Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the Gupta Era known for?
a) The rise of the Maurya Empire
b) Achievements in art, literature, and science
c) The fall of the Harappan civilization
d) The start of Islamic rule in India
Ans: b) Achievements in art, literature, and science
The Gupta Era is known for significant advancements in art, literature, science, and governance, marking a period of cultural flourishing.
Q2: Who was the father of Chandragupta II?
a) Samudragupta
b) Samudraka
c) Ashoka
d) Dhanananda
Ans: a) Samudragupta
Samudragupta, a powerful warrior king, was the father of Chandragupta II, who expanded the Gupta Empire.
Q3: What was the name of the Gupta ruler who performed the Ashvamedha Yajña?
a) Chandragupta II
b) Samudragupta
c) Ashoka
d) Harisena
Ans: b) Samudragupta
Samudragupta performed the Ashvamedha Yajña, a Vedic ritual to assert his sovereignty.
Q4: Which foreign traveler visited India during the Gupta period?
a) Hiuen Tsang
b) Faxian
c) Marco Polo
d) Ibn Battuta
Ans: b) Faxian
Faxian, a Chinese traveler, visited India in the early 5th century CE and documented his observations of Indian society during the Gupta period.
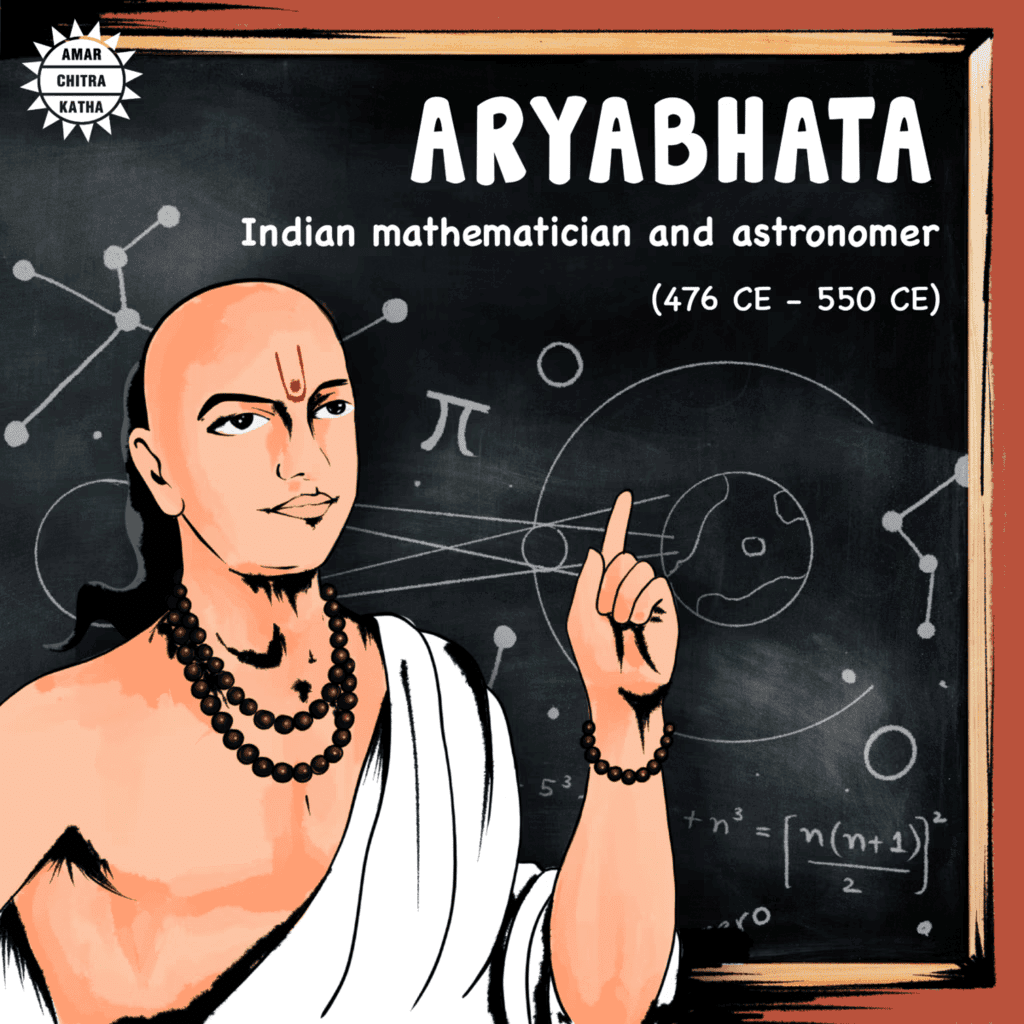
Q5: What was a significant contribution of Āryabhaṭa in the Gupta period?
a) He wrote about architecture and sculpture.
b) He made advances in mathematics and astronomy.
c) He created the first coinage system.
d) He founded the Nalanda University.
Ans: b) He made advances in mathematics and astronomy.
Āryabhaṭa is known for his work in mathematics and astronomy, including his theories on the Earth’s rotation and the calculation of pi.
Q6: What was the main trade commodity of the Gupta Empire?
a) Spices and textiles
b) Coins and gold
c) Iron and steel
d) Silk and porcelain
Ans: a) Spices and textiles
The Gupta Empire was known for its trade in spices, textiles, gemstones, and other goods, with active trade routes extending to other parts of the world.

Gupta Coins
Q7: Which Gupta king is known for promoting the arts and literature, and for ruling over the empire at its height?
a) Chandragupta I
b) Samudragupta
c) Chandragupta II
d) Harisena
Ans: c) Chandragupta II
Chandragupta II, also known as Vikramaditya, ruled during the peak of the Gupta Empire, promoting arts, literature, and scientific advancements.
Q8: What was the primary purpose of the Iron Pillar in Delhi?
a) To honor the Mauryan Empire
b) To commemorate military victories
c) To demonstrate Gupta advancements in metallurgy
d) To mark the boundaries of the Gupta Empire
Ans: c) To demonstrate Gupta advancements in metallurgy
The Iron Pillar in Delhi is famous for its rust-resistant iron, showcasing the Gupta’s advanced knowledge of metallurgy.
Q9: Which language flourished during the Gupta period and became central to literature and philosophy?
a) Prakrit
b) Sanskrit
c) Pali
d) Tamil
Ans: b) Sanskrit
Sanskrit became the primary language for literature, philosophy, and religious texts during the Gupta period, with many famous works being written in it.
Q10: Which Gupta ruler was particularly noted for his patronage of scholars and artists?
a) Samudragupta
b) Chandragupta II
c) Harisena
d) Kumaragupta
Ans: b) Chandragupta II
Chandragupta II, also known as Vikramaditya, was famous for his patronage of scholars and artists, and his court was home to many renowned intellectuals.

King Vikramaditya
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The Gupta Empire is often referred to as the __________ Age due to its cultural and intellectual achievements.
Ans: Classical
The Gupta period is called the Classical Age because of the significant progress made in various fields, including art, literature, and science.
Q2: The Gupta rulers used __________ to expand their empire, combining military conquests and alliances.
Ans: Diplomacy
Gupta rulers used a combination of military power and diplomatic alliances to expand their empire.
Q3: The __________ Pillar in Delhi, dating back to the Gupta period, showcases the empire’s achievements in metallurgy.
Ans: Iron
The Iron Pillar in Delhi demonstrates the Gupta Empire’s advanced knowledge of ironworking, as it resists rust even after centuries.

Iron Pillar, Mehraulli, Delhi
Q4: __________ was a famous Chinese traveler who visited India during the Gupta period and wrote about his experiences.
Ans: Faxian
Faxian, a Chinese monk, traveled to India in the early 5th century CE, documenting his observations of Gupta society.
Q5: The Gupta period is noted for advancements in __________, with scholars like Āryabhaṭa making significant contributions.
Ans: Mathematics and astronomy
Āryabhaṭa made major contributions to mathematics and astronomy, including his theories on the Earth’s rotation.
Q6: The Gupta rulers were also known for their patronage of __________, with scholars like Kālidāsa writing famous literary works.
Ans: Literature
The Gupta rulers, particularly Chandragupta II, supported literature, and Kālidāsa became one of the most famous poets of this period)
Q7: Gupta administration was efficient, with local leaders receiving __________ to manage their territories.
Ans: Land grants
The Guptas used land grants to allow local rulers to govern territories while ensuring they paid tribute and supported the empire.
Q8: __________, a famous work by Varāhamihira, covers topics like astrology, weather forecasting, and architecture.
Ans: Brihat Samhita
Varāhamihira’s Brihat Samhita was a comprehensive work that covered various topics, including astrology and architecture.
Q9: The Gupta rulers supported __________ by funding institutions like Nālandā University.
Ans: Education
The Gupta rulers promoted education by supporting centers of learning such as Nālandā University, which attracted scholars from across Asia.
Q10: The Gupta period saw significant progress in __________, with the development of beautiful sculptures and paintings in places like Ajanta and Udayagiri.
Ans: Art
The Gupta period was a golden age for Indian art, with advancements in sculpture and painting, particularly in places like Ajanta and Udayagiri Caves.

Ajanta Caves
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What was the capital of the Gupta Empire?
Ans: Pataliputra.
Q2: What is the significance of the Iron Pillar in Delhi?
Ans: It demonstrates Gupta advances in metallurgy as it resists rust.
Q3: Who was Faxian?
Ans: A Chinese traveler who visited India during the Gupta period and wrote about it.
Q4: What was the primary language used for literature during the Gupta period?
Ans: Sanskrit.

Nalanda University
Short Answer Questions
Q1: How did the Gupta Empire support art and culture?
Ans: The Gupta rulers, especially Chandragupta II, supported art and culture by patronizing artists, poets, and scholars, leading to advancements in literature, sculpture, and architecture.
Q2: What was the role of diplomacy in the Gupta Empire?
Ans: The Gupta Empire used diplomacy to form alliances with other kingdoms, ensuring stability and helping expand their influence across India.
Q3: How did the Gupta Empire impact mathematics and astronomy?
Ans: Scholars like Āryabhaṭa made significant contributions, including calculations on the Earth’s size, motions of celestial bodies, and the concept of zero.
Q4: Why is the Gupta period called the Classical Age?
Ans: It is called the Classical Age because of the remarkable achievements in art, literature, science, and governance that shaped the future of India.
Q5: What was the significance of Nālandā University?
Ans: Nālandā University was a major center of learning supported by the Guptas, attracting scholars from around the world and contributing to the spread of knowledge.
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)
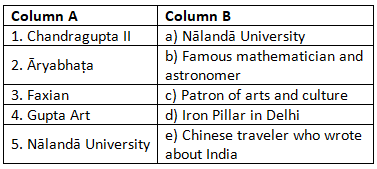
Ans: Matched Pairs and Explanations:
- 1 → c: Chandragupta II was known for his patronage of arts and culture, which flourished during his reign.
- 2 → b: Āryabhaṭa made major contributions to mathematics and astronomy, particularly in the study of the Earth’s rotation.
- 3 → e: Faxian, the Chinese traveler, visited India and wrote about his observations of Gupta society.
- 4 → d: Gupta art, exemplified by the Iron Pillar, showcases their advanced skills in sculpture and metalworking.
- 5 → a: Nālandā University was a prominent learning center during the Gupta period, supported by Gupta rulers.