रेखाएँ और कोण
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 15,16,17)
Q.1. (a)रिहान ने एक कागज पर एक बिंदु अंकित किया। वह उस बिंदु से जाने वाली कितनी रेखाएँ बना सकता है?
(b)शीतल ने एक कागज पर दो बिंदु अंकित किए। वह उन दोनों बिंदुओं से गुजरती हुई कितनी भिन्न रेखाएँ बना सकती है?
क्या आप रिहान और शीतल को उनके उत्तर ज्ञात करने में मदद कर सकते हैं?
उत्तर: (a) अनगिनत रेखाएँ खींची जा सकती हैं।
(b) केवल एक रेखा।
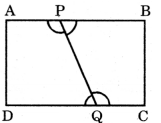
2. आकृति 2.4 में दिए गए रेखाखंडों के नाम लिखिए। पाँच अंकित बिंदुओं में से कौन-से केवल एक रेखाखंड पर स्थित हैं? कौन-से बिंदु किन्हीं दो रेखाखंडों पर स्थित हैं?
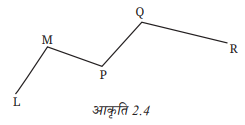
उत्तर: रेखाखंडों के नाम:
LM, MP, PQ, QR, RP
केवल एक रेखाखंड पर स्थित बिंदु:
LM, QR
दो रेखाखंडों पर स्थित बिंदु:
- M (LM और MP पर)
- P (MP और PQ तथा PR पर)
- R (QR और RP पर)
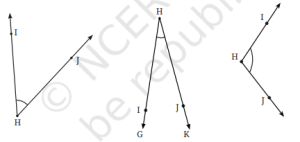
3. आकृति 2.5 में दी गई किरणों के नाम लिखिए। क्या T प्रत्येक किरण का प्रारंभिक बिंदु है?
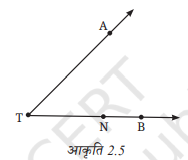
उत्तर:
किरण TA, किरण TN, किरण TB
(प्रत्येक किरण में पहला अक्षर प्रारंभिक बिंदु होता है और दूसरा अक्षर उस दिशा में कोई बिंदु जो किरण पर स्थित होता है।)
हाँ, T प्रत्येक किरण का प्रारंभिक बिंदु है।
इसलिए, T सभी किरणों का प्रारंभिक बिंदु है।
4. एक कच्ची (rough) आकृति बनाइए और नीचे दिए गए प्रत्येक बिंदु का उपयुक्त नामांकन कीजिए-
a. OP और OQ बिंदु O पर मिलते हैं।
b. XY और PQ बिंदु M पर प्रतिच्छेद करते हैं।
c. रेखा 1 पर बिंदु E और F स्थित हैं पर बिंदु D स्थित नहीं है।
d. बिंदु P, AB पर स्थित है।
उत्तर: a.
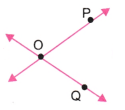
b.
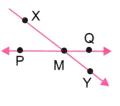
c.

d.
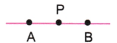
5. आकृति 2.6 में निम्नलिखित के नाम बताइए-
a. पाँच बिंदु
b. एक रेखा
c. चार किरणें
d. पाँच रेखाखंड
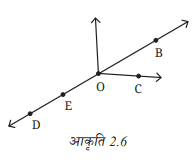
उत्तर: a. पाँच बिंदु: – D, E, O, C, B
b. एक रेखा:
रेखा DE या DOB या DB (क्योंकि यह रेखा दोनों दिशाओं में अनंत तक जाती है और D, E, O, B उस पर स्थित हैं)
c. चार किरणें:
- OB (O से शुरू होकर B की दिशा में बढ़ती हुई किरण)
- OC (O से C की दिशा में)
- OD (O से D की ओर)
- OE (O से E की ओर — यह भी किरण मानी जा सकती है)
d. पाँच रेखाखंड: DE, EO, OC, CB, OB
6. आकृति 2.7 में OA एक किरण है। यह O से शुरू होती है और बिंदु A से गुजरती है। यह बिंदु B से भी गुजरती है।
a. क्या हम इसे OB भी नाम दे सकते हैं? क्यों?
b. क्या हम OA को AO लिख सकते हैं? क्यों अथवा क्यों नहीं?
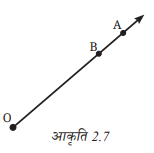
उत्तर: a. हाँ, हम इसे OB नाम दे सकते हैं,
क्योंकि किरण O से शुरू होती है और B बिंदु उस पर स्थित है।
→ किरण की दिशा वही रहेगी (O से आगे की ओर),
→ और चूँकि किरण OB भी उसी दिशा में जा रही है जिसमें OA है,
इसलिए OB भी एक मान्य नाम है।
b. नहीं, हम OA को AO नहीं लिख सकते,
क्योंकि किरण का नाम हमेशा प्रारंभिक बिंदु से शुरू होता है।
→ यहाँ किरण O से शुरू होती है, इसलिए पहले O आना चाहिए।
→ AO लिखने से यह अर्थ निकलता है कि किरण A से शुरू होकर O की ओर जा रही है, जो गलत है।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 19,20)
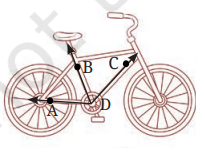
1. क्या आप दी गई आकृतियों में कोण ढूँढ़ सकते हैं? किसी भी एक कोण की भुजाएँ बनाइए और शीर्ष का नाम दीजिए।
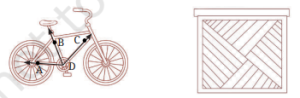

उत्तर:
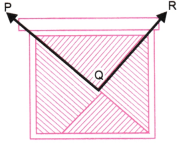
कोण ∠BDC का शीर्ष (vertex) D है।
कोण ∠PQR का शीर्ष (vertex) Q है।
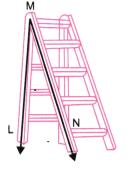
कोण ∠LMN का शीर्ष (vertex) M है।
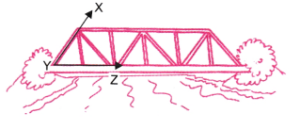
कोण ∠XYZ का शीर्ष (Vertex) Y है।
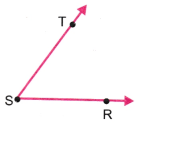
2. भुजा ST और SR को चिह्नित करते हुए कोण बनाइए।
उत्तर:
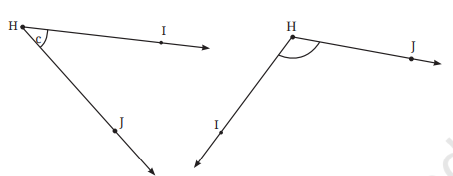
3. व्याख्या कीजिए कि ∠APC को ∠P क्यों नहीं लिखा जा सकता?
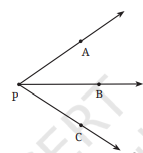
उत्तर: ∠APC को ∠P इसलिए नहीं लिखा जा सकता है, क्योंकि इस आकृति में ऐसे दो कोण ∠APB और ∠BPC हैं, जिनका शीर्ष भी P ही है।
4. नीचे दी गई आकृति में अंकित कोणों के नाम लिखिए।
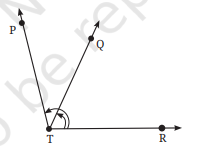
उत्तर: ये कोण ∠PTR और ∠QTR हैं।
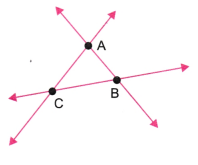
5. अपने कागज पर तीन बिंदु इस प्रकार अंकित कीजिए कि वे एक रेखा पर स्थित न हों। उन्हें A, B और C से चिह्नित कीजिए। सभी संभव रेखाएँ खींचिए, जो इन बिंदु-युग्मों से गुजरती हों। इस प्रकार आपको कितनी रेखाएँ प्राप्त होती हैं? उनके नाम भी बताइए। A, B और C का प्रयोग करते हुए आप कितने कोण बना सकते हैं? उन सभी के नाम लिखिए और आकृति 2.9 के अनुसार उनमें से प्रत्येक को एक चाप के साथ चिह्नित कीजिए|
उत्तर: हमें तीन रेखाएँ प्राप्त होती हैं।
ये हैं: रेखा AB, रेखा BC और रेखा CA।
साथ ही, हमें तीन कोण प्राप्त होते हैं।
ये हैं: ∠ABC, ∠BCA और ∠CAB।
6. अपने कागज पर चार बिंदु इस प्रकार अंकित कीजिए कि उनमें से कोई भी तीन बिंदु एक रेखा पर न हों। उन्हें A, B, C और D से चिह्नित कीजिए। सभी संभव रेखाएँ खींचिए, जो इन बिंदु-युग्मों से गुजरती हों। इस प्रकार आपको कितनी रेखाएँ प्राप्त होती हैं? उनके नाम भी बताइए। आप A, B, C और D से कितने कोणों का नामकरण कर सकते हैं? उन्हें लिखिए और उनमें से प्रत्येक को आकृति 2.9 के अनुसार चाप द्वारा अंकित कीजिए।
उत्तर:
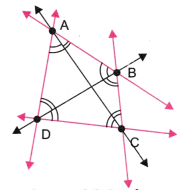
हमें छः रेखाएँ प्राप्त होती हैं।
ये हैं: रेखा AB, रेखा BC, रेखा CD, रेखा DA, रेखा AC और रेखा BD।
साथ ही, हमें बारह कोण प्राप्त होते हैं।
ये हैं: ∠BAC, ∠CAD, ∠BAD, ∠ABD, ∠DBC, ∠ABC, ∠BCA, ∠ACD, ∠BCD, ∠CDB, ∠CDA, और ∠BDA।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 23)
1. एक आयताकर कागज को मोड़िए। अब घुमाव के निशान पर एक रेखा खींचिए। घुमाव और कागज की भुजाओं के बीच बने कोणों को नाम दीजिए और उन कोणों की तुलना कीजिए। आयताकार कागज को घुमाकर विभिन्न कोण बनाइए एवं उनकी तुलना कीजिए। यह भी बताइए कि इनमें से कौन-सा कोण सबसे बड़ा है और कौन-सा कोण सबसे छोटा है?

उत्तर: मोड़ के निशान PQ और भुजाओं द्वारा बनाए गए कोण ∠APQ, ∠BPQ, ∠DQP और ∠CQP हैं। ∠APQ और ∠CQP बराबर हैं तथा ये दोनों कोण सबसे बड़े हैं। ∠BPQ और ∠DQP बराबर हैं तथा ये दोनों कोण सबसे छोटे हैं।
2. प्रत्येक स्थिति में बताइए कि कौन-सा कोण बड़ा है और क्यों?
a. ∠AOB या ∠XOY
b. ∠AOB या ∠XOB
c. ∠XOB या ∠XOC
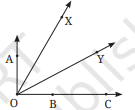
अपने मित्रों से चर्चा कीजिए कि आपने यह निर्णय कैसे लिया कि कौन-सा कोण बड़ा है।
उत्तर: a. (∠AOB > ∠XOY), क्योंकि ∠XOY, ∠AOB के भीतर आता है। इसका अर्थ है कि ∠XOY, ∠AOB का एक भाग है।
b. (∠AOB > ∠XOB), क्योंकि ∠XOB, ∠AOB के भीतर आता है। इसका अर्थ है कि ∠XOB, ∠AOB का एक भाग है।
c. (∠XOB = ∠XOC), क्योंकि दोनों कोण एक ही किरणों द्वारा बनाए गए हैं।
3. कौन-सा कोण बड़ा है- ∠XOY या ∠AOB? कारण बताइए।
उत्तर: क्योंकि ∠AOB, ∠XOY के भीतर आता है।
∠AOB, O से शुरू होकर A और B के बीच बना है,
जबकि ∠XOY अधिक फैला हुआ है — X से Y तक का कोण है,
जो पूरे ∠AOB को समाहित करता है और उससे अधिक है।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 29,30,31)
1. आपकी कक्षा की खिड़कियों में कितने समकोण हैