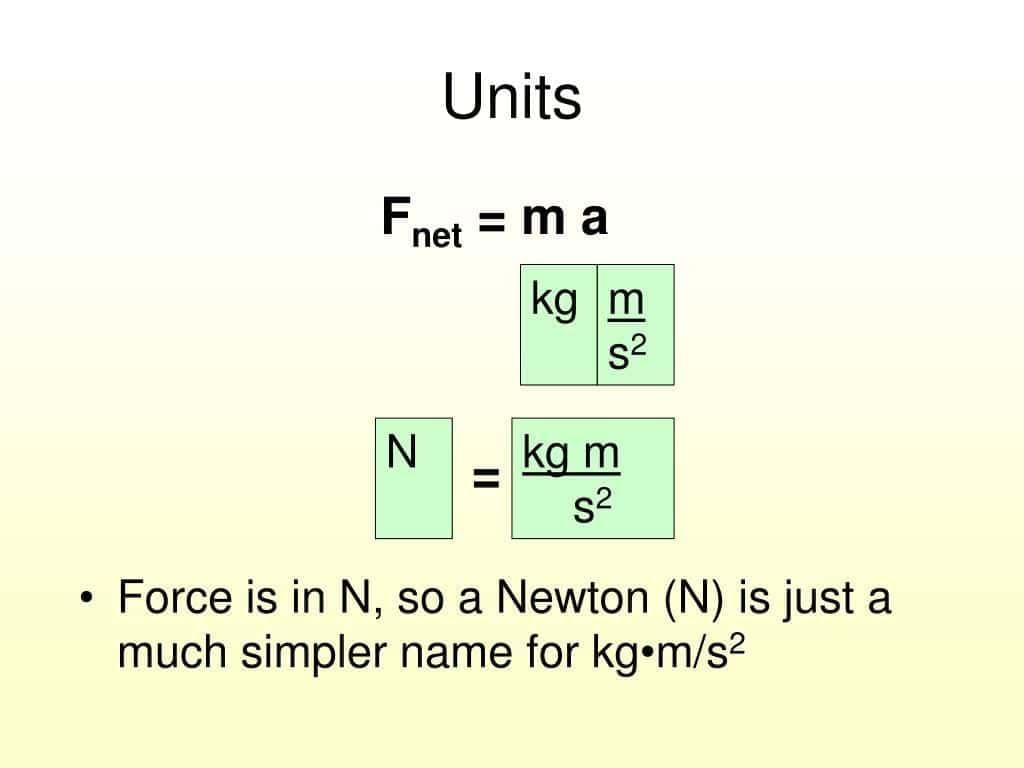 The SI unit of force is:
The SI unit of force is:
a) Joule (J)
b) Watt (W)
c) Newton (N)
d) Pascal (Pa)
Answer: c) Newton (N)
Force is measured in newtons.- Friction is a force that:
a) Aids motion
b) Always increases speed
c) Opposes motion between surfaces in contact
d) Acts only in liquids
Answer: c) Opposes motion between surfaces in contact
Friction resists motion; rough surfaces give more friction. - Which is a non-contact force?
a) Muscular force
b) Friction
c) Magnetic force
d) Push with a stick
Answer: c) Magnetic force
It acts without physical contact. - Gravity is:
a) Sometimes attractive, sometimes repulsive
b) Always repulsive
c) Always attractive
d) Only acts on Earth
Answer: c) Always attractive
Gravitational force only attracts. - Weight is measured in:
a) Kilogram (kg)
b) Newton (N)
c) Meter (m)
d) Joule (J)
Answer: b) Newton (N)
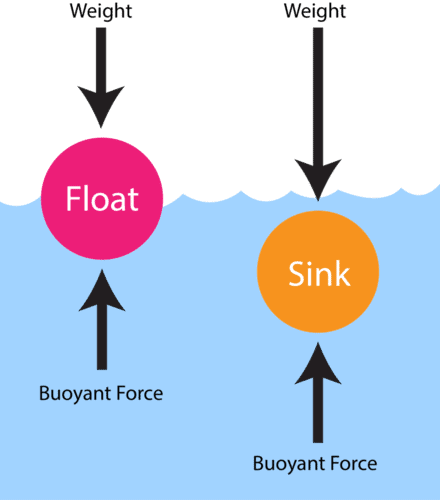
Weight is a force; its SI unit is newton. - An object floats in a liquid when:
a) Weight > buoyant force
b) Weight = buoyant force
c) Weight < buoyant force
d) There is no gravity
Answer: b) Weight = buoyant force
Floating occurs when upthrust equals weight.
Q2. Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
- A force is a __________ or a __________.
Answer: push; pull
Both pushes and pulls are forces. - If an object’s speed or direction changes, a __________ has acted.
Answer: force
Explanation: Force causes change in motion or shape. - The SI unit of force is the __________ (symbol: N).
Answer: newton
Standard unit for force. 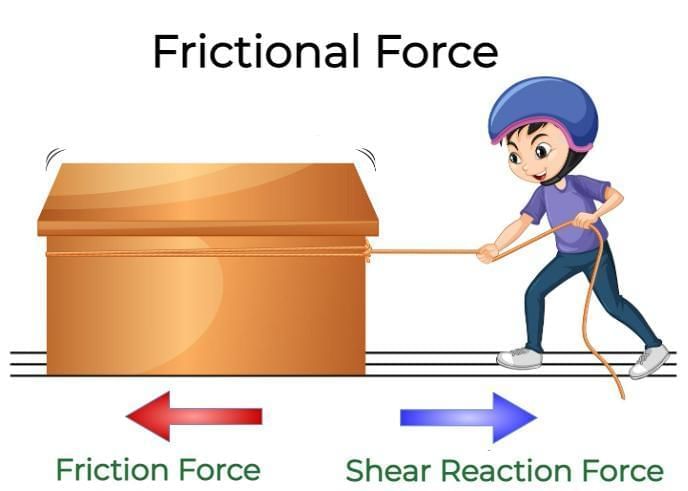 Friction always acts in a direction __________ to motion.
Friction always acts in a direction __________ to motion.
Answer: opposite
It resists motion between surfaces.- Forces that act without contact are called __________ forces.
Answer: non-contact
Examples: magnetic, electrostatic, gravitational. - The force with which Earth pulls objects is called __________.
Answer: gravity (or gravitational force)
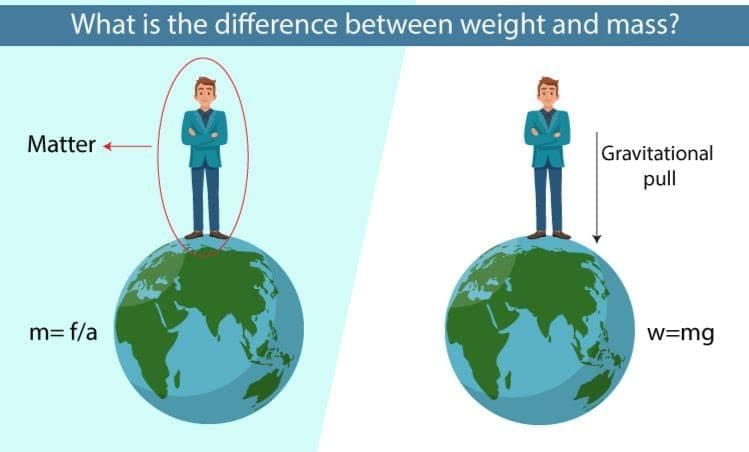
Gravity attracts objects to Earth. - Weight is a __________ and is measured in newtons.
Answer: force
Weight = mass × gravitational acceleration. - The device used to measure weight (force) in newtons is a __________ balance.
Answer: spring
Stretch of the spring indicates force. - The upward force exerted by a liquid on an immersed object is called __________ force.
Answer: buoyant (or upthrust)
It acts opposite to weight. - An object sinks when its __________ is greater than the buoyant force.
Answer: weight
If weight > upthrust, the object sinks.
Q3. Short Answer QuestionsInstruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
- How does friction depend on the nature of surfaces?
Answer: Rough surfaces have more tiny irregularities, leading to higher friction; smooth surfaces have fewer irregularities, so friction is less. - Explain why cycling uphill feels harder than cycling downhill.
Answer: Uphill, you work against gravity and friction, requiring greater muscular force. Downhill, gravity aids motion, so you need little or no pedaling. - What does “forces work in pairs” mean?
Answer: When you push an object, it exerts an equal and opposite force on you. The interaction ends when contact ends. - How do we find the least count of a spring balance?
Answer: Divide the value between two major marks by the number of small divisions between them. - Why do streamlined shapes help in air or water?
Answer: They reduce fluid friction (drag), allowing objects like cars, planes, and boats to move more easily.

