
Q1: Choose the correct option for each question.
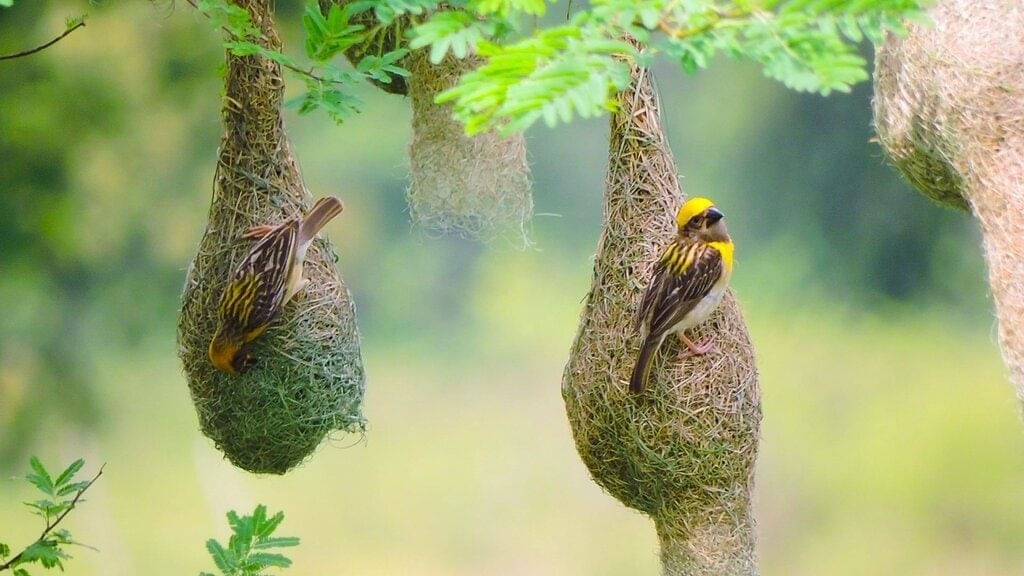
(i) What do birds like the male baya weaver build their nests from?
A) Plastic
B) Grass
C) Leaves
D) Twigs
Ans: B) GrassBaya in its Nest
(ii) What tool was used to weave fabrics in India 4,000 years ago?
A) Needle
B) Loom
C) Charkha
D) Spinning Wheel
Ans: B) Loom
(iii) Which of the following is a unique handloom tradition of Tamil Nadu?
A) Ikat
B) Pashmina
C) Kanjeevaram
D) Bandhani
Ans: C) Kanjeevaram
(iv) What is the process called when cotton fibres are twisted into thread?
A) Weaving
B) Spinning
C) Knitting
D) Stitching
Ans: B) Spinning
(v) Which material is used to make Pashmina shawls?
A) Cotton
B) Wool
C) Silk
D) Jute
Ans: B) Wool
Q2: Match the items in Column A with the correct descriptions in Column B.
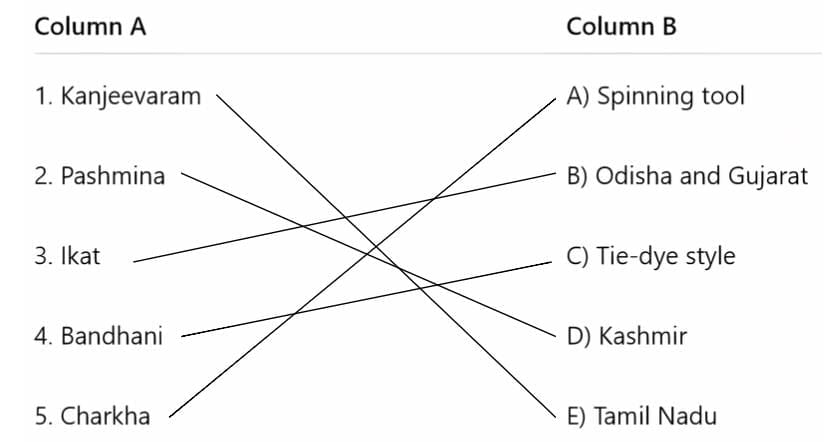
Ans:
Q3: Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the chapter.
(i) The tailorbird stitches big leaves together to make a ______.
(ii) Indian muslin was so fine it was called “woven ______.”
(iii) Weaving supports culture and people’s ______.
(iv) The process of making thread from fibers using a charkha is known as ______.
(v) Old clothes can be turned into ______ by joining small pieces together.

Ans:
(i) The tailorbird stitches big leaves together to make a nest.
(ii) Indian muslin was so fine it was called “woven air.”Indian Muslin(iii) Weaving supports culture and people’s livelihoods.
(iv) The process of making thread from fibres using a charkha is known as spinning.
(v) Old clothes can be turned into quilts by joining small pieces together.
Q4: State whether the following statements are True or False. Correct the false statements.
(i) The Baya weaver is an expert weaver who makes rough nests.
Ans: False
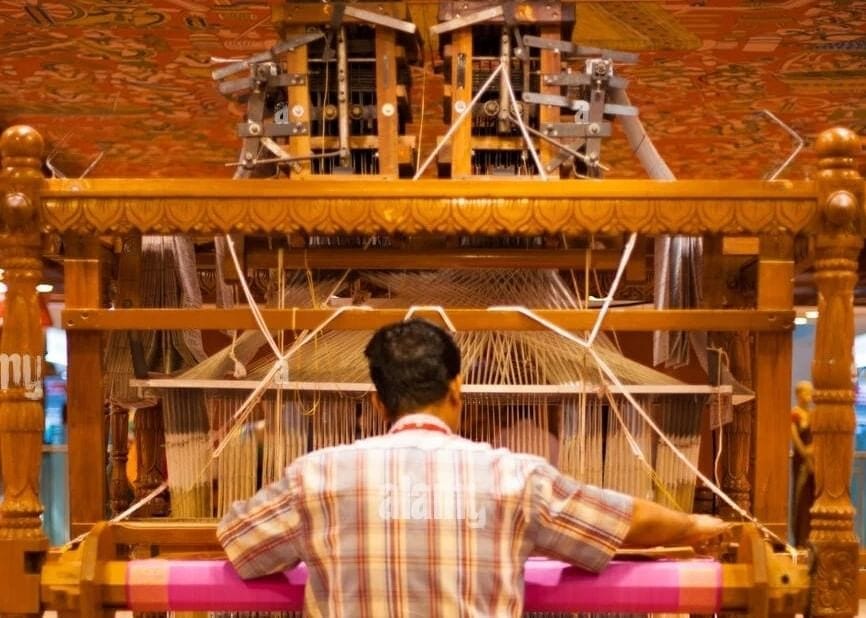

(ii) Handloom weaving requires the use of electricity.
Ans: FalseMan weaving using Handloom
(iii) Both natural and synthetic fibres are used in clothing.
Ans: True
(iv) The tailorbird uses its beak to sew leaves.
Ans: True
(v) India is the largest producer of silk in the world.
Ans: False
Q5: Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
(i) What do birds like the male baya weaver do to make their nests?
Ans: The male baya weaver bird builds pouch-shaped nests using grass. It weaves the grass strands over and under to create a safe place for its eggs.
(ii) How do people in India keep the art of weaving alive?
Ans: People in India keep weaving alive by using handlooms. Skilled weavers make beautiful fabrics by hand, and this tradition supports families and their culture.

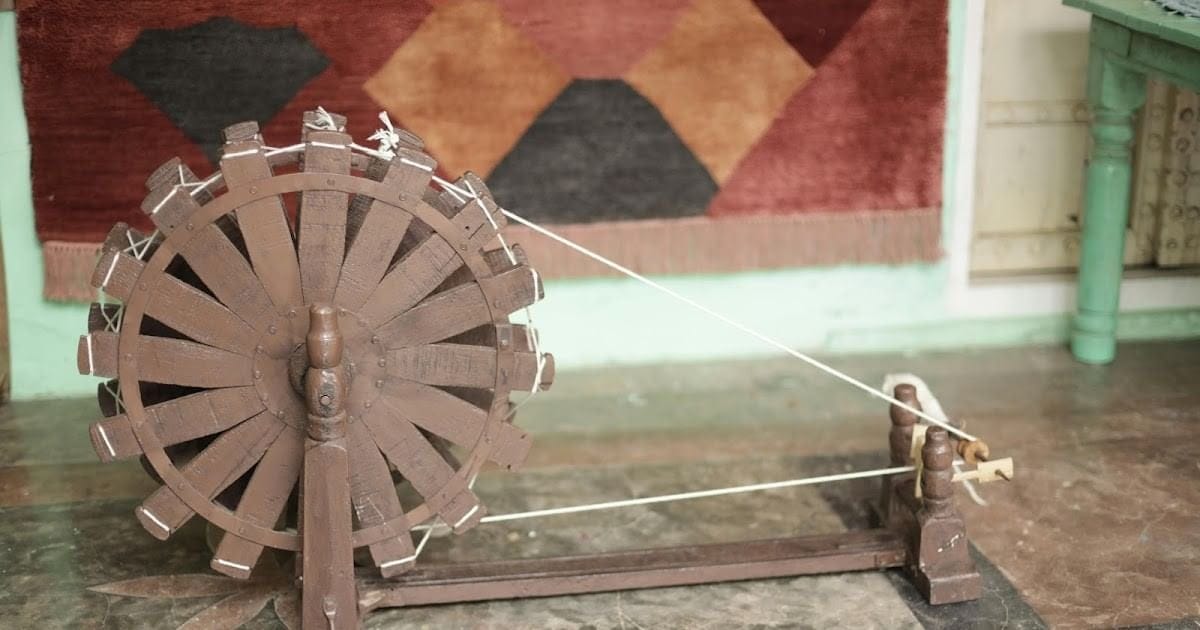
(iii) What is a charkha, and what is it used for?
Ans: A charkha is a spinning wheel that helps to twist cotton fibres into thread or yarn. It is used to make strong threads for weaving cloth.Lady twisting fibre into yarn using Charkha
(iv) What can you do with running stitches?
Ans: You can use running stitches for mending clothes, basic sewing, embroidery, and even making crafts. They help hold pieces of fabric together.
(v) How do people recycle old clothes in India?
Ans: In India, people often pass old clothes to younger siblings or turn them into new items like quilts. This way, they reuse fabric and reduce waste.

Q6: Answer the following questions in 4-6 sentences each. Use examples from the chapter to support your answers.
(i) Explain the process of making thread from cotton and how it is used to make cloth.
Ans: Thread is made from cotton through a process called spinning. First, we take cotton fibres and twist them together to make them stronger. A charkha (spinning wheel) helps us spin cotton into thread, just like winding cotton around a pencil.Charkha/Spinning wheelKey steps:
- Pull cotton fibres and twist them slowly
- Use a spinning wheel to make long, strong threads
- These threads are then woven together on a loom
- Weaving means crossing threads over and under to make cloth
- This cloth can be used to make clothes, bags, and other items
(ii) How do natural and synthetic fibres differ? Give examples of each type.
Ans: Natural and synthetic fibres are very different in how they are made. Natural fibres come from plants, animals, and insects found in nature. Synthetic fibres are made by humans using artificial materials in factories.
Natural fibres:
- Cotton (from cotton plants)
- Silk (from silk moth cocoons)
- Wool (from sheep and goats)
- Jute and bamboo (from plants)
Synthetic fibres:
- Nylon, Polyester, Rayon, Terylene
- Made in factories using chemicals
- Both types are useful for making different clothes and materials
(iii) Describe the traditional embroidery work done in different parts of India.
Ans: India has beautiful traditional embroidery styles that tell stories about different places and people. Each region has its own special way of decorating cloth with colourful threads and patterns.
Famous Indian embroideries:
- Chikankari – from Lucknow, UP (delicate white work)
- Phulkari – from Punjab (bright flower patterns)
- Kantha – from Bengal, Odisha (running stitch designs)
- Bandhani – from Rajasthan (tie-dye dots and circles)
- Kashmiri – from Kashmir (fine thread work)

(iv) Why should we recycle and reuse old clothes? How can we do this?
Ans: Recycling old clothes is important because it helps reduce waste and saves money. In India, people have always believed in not throwing away clothes that can still be useful.
Why recycle clothes:
- Saves money and reduces waste
- Helps the environment by using fewer new materials
- Continues our traditional values of not wasting things
How to reuse clothes:
- Give small clothes to younger siblings or other children
- Make cleaning cloths from old shirts
- Create beautiful quilts by joining small pieces together
- Turn old sarees into pillow covers or bags
- Use cloth pieces for craft activities and decorations
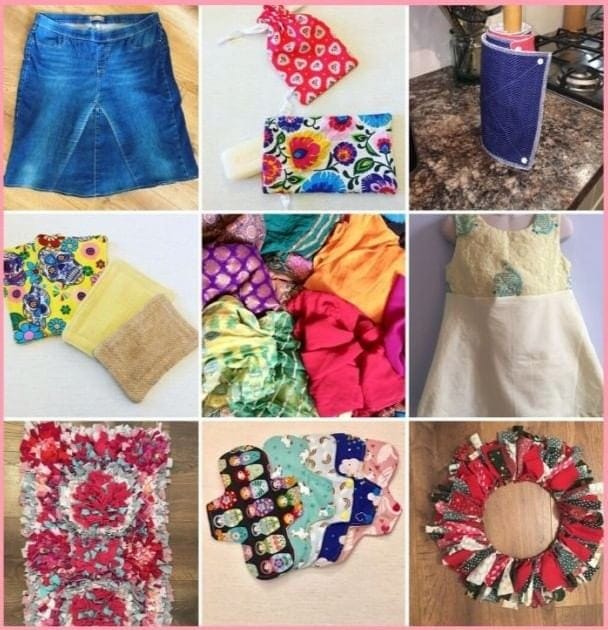

Different ways of reusing old clothes