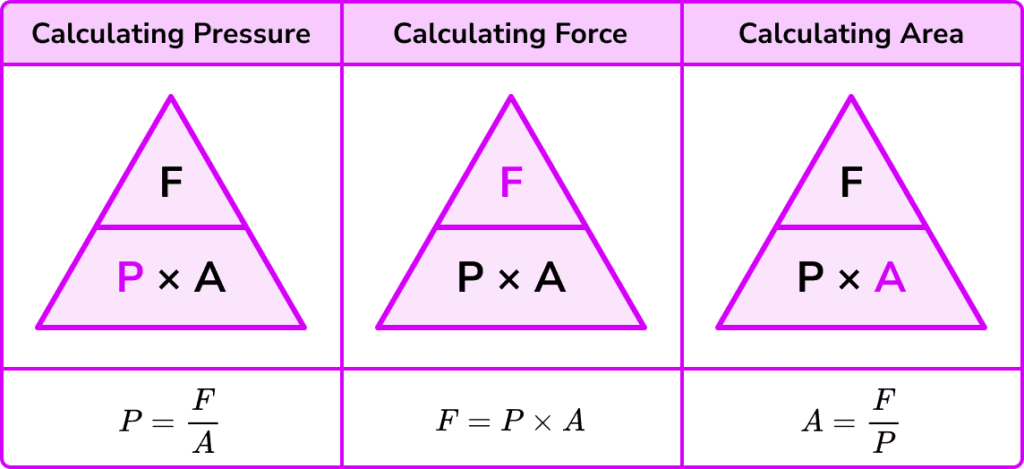
Q1. What is pressure in science?
Answer: Pressure is the force applied per unit area.
Q2. Which component of force is used to calculate pressure on a surface?
Answer: Only the force perpendicular to the surface is used to calculate pressure.
Q3. Why do broad bag straps feel more comfortable than narrow ones?
Answer: Broad straps spread the same force over a larger area, reducing pressure on the shoulders.
Q4. Why does a sharp nail pierce wood more easily than a blunt one?
Answer: A sharp nail has a smaller area at the tip, creating higher pressure for the same force.
Q5. What is the SI unit of pressure?
Answer: The SI unit of pressure is the pascal (Pa), which is N/m².
Q6. How does the height of a water column affect liquid pressure at the bottom?
Answer: Greater height of the water column increases the liquid pressure at the bottom.
Q7. Do liquids exert pressure only downward?
Answer: No, liquids exert pressure in all directions, including sideways on container walls.
Q8. Why are dams built broader at the base?
Answer: Dams are broader at the base to withstand the higher water pressure at greater depths.
Q9. What is atmospheric pressure?
Answer: Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by the air in the atmosphere on all objects.
Q10. Why does a rubber sucker stick to a smooth surface?
Answer: It sticks because outside air pressure is greater than the pressure under the sucker.
Q11. Why aren’t we crushed by atmospheric pressure?
Answer: We aren’t crushed because the pressure inside our bodies balances the outside atmospheric pressure.
Q12. In which units is air pressure commonly reported in weather reports?
Answer: Air pressure is commonly reported in millibar (mb) or hectopascal (hPa).
Q13. In which direction does air move to form wind?
Answer: Air moves from a region of high pressure to a region of low pressure.
Q14. What causes a sea breeze during the day?
Answer: A sea breeze occurs when cooler air from the sea moves toward warmer low-pressure air over land.
Q15. What causes a land breeze at night?
Answer: A land breeze occurs when cooler air from land moves toward the warmer low-pressure air over the sea.
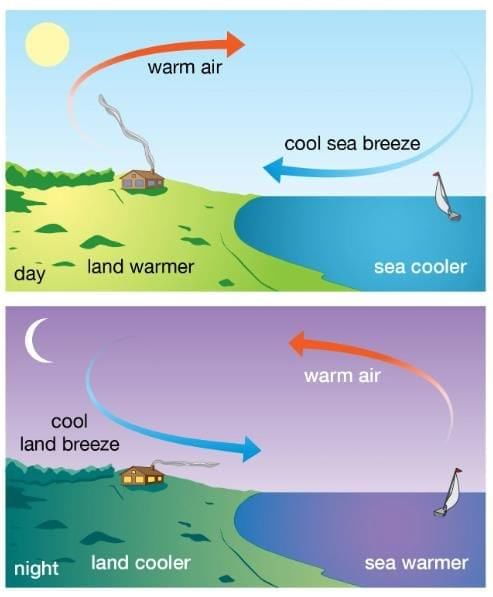
Land and Sea Breeze
Q16. How do high-speed winds affect air pressure in an area?