Q4. Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.

Correct Matches:
- Muscular force — c) Force due to muscles in humans/animals
Explanation: Movements like lifting, pushing, and pulling use muscles. - Friction — d) Opposes motion between surfaces in contact
Explanation: It resists sliding/rolling and depends on surface roughness. - Magnetic force — e) Acts at a distance between magnets
Explanation: Magnets attract/repel without contact. - Weight — b) Pull of Earth on an object
Explanation: Weight is gravitational force; measured in newtons. - Buoyant force — a) Upward force by a liquid
Explanation: Liquids push up on immersed objects; this is upthrust.

Q5. Application/Reasoning (Short Problems)
Instruction: Answer the following briefly in 2–3 lines.
- A wooden block is pushed on a rough table and stops after some distance. Why?
Answer: Friction between the block and table opposes motion and converts kinetic energy to heat, bringing the block to rest. - A 1 kg object has a weight of about 10 N on Earth. What will be its weight on the Moon (g ≈ 1.6 m/s²)?
Answer: About 1.6 N. Explanation: Weight = mass × g = 1 kg × 1.6 m/s². - A spring balance has marks 0 to 5 N with 10 equal divisions between each newton. What is its least count?
Answer: 0.1 N per division. Explanation: 1 N ÷ 10 divisions = 0.1 N. - Two balloons rubbed with wool repel each other. Which force is acting and why?
Answer: Electrostatic force; both balloons have like static charges, so they repel. - A stone sinks in water but a sealed empty plastic bottle floats. Why?
Answer: The stone’s weight is greater than buoyant force, so it sinks. The bottle’s average density is less and upthrust balances its weight, so it floats.