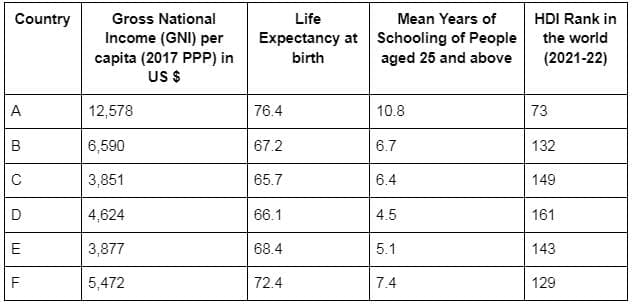
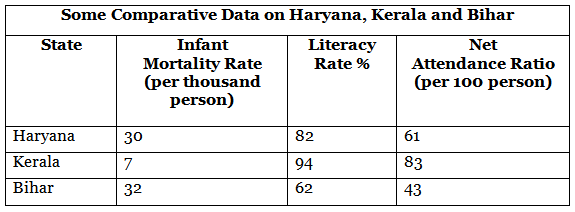
Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: ‘X’ lives in a town. He cultivates flowers along with animal husbandry. The work of ‘X’ will fall under which sector of the economy? (1 Mark)
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
Ans: (a)
Flower cultivation and animal husbandry use natural resources (land, biological processes) and produce natural goods (flowers, milk), so they belong to the primary (agriculture and related) sector.
Q2: The work of which of the following comes in the secondary sector of the economy? (1 Mark)
(a) Bee-keeper
(b) Moneylender
(c) Basket weaver
(d) Fisherman
Ans: (c) Basket weaver
A basket weaver converts raw natural materials into a manufactured good (a basket), so this activity belongs to the secondary (industrial) sector.
Q3: Explain the difference between public and private sector of Indian economy with example. (3 Marks)
Ans:
Public sector: Owned and run by the government. The government provides big services that are needed by everyone and may be too expensive for private companies to do cheaply.
Example: Railways or the Post Office.
Private sector: Owned by private people or companies. They run businesses to earn profit by selling goods and services.
Example: TISCO or Reliance.
Main difference (one line): Public sector is owned and managed by the government to serve people, while private sector is owned by individuals/companies to make profit.
Q4: Rakhi has done an economic survey of her area. The survey has revealed that people earn their livelihood by doing different jobs. The table prepared by Rakhi is given below. Study the table carefully and answer the Question that follows: (1 Mark)
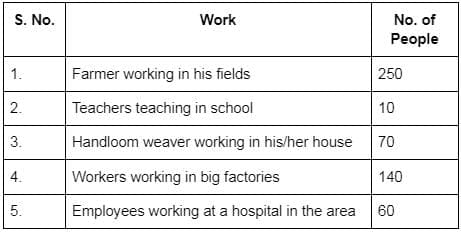
How many people are working in the organised sector?
(a) 380
(b) 140
(c) 320
(d) 210
Ans: (d) 210
Organised sector includes regular, registered places of work (e.g., schools, big factories, hospitals). So add teachers (10) + factory workers (140) + hospital employees (60) = 210.
Q5: Rakhi has done an economic survey of her area. The survey has revealed that people earn their livelihood by doing different jobs. The table prepared by Rakhi is given below. Study the table carefully and answer the Q that follows:
How many people are working in the unorganised sector? (1 Mark)
(a) 380
(b) 210
(c) 320
(d) 140
Ans: (c) 320
Total people = 530. Organised sector workers = teachers (10) + factory workers (140) + hospital employees (60) = 210.
So unorganised = 530 − 210 = 320 (farmers 250 + handloom weavers 70).
Q6: The total value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a particular year is called ______. (1 Mark)
(a) Per Capita Income
(b) Per Capita Production
(c) Gross National Income
(d) Gross Domestic Product
Ans: (d) Gross Domestic Product
GDP is defined as the value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a particular year, as explained in the chapter.
Q7: Identify the sector based on the following characteristics and choose the correct option: (1 Mark)
(i) The objective of this sector is to earn profit.
(ii) This sector is owned by a person or company.
(iii) Tata Iron and Steel is an example of this sector.
(a) Cooperative Sector
(b) Unorganised Sector
(c) Public Sector
(d) Private Sector
Ans: (d) Private Sector
The private sector is owned by individuals or companies and aims to earn profit; TISCO (Tata Iron and Steel) is given in the chapter as an example of a private firm.
Q8: Identify the odd one out: (1 Mark)
(a) Hindustan Computers Limited
(b) Bharti Airtel Limited
(c) Hindustan Unilever Limited
(d) Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
Ans: (d) Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited
The odd one out is the public sector enterprise—BHEL—while the other three are privately owned companies. The classification here is based on ownership (public vs private) as explained in the chapter.
Q9: Find the odd one out: (1 Mark)
(a) Hindustan Computers Limited
(b) Hindustan Unilever
(c) Bharti Airtel Limited
(d) Indian Postal Service
Ans: (d) Indian Postal Service
Indian Postal Service is a public (government) service, while the others are private companies. The classification is by ownership (public vs private) as explained in the chapter.
Q10: Choose the correct option to fill the blank: (1 Mark)
(a) Nature of social activities
(b) Nature of political activities
(c) Nature of production activities
(d) Nature of government activities
Ans: (c) Nature of production activities
The primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors are classified based on the nature of production activities — whether goods are produced using natural resources, manufactured, or provided as services.
Q11: Explain the difference between organised and unorganised sector of the economy with examples. (3 Marks)
Ans: Difference between Organised and Unorganised Sector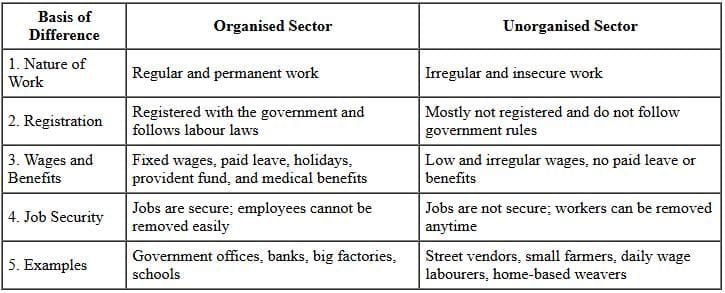
Q12: Evaluate the contribution of the tertiary sector in Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in India. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Over the years, the tertiary sector has become the largest producing sector in India.
- Between 1977–78 and 2017–18, production in all three sectors increased, but it increased the most in the tertiary sector.
- In 2017–18, the tertiary (service) sector replaced the primary sector as the biggest contributor to GDP.
- The growth of this sector is due to:
- Need for basic services like education, health, banking, transport, and communication.
- Development of agriculture and industry, which increased demand for transport, trade, and storage.
- Rising income levels and demand for new services like tourism, private schools, and hospitals.
- Expansion of IT and communication-based services in recent years.
Conclusion: The tertiary sector plays a key role in India’s economic growth and now contributes the largest share to GDP.
Q13: Analyse the problem of underemployment in the agriculture sector in India. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- In India, many people work in the agriculture sector, but their work does not increase total production.
- There are more workers than needed; even if some stop working, output remains the same.
- This situation is called underemployment or disguised unemployment.
- For example, a small farmer’s whole family works on a tiny plot though fewer people are enough.
Conclusion: Underemployment in agriculture shows that many workers are not fully used, leading to low income and productivity.
Q14: Explain the role of the primary sector in employment generation in India. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- The primary sector (agriculture and related activities) is the largest source of employment in India.
- Even though its share in the total production has reduced, it still employs more than half of the workers in the country.
- Most people depend on farming, fishing, forestry, and animal husbandry for their livelihood.
- However, many of these workers face underemployment, as there are more people working than required.
Conclusion: The primary sector provides the maximum jobs in India but often with low productivity and disguised unemployment.
Q15: Analyse the changes taking place in the sectors of the Indian economy in the context of Gross Domestic Product. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- In 1977–78, the primary sector (mainly agriculture) was the largest contributor to India’s GDP.
- Over the years, the secondary sector (industries) and especially the tertiary sector (services) have grown rapidly.
- By 2017–18, the tertiary sector became the largest producing sector, replacing the primary sector.
- Services like transport, banking, communication, education, and IT have expanded fast.
Conclusion: The share of the primary sector in GDP has fallen, while the tertiary sector has shown the highest growth, becoming the main contributor to India’s economic production.
Q16: Suppose you are the Sarpanch of your village. What suggestions will you give for creating additional employment in the village, so that the problem of unemployment of the residents of rural areas can be reduced? (5 Marks)
Ans:
As a Sarpanch, I would suggest the following steps to create more employmentin the village:
- Improve Irrigation Facilities:
- Construct wells, canals, or tanks to provide water for farming.
- This will allow farmers to grow more than one crop in a year and create extra work.
- Promote Small-Scale Industries:
- Set up dal mills, food processing units, or cold storages for crops like pulses, potatoes, and onions.
- This will provide jobs to youth and reduce dependence on farming alone.
- Encourage Rural Services:
- Develop transport, repair shops, tailoring, and local trade.
- It will give employment in the tertiary sector within the village.
- Provide Cheap Credit:
- Help farmers get easy loans from banks or cooperatives to buy seeds, tools, and pumpsets.
- This will improve productivity and income.
- Implement Government Schemes:
- Effectively use the MGNREGA 2005 (Right to Work) scheme to give 100 days of guaranteed employment.
- Take up works like road building, water harvesting, and land improvement.
Conclusion: By improving irrigation, promoting industries, services, and government employment schemes, the village can reduce unemployment and improve the standard of living of its people.
Q17: Read the given source and answer the questions that follow: (4 Marks)
Organised Sector: Kanta works in the organised sector. Organised sector covers those enterprises or places of work where the terms of employment are regular and therefore, people have assured work. They are registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations which are given in various laws such as the Factories Act, Minimum Wages Act, Payment of Gratuity Act, Shops and Establishments Act, etc. It is called Organised Sector because it has some formal processes and procedures. Some of these people may not be employed by anyone but may work on their own, but they too have to register themselves with the government and follow the rules and regulations.
(i) Mention any one feature of the working conditions of the organised sector. (1 Mark)
(ii) Explain any one benefit provided by the employers to the organised sector employees. (1 Mark)
(iii) Why is it necessary for all self-employed people to register with the government? (2 Marks)
Ans:
(i) Feature of Working Conditions:
One feature of the organised sector is that the terms of employment are regular, and workers have assured and secure jobs.
(ii) Benefit Provided:
- Workers in the organised sector get benefits like paid leave, provident fund, medical facilities, and pensions after retirement.
(ii) Need for Registration of Self-Employed:
- It is necessary for self-employed people to register with the government because it ensures that they follow rules and regulations such as payment of minimum wages and safety laws.
Registration also helps the government to monitor working conditions and provide legal protection, ensuring fairness and security for workers.
Q18: Analyse the significance of the Primary Sector in the Indian economy. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- The primary sector includes agriculture, fishing, forestry, dairy, and mining — activities that use natural resources directly.
- It is the base of all other sectors, as raw materials for industries (like cotton for textiles, sugarcane for sugar) come from it.
- The primary sector also provides employment to more than half of India’s workers, especially in rural areas.
- It plays a vital role in ensuring food security and supports industries and services linked to farming and trade.
Conclusion: The primary sector is the foundation of India’s economy, as it provides raw materials, jobs, and livelihood to a large part of the population.
Q19: Examine the factors driving the growth of the Tertiary Sector in India. (3 Marks)
Ans:
The tertiary sector(service sector) has grown rapidly in India due to the following factors:
- Basic Services:
- The government provides essential services like education, health, banking, transport, and communication, which are part of the tertiary sector.
- Support to Other Sectors:
- Growth of agriculture and industries increases the demand for transport, trade, storage, and banking services.
- Rising Income and Demand:
- As people’s income levels increase, they spend more on services like tourism, private schools, and hospitals.
- Information and Technology Services:
- In recent years, IT and communication-based services like call centres, software companies, and internet services have expanded quickly.
Conclusion: These factors together have made the tertiary sector the largest contributor to India’s GDP and a key part of economic growth.
Q20: Suggest any three measures to increase employment opportunities in urban areas in India. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Promote Small-Scale Industries:
- Encourage setting up of small factories, workshops, and business units in cities to create more jobs for skilled and unskilled workers.
- Develop the Service Sector:
- Expand services like transport, banking, IT, tourism, and retail trade, which can provide a large number of employment opportunities.
- Support Self-Employment:
- Provide loans and training to youth to start small businesses, shops, or repair centres through banks and government schemes.
Conclusion: By promoting industries, improving services, and supporting self-employment, cities can generate more jobs and reduce urban unemployment.
Q21: “In India, workers in the organised sector enjoy security of employment.” Examine the statement by giving appropriate arguments. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Workers in the organised sector have regular and secure jobs because their employment is governed by government laws such as the Factories Act and Minimum Wages Act.
- They receive fixed salaries, paid leave, overtime payment, and medical benefits.
- The employer cannot remove them without proper notice or reason, which ensures job security.
- They are also entitled to provident fund, gratuity, and pension after retirement.
Conclusion: Hence, organised sector workers in India enjoy security and stability in employment, unlike those in the unorganised sector who face low pay and job uncertainty.
Q22: Study the given flowchart and answer the questions that follows: (5 Marks)
Explain the steel manufacturing process on the basis of the above flowchart.
Ans:
The given flowchart explains the process of steel manufacturing in a step-by-step manner:
- Transport of Raw Material to Plant:
- Raw materials such as iron ore, coal, and limestone are transported to the steel plant. These are the main inputs for steel production.
- Blast Furnace – Melting:
- The raw materials are melted in a blast furnace at a very high temperature.
- This process helps in separating impurities and produces a basic form of iron known as pig iron.
- Pig Iron Production:
- The molten metal obtained from the blast furnace is pig iron, which is an intermediate product.
- Pig iron still contains impurities and is not strong enough for use.
- Steel Making:
- Pig iron is further purified and refined in steel-making furnaces.
- Carbon and other elements are added or removed to obtain different grades of steel with desired properties.
- Shaping Metal:
- Finally, the molten steel is cooled and shaped into sheets, rods, bars, or other forms for industrial use.
- Conclusion:
The steel manufacturing process involves conversion of raw materials into finished steel through stages of melting, purification, and shaping — making it a key activity of the secondary (industrial) sector.
Q23: How are final goods and services calculated? Explain through one example. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- The value of final goods and services produced in each sector during a year is used to calculate total production.
- Only final goods are counted because their value already includes the cost of intermediate goods used in making them.
- Counting both would mean double counting.
Example:
A farmer sells wheat to a flour mill for ₹20 per kg. The mill makes flour and sells it to a biscuit company for ₹25 per kg. The biscuit company makes biscuits and sells them to consumers for ₹80.
Here, only the final good (biscuits) worth ₹80 is counted in GDP because it already includes the value of wheat and flour.
Conclusion: Hence, GDP includes only the value of final goods and services to avoid counting the same product multiple times.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: Examine the role of Public sector in the development of the country. (CBSE 2024)
Ans: The public sector plays a vital role in the country’s economy by fulfilling various functions:
(1) Developing and investing in infrastructure, such as ports, roads, bridges, and telecommunications, is one of the public sector’s primary responsibilities. The foundation of the economy is this infrastructure, which makes communication, trade, and commerce possible.
(2) The provision of fundamental social services including housing, healthcare, and education falls under the responsibility of the public sector.
(3) The public sector’s establishment and enforcement of laws governing economic activity is another essential function. This entails keeping an eye on business activities, guaranteeing consumer safety, and preserving the sustainability of the environment.

Previous Year Questions 2023
Q2: Which one of the following pair is correctly matched? (2023)
(a) Primary Sector – Fisherman
(b) Secondary Sector – Priest
(c) Tertiary Sector – Basket Weaver
(d) Quarternary Sector – Gardener
Ans: (a)
The primary sector involves activities that extract or harvest natural resources, such as agriculture and fishing. Fishermen are part of this sector because they catch fish directly from water bodies. Therefore, option (a) is the correct match. The other pairs do not align with their respective sectors.
Q3: Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched? (CBSE 2023)
(a) Primary Sector – Flower Cultivator
(b) Secondary Sector – Milk Vendor
(c) Tertiary Sector – Fisherman
(d) Manufacturing Sector – Gardener
Ans: (a)
The primary sector includes activities that involve the extraction and cultivation of natural resources, such as farming and flower cultivation. A flower cultivator fits into this category because they grow flowers directly from the soil. Therefore, option (a) is the correct match, while the other pairs do not accurately represent their respective sectors.
Q4: Kanta works in an office. She gets her salary regularly at the end of every month. In addition to the salary, she also gets other benefits laid down by the government. In which of the following sector Kanta is working? (2023)
(a) Organised Sector
(b) Unorganised Sector
(c) Primary Sector
(d) Quarternary Sector
Ans: (a)
Kanta works in the organized sector because she receives a regular salary and additional benefits provided by the government, such as health insurance or retirement plans. The organized sector consists of jobs with formal contracts and worker protections. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q5: Which of the following organisation is providing data regarding employment in India? (2023)
(a) National Statistical Office
(b) Niti Aayog
(c) National Informatics Centre
(d) Public Service Commission
Ans: (a)
The National Statistical Office (NSO) is responsible for collecting and providing data about various aspects of the economy, including employment in India. It conducts surveys and research to help understand employment trends and statistics. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q6: Which one of the following sectors contribute highest in the GDP of India? (CBSE 2023)
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
Ans: (c)
The tertiary sector contributes the highest to India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This sector includes services such as retail, healthcare, education, and information technology, which have grown significantly and now represent a large part of the economy. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q7: Compare the employment conditions prevailing in the organised and unorganised sector. (2023)
Ans: Employment conditions under :
(a) Organised sector
(i) Rules and regulations (labour laws) as proposed by the government are followed.
(ii) Formal processes and procedures are followed.
(iii) Security of employment to workers, who are employed for full time is ensured.
(iv) Working hours fixed, overtime is paid for extra hours of work.
(v) Workers get benefits like provident fund, gratuity, medical benefits, paid leave, etc.
(b) Unorganised sector
(i) Outside the control of the government laws.
(ii) Small and scattered units.
(iii) Rules and regulations are not followed
(iv) Low-paid and irregular jobs
(v) High degree of insecurity.
(vi) No provision for overtime, paid leave, holidays, etc.
Q8: Explain how Tertiary Sector’ is different from other sectors. (2023)
Ans: Tertiary sector is different from other sectors because:
(i) The activities of the tertiary sector help in the development of secondary and primary sectors.
(ii) Tertiary sector activities do not produce goods by themselves, but they support or aid the process of production in other sectors.
(iii) To help in the trade or production, credit would be required, hence the need to borrow from banks would arise, and communication through phones or letters are also a necessity to complete the processes involved in production and trade.
(iv) After production, the need to store the produce in go downs or cold storage facilities will also arise.
Q9: Why is ‘Tertiary Sector ’ becoming important in India? Explain. (CBSE 2023)
Ans: Tertiary sector is becoming important in India because:
(1) Several services such as hospitals, educational institutions, post and telegraph services, police stations, courts, village administrative offices, municipal corporations, defence, transport, banks, insurance companies, etc., are required with the world globalising and advancing. This imparts significance to the sector.
(2) The development of agriculture and industry leads to the development of services. Greater the development, greater the progress of this sector.
(3) Over the past decade, new services based on information and communication technology have become important and essential.
Q10: Why is there a need to protect workers in the Unorganised Sector? Explain. (CBSE 2023)
Ans: There is a need to protect workers in the Unorganised sector because:
(1) Jobs in this sector are low-paid and not regular. There is no fixed provision of medical leaves, overtime, paid holidays etc.
(2) Employment is not secure. People can be asked to leave anytime without any notice.
(3) There is immense competition in the unorganised sector despite the low growth it offers
 | Get additional INR 200 off today with EDUREV200 coupon. |
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q11: Activities that help in the development of Primary and Secondary sectors come under which one of the following sectors? (Term-1,2021-22)
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
Ans: (c)
Tertiary sector generates services rather than goods. They promote primary and secondary sectors by providing expertise, finance, transportation, advertisement, etc.
Q12: At the initial stages of development, which one of the following sectors was the most important of economic activity? (Term-1,2021-22)
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
Ans: (a)
It has been noted from the history of many newly developed countries that at initial stages of development, primary sector was the most important sector of economic activity.
Q13: Activities in which natural products are changed into other forms come under which one of the following sectors? (Term-1,2021-22)
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
Ans: (b)
Manufacturing industries are secondary activities. They change natural products into other forms.
Q14: The products received by exploiting natural resources come under which one of the following sectors? (Term-1,2021-22)
(a) Quaternary
(b) Tertiary
(c) Secondary
(d) Primary
Ans: (d)
Products obtained by exploiting natural resources, such as agriculture, fishing, and mining, fall under the primary sector. This sector involves activities that directly use natural resources to produce goods. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q15: Read the source given below and attempt any 5 questions. (Term-1,2021-22)
Take the case of Laxmi with her two-hectare plot of unirrigated land. The government can spend some money or banks can provide a loan, to construct a well for her family to irrigate the land. Laxmi will then be able to irrigate her land and take a second crop, wheat, during the rabi season. Let us suppose that one hectare of wheat can provide employment to two people for 50 days (including sowing, watering, fertiliser application and harvesting). So two more members of the family can be employed in her own field. Now suppose a new dam is constructed and canals are dug to irrigate many such farms. This could lead to a lot of employment generation within the agriculture sector itself reducing the problem of underemployment.
(i) Which one of the following economic sectors is Laxmi related to?
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
Ans: (a)
Laxmi works on agricultural land. It is a primary sector.
(ii) Which one of the following categories of farmers is Laxmi related to?
(a) Big
(b) Medium
(c) Marginal
(d) Agricultural labourer
Ans: (b)
A farmer cultivating 2 to 4 hectare is a medium farmer.
(iii) In which one of the following sectors is underemployment seen at the maximum?
(a) Industry
(b) Agriculture
(c) Trade
(d) Commerce
Ans: (b)
More people are engaged in agriculture than needed. It is underemployment.
(iv) How does construction of dams and canals create employment in large numbers in rural areas?
(a) Large number of engineers are needed
(b) Large number of technicians are also required
(c) Adjustment of large number of unskilled labourers
(d) Executives and administrators can easily be adjusted
Ans: (c)
The construction of dams and canals requires a lot of unskilled laborers to help with physical tasks like digging, transporting materials, and building structures. This creates employment opportunities for many people in rural areas who may not have other job options, making option (c) the correct answer.
(v) Which one of the following is the main result of increasing irrigation facilities in the field of agriculture?
(a) Increase in production
(b) Increase in productivity
(c) Change in cropping pattern
(d) Promote high yielding of crops
Ans: (c)
Increasing irrigation has changed the cropping pattern of many regions with farmers shifting to water intensive and commercial crops.
(vi) Which one of the following means of irrigation generally comes under the Public Sector?
(a) Well
(b) Tubewell
(c) Tank
(d) Canal
Ans: (d)
Canals are constructed and maintained by the government. It comes under Public Sector.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q16: Which one of the following activities comes under ‘Primary sector’? (2021C)
(a) Mining
(b) Transport
(c) Education
(d) Storage
Ans: (a)
Mining is classified under the primary sector because it involves extracting natural resources directly from the earth. The primary sector includes activities that utilize natural resources, such as agriculture, fishing, and mining. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer, while the other options belong to the secondary and tertiary sectors.
Q17: How do the workers of the organized sector receive the benefits of employment security? Explain with examples. (2021C)
OR
Why do people prefer to work in an organized sector? Explain. (2015)
Ans: People enjoy working in the organised sector as there is a proper and systematic way to get the work done from the employees.
Benefits of organised sector:
(i) People enjoy security of employment.
(ii) Work for fixed hours.
(iii) If they work more, they get overtime allowances.
(iv) They have registered by the government and have to follow its rules and regulations which are given in various laws such as Factories Act, Shop Act etc.
Examples are Reliance Industries Limited, Tata Motors etc.
| Also read: Long Answer Questions: Sectors of the Indian Economy |
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q18: “Tertiary sector activities help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors”. Evaluate the statement. (CBSE 2020)
Ans: Transport, storage, communication, banking and trade are some examples of tertiary sector. Since, these activities generate services rather than goods, they promote primary and secondary sector by:
(i) Providing expertise and finance
(ii) They are helpful for advertisement and marketing.
(iii) Provide transportation and communication facilities.
Q19: “Primary sector was the most important sector of economic activity at initial stages of development.” Evaluate the statement. (2020)
Ans: Primary sector was the important sector of economic activity at the initial stages of development.
(i) It is concerned with the extraction of raw materials i.e., mining, fishing, farming, etc.
(ii) It gives employment to the large population.
(iii) It enables the workers to leave the agricultural sector and move to other secondary and tertiary sectors.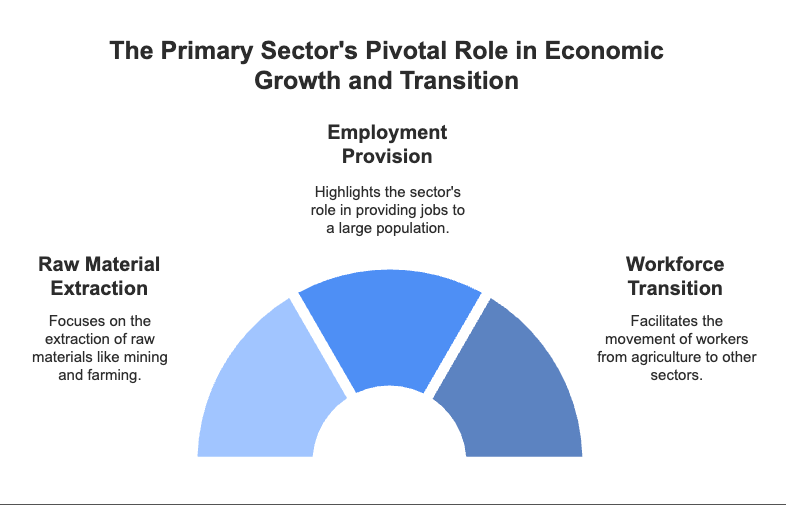
Q20: Suggest any three measures through which underemployment in the agriculture sector can be minimized. (2020)
Ans: Underemployment is a situation where there is under-utilisation of labour, either they are not in job where they can use their skill or they do not get full time job. these methods may help to solve the problem of underemployment
(i) One or two members of farmers family can work in the farms of big landlord and earn wages.
(ii) More irrigated facilities can be provided to grow two or three crops in a year.
(iii) By opening processing units of agriculture production, more employment opportunities can be created.
Q21: Why is the ‘tertiary sector’ becoming important in India? Explain any three reasons. (2020, Delhi 2019)
Ans: Tertiary sector in India has been growing rapidly for a number of reasons. In the year 2013-14, the tertiary sector has emerged as the largest sector in India replacing the primary sector. The reason for the growth of the tertiary sector are as follows –
(a) Basic services such as hospitals, educational institutions, post and telegraph services, police stations, courts, village administrative offices, municipal corporations, defence, transport, banks, insurance companies, requires a large number of people to be engaged in these tertiary sector activities. “
(b) The growth of agriculture and industry leads to the development of services such as transport, trade and storage. The demand for these services increases when the primary and secondary sectors are well developed.
(c) As the income rise certain sections of people start demanding many more services like eating out, tourism, shopping, private hospitals, private schools, professional training etc. We can see these changes in the big cities.
Q22: “All the services of the “service sector” are not growing equally well.” Evaluate the statement. (2020)
Ans: (i) Service sector in India employs many different kinds of people. At one end there are a limited number of services that employ highly skilled and educated workers, such as managers, lawyers, accountants, etc.
(ii) At the other end, there are a very large number of workers engaged in services, such as small shopkeepers, repair persons, transport persons. These people barely manage to earn a living and yet perform these services.
(iii) There is no alternative opportunity for them. Only a part of this sector is growing in importance.
Q23: Suggest any three ways to save workers of unorganized sector from exploitation. (2020)
Ans: Workers can be saved from unorganised sector possible in the following way:
(i) Social security to workers.
(ii) Support from Labour Ministry
(iii) Provide support for the conversion of unorganised sector to organised sector.
Q24: In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion(A) and Reason (R). Read the statements and choose the correct option: (2020)
Assertion (A): The Government of India buys wheat and rice from farmers at fair price.
Reason (R): Public sector contributes to the economic development.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans: (b)
The Assertion (A) is true because the Government of India does buy wheat and rice from farmers at a fair price to ensure food security. The Reason (R) is also true as the public sector plays a significant role in economic development by providing services and stability. However, the reason does not explain why the government buys wheat and rice; they are related but not directly connected. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q25: How is Public sector different from Private sector? (2020)
Ans: Public sector is controlled by the Government whereas private sector is under the control of an individual or a firm.
Q26: Suggest any three ways to improve the condition of the public sector at grass root level. (2020)
Ans: Reforms to improve public sector:
(i) More investment by Government at grass root level.
(ii) More banks and cooperatives.
(iii) Infrastructural development at grass root level.
(iv) Health and education profits at grass root level.
Q27: How is GDP calculated? (CBSE 2020)
Ans: GDP in India is calculated by adding the total value of the final goods and services produced by all three sectors. Only final goods and services are counted to get the final value.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q28: Distinguish between ‘primary’ and ‘secondary’ sectors. (Delhi 2019)
Ans: When the economic activity depends mainly on exploitation of natural resource, then that activity comes under the primary sector. Agriculture and its related activities are the primary sectors of the economy, so farming is an example of primary sector activity. While the activities in which natural products are changed into other forms comes under secondary sector.
Q29: Highlight any five features of ‘Public Sector.’ (Al 2019)
Ans: The features of the public sector can be enumerated as follows:
(i) Some projects need spending of large sums of money, which is beyond the capacity of the private sector. Collecting money from thousands of people who use these facilities is not easy. This is seen in various public conveniences.
(ii) In certain cases of national security such as the defense forces, only the public sector can be trusted. Large scale operations of governing the banks and management of money circulation can only be done by the public sector.
(iii) Even if they do provide these things the private sector is more likely to charge a high rate for their use. Examples are construction of roads, bridges, railways, harbors, metro rail, providing irrigation through dams etc.
(iv) Only the governments can undertake such heavy spending and ensure that these facilities are available for everyone. There are some activities, which the government has to support.
(v) In some cases, the government subsidizes the goods that are meant for the poor. This includes cooking gas, fertilisers, irrigation, electricity in rural sector support purchase price of farm produce, primary education and medical care etc.
Q30: Explain why the service sector is gaining more importance in the global economy. (2019,2017)
Ans: Tertiary sector in India has been growing rapidly for a number of reasons:
(i) In a developing country, the government has to take the responsibility for the provision of basic services for example, hospitals, educational institutions, post and telegraph services, police stations, courts, village administrative offices, municipal corporations, defence, transport, banks, insurance companies, etc.
(ii) The development of agriculture and industry leads to the development of services, such as trade, transport, storage, etc. Greater the development of the primary and secondary sectors, more would be the demand for such services.
(iii) As income levels rise, certain sections of people start demanding many more services, such as eating out, tourism, shopping, private hospitals; private schools, professional at training, etc. This change was quite sharp in cities, especially in big cities.
(iv) Over the past decade or so, certain new services, such as those based on information and communication technology have become important and essential.
(v) Government policy of privatisation has also led to growth of this sector.
(vi) A large number of workers are engaged in services, such as small shopkeepers, repair persons, transport persons, etc.
(vii) However, the entire sector has not grown. Large numbers of people engaged as construction workers, maids, peons, small shopkeepers, etc. do not find any change in their life.
Q31: How does the public sector contribute to the economic development of a nation? Explain. (2019,2014)
Ans: The public sector contributes to the economic development of a nation in the following ways:
- It promotes rapid economic development through the creation and expansion of infrastructure in underdeveloped areas.
- It creates employment opportunities through various projects.
- It generates financial resources for economic and social development.
- It ensures balanced regional development.
- It encourages the development of small, medium, and cottage industries as ancillaries.
- It ensures the easy availability of goods at moderate rates.
- It contributes to community development by providing health and educational services.
Q32: Which of the following professions belongs to the Tertiary Sector of the economy?
(a) Fisherman
(b) Farmer
(c) Woodcutter
(d) Teacher (CBSE 2019)
Ans: (d)
(i) The Tertiary Sector (or Service Sector) includes professions that provide services rather than goods. This sector supports the primary and secondary sectors by offering services like education, healthcare, banking, transportation, and communication.
(ii) A teacher provides an educational service, which is part of the tertiary sector.
The other options belong to the Primary Sector:
(a) Fisherman: Engaged in fishing, which is part of the primary sector as it involves direct extraction of natural resources.
(b) Farmer: Involved in agriculture, which is also part of the primary sector.
(c) Woodcutter: Involved in forestry, another primary sector activity that involves resource extraction.
Therefore, the correct answer is (d) Teacher.
Q33: There are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Mark your answer as per the codes provided below:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is correct but (R) is wrong.
(d) (A) is wrong but (R) is correct.
Assertion (A): Not every good or service that is produced and sold needs to be counted to know the total production in each sector.
Reason (R): The value of final goods already includes the value of all the intermediate goods. (CBSE 2019)
Ans: (a)
Assertion (A): Not every good or service that is produced and sold needs to be counted to know the total production in each sector. This statement is true because, in calculating the total production, only the value of final goods is counted to avoid double-counting.
Reason (R): The value of final goods already includes the value of all the intermediate goods. This statement is also true. When calculating GDP, the value of intermediate goods (which are used to produce final goods) is not counted separately, as it is already included in the price of the final product.
Since (R) provides the correct explanation of (A), the correct answer is (a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Q34: How can more employment be generated in the agriculture sector? Explain any three methods. (CBSE 2019, 15)
Ans: More employment can be generated in the agriculture sector alone in the following ways:
(1) Increase in irrigation facilities: Without irrigation, only a single crop can be grown in most agricultural fields, which means less working opportunities, but if irrigation is provided, two or three crops can be grown on the same field. So, more people will be employed.
(2) Provide basic facilities: Government should provide basic infrastructure in agriculture related facilities such as transportation (building of roads), irrigation, banking to ease the work of farmers. Subsidies can be provided. Dams and storages can be built.
(3) Provide them easy loan: If people are provided easy bank loans, then they could start small businesses, which will make them self-dependent.
Q35: Workers are exploited in the unorganised sector.” Give reasons to support this statement. (CBSE 2019)
Ans: Employment conditions in the unorganised sector:
(1) There are rules and regulations but these are not followed.
(2) Jobs are low paid and not secured.
(3) No provisions for over time, holidays, sick leaves etc.
(4) People can be asked to leave without any reason.
(5) They are largely outside the control of government.

Previous Year Questions 2018
Q36: When we produce goods by exploiting the natural resources, in which category of economic sector such activities come? (CBSE 2018)
Ans: When goods are produced by exploiting the natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector.
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q37: Why tertiary sector is also called the service sector? (2017, 2014)
Ans: Tertiary sector is the sector which provides services, such as banking, selling, transportation, etc. These services actually help in proper functioning of the primary and secondary sectors.
Q38: Mention any one feature of the organised sector. (2017)
Ans: A worker in the organized sector is assured of regular work, regular salary, and other benefits.
Q39: What do you understand by underemployment? (2017)
Ans: Underemployment refers to the condition in which people in the labor force are employed at less than full-time or regular jobs, or at jobs inadequate with respect to their training or economic needs.
Q40: What historical changes have been brought about in the primary economy? (2017)
Ans: The primary economy has undergone significant historical changes over the years. Some of these changes include:
- New technologies have brought big changes to how things are done in farming, mining, and fishing. Machines and modern tools make these jobs faster and better.
- In farming, the Green Revolution changed everything. New types of crops, better ways to water them, and using chemicals like fertilizers and pesticides meant way more food could be grown. Farming isn’t just about the same old crops anymore. New kinds of plants are being grown in different places, and things like growing flowers or fancy fruits (like horticulture and floriculture) are becoming more popular. This helps get even more food and money.
- Nowadays, there’s a lot of talk about taking care of the environment. So, in the primary sector, people are thinking more about how to do things in a way that doesn’t hurt the Earth. This means saving natural resources, keeping different plants and animals safe, and using methods that don’t hurt the environment.
- All these changes over time have made the primary sector better at what it does. It’s more productive, cares more about the environment, and can adapt to new problems and needs.
Q41: How are the three sectors of the economy different from each other? Explain. (2017)
Ans: The three sectors of the economy, namely the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors, are distinct from each other based on the nature of their activities.
Here’s an explanation of their differences:
- The primary sector deals with getting natural resources from the environment and using them. It includes stuff like farming, cutting down trees, mining, fishing, and taking care of animals.
- The secondary sector is all about turning those raw materials from the primary sector into finished products. This includes making things like cars, buildings, and electricity.
- The tertiary sector is focused on giving services instead of making stuff. So, things like transportation, banking, healthcare, and tourism fall under this sector.
- Each sector depends on the others to work. The primary sector gives raw materials, the secondary sector makes them into stuff we use, and the tertiary sector helps both of them by providing services. Together, they help a country’s economy grow and develop.
Q42: Compare the employment conditions of workers in the organised and unorganised sectors. (2017,2016)
Ans: In the organised sector:
- Rules and regulations (labour laws) as proposed by the government are followed.
- Formal processes and procedures are followed.
- Security of employment to workers, who are employed for full time is ensured.
- Working hours fixed, overtime is paid for extra hours of work.
- Workers get benefits like provident fund, gratuity, medical benefits, paid leave, etc.
In the unorganised sector:
- Outside the control of the government laws.
- Small and scattered units.
- Rules and regulations are not followed.
- Low-paid and irregular jobs.
- High degree of insecurity.
- No provision for overtime, paid leave, holidays, etc.
Q43: Describe any five provisions of ‘National Rural Employment Guarantee’ Act 2005. (2017)
Ans: Provisions of National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA), 2005 are:
- It provides 100 days assured employment every year to each rural household.
- One-third of the proposed jobs are reserved for women.
- If an applicant is not employed within 15 days he/she is entitled to a daily unemployment allowance.
- The government has to establish Central Employment Guarantee Funds and state employment guarantee funds for the implementation of the scheme.
- The scheme is to be extended to 600 districts.
| Also read: Long Answer Questions: Sectors of the Indian Economy |
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q44: When was Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act implemented? (2016)
Ans: The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act was implemented in the year 2005.
Q45: What is disguised unemployment? (2016)
Ans: Disguised unemployment refers to a situation where labor that is employed in a job is not actually utilized for the production of goods and services.
Q46: State the meaning of under-employment. (2016)
Ans: Underemployment happens when workers are working at less than their capabilities. The underemployment of workers is not reflected in official unemployment statistics because of the way they are compiled.
Q47: In which sector is Seasonal and Disguised Unemployment most prevalent in India? (2016)
Ans: Seasonal and disguised unemployment are most prevalent in the agriculture sector (Primary sector).
Q48: What is another name for underemployment? (2016)
Ans: Overstaffing or hidden unemployment.
Q49: Suggest any one way to solve the underemployment situation in rural areas in India. (2016)
Ans: The government can spend money on the development of infrastructure projects, such as construction of roads, canals, etc. The government can provide easy credit to people and encourage entrepreneurship.
Q50: Mention any one factor responsible for the growth of the service sector in the Indian economy. (2016)
Ans: As income levels rose, a certain section of the population started demanding many services like eating out, tourism, private hospitals, etc. The rise of information and communication technology can be largely attributed to improvement in telecommunication and power sectors.
Q51: Which sector has gained prominence over the last thirty years? (2016)
Ans: The tertiary sector has gained prominence over the last thirty years.
Q52: TISCO and Reliance are owned by which sector? (2016)
Ans: TISCO and Reliance are owned by the private sector.
Q53: Describe the estimates of the Planning Commission to create jobs in tourism and education. (2016)
Ans: Regarding jobs in education:
- The Planning Commission estimates that nearly 20 lakh jobs can be created in the education sector alone.
- More teachers and infrastructure will be required to accommodate more children in schools.
Regarding jobs in tourism
- The Planning Commission estimates that nearly 35 lakh jobs can be created in the tourism sector.
- Regional crafts, cottage industry, and new services like IT also have the potential to generate jobs.
Q54: Suggest any five measures to reduce unemployment. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: To reduce unemployment, the following measures can be taken:
- Planned development by accelerating industrialization and stimulating demand for goods and services.
- Creation of more employment opportunities in rural areas by processing farm produce, promoting cooperative farming, and developing allied activities and cottage industries.
- Planning projects to eliminate seasonal unemployment and providing micro-finance and community self-help in both rural and urban areas.
- Demonstrating and promoting adaptive technology through educational programs to encourage entrepreneurial spirit.
- Launching self-employment schemes in services or small manufacturing, connected to core activities in rural/urban areas, to enable unemployed youth to start their own business or small-scale firms.
Previous Year Questions 2014
Q55: Why is agriculture the most labour-absorbing sector in India? How does disguised unemployment make it worse? Explain with an example. (CBSE 2014)
Ans: (1) Agriculture is the most labour absorbing sector because there are not many jobs created in the tertiary and the secondary sector.
(2) Farming does not require a lot of initial investment or very hard training.
(3) Families are involved in agriculture and hence, it becomes an inherited skill.
(4) Agricultural products have huge demand in the market and can be sold without any processing.
(5) Disguised unemployment which involves employment of more than the required people in a job reduces the productivity of the people and their effort gets divided without earning much.
 Q56: How does the public sector contribute to the economic development of a nation? Explain. (CBSE 2014)
Q56: How does the public sector contribute to the economic development of a nation? Explain. (CBSE 2014)
Ans: The public sector contributes to the economic development of a nation in the following ways:
(1) The public sector promotes rapid economic development through the construction of infrastructure.
(2) It creates employment opportunities.
(3) It helps to generate revenue to support the holistic development of all classes and castes.
(4) It encourages the development of small, medium and cottage industries, which provide opportunities for the vulnerable groups.
(5) It ensures easy availability of goods at moderate rates.
 (a) Pakistan
(a) Pakistan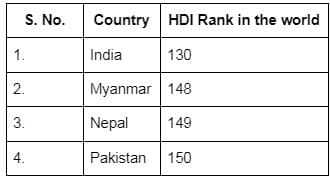
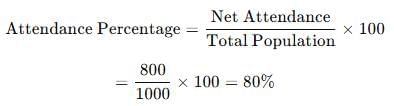
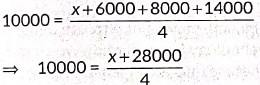


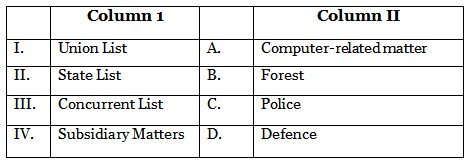
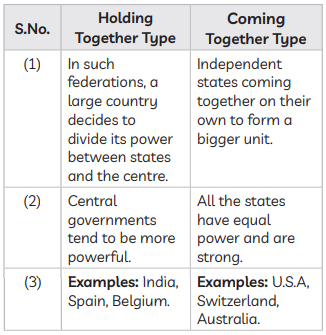

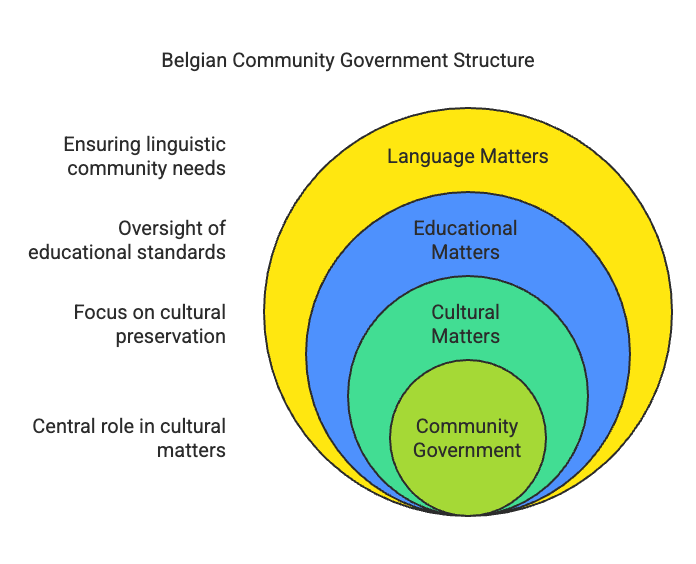
 Q15: Under which of the following is power shared in the ‘Community Government’ of Belgium? (2020)
Q15: Under which of the following is power shared in the ‘Community Government’ of Belgium? (2020)

 IT Innovation
IT Innovation Agro-Industrial Growth
Agro-Industrial Growth

 Sustainable Energy
Sustainable Energy Minerals
Minerals Biogas Energy
Biogas Energy