Answer: High-speed winds lower the air pressure in the area where they flow rapidly.
Q17. Why can strong winds blow off a weak roof?
Answer: Strong winds create low pressure above the roof, and higher inside pressure can push the roof up.
Q18. What is a thunderstorm?
Answer: A thunderstorm is a storm with lightning and thunder caused by charged clouds and rapid air movement.
Q19. How is lightning formed in a cloud?
Answer: Lightning forms when charge buildup breaks air’s resistance, causing a sudden flow of charges as a bright flash.
Q20. What safety action should you take during lightning outdoors?
Answer: You should avoid tall objects and crouch in a low, open area without lying flat.
Q21. What is the function of a lightning conductor on a building?
Answer: A lightning conductor safely carries electric charges from lightning into the ground.
Q22. What is a cyclone?
Answer: A cyclone is a large spinning storm over warm oceans with very low pressure at the center and high-speed winds.
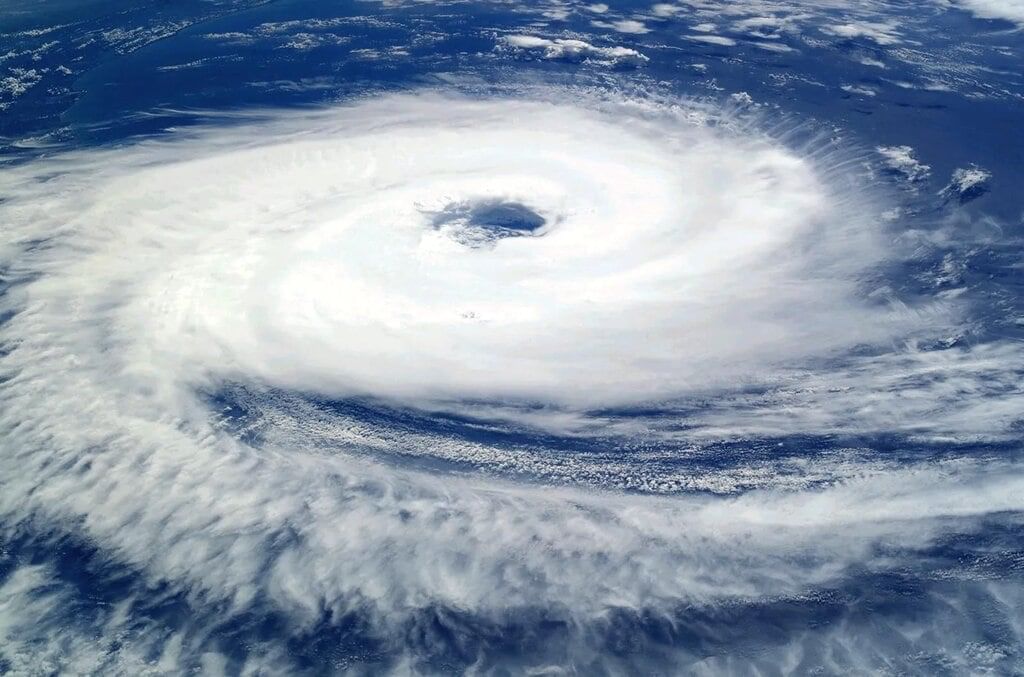

Cyclone
Q23. What provides energy to a cyclone over the ocean?
Answer: Warm, moist air and heat released during condensation provide energy to a cyclone.
Q24. What is a storm surge?
Answer: A storm surge is a high wall of seawater pushed toward land by strong cyclone winds, causing coastal flooding.
Q25. Why do cyclones weaken after landfall?
Answer: Cyclones weaken after landfall because they lose their supply of warm, moist air from the ocean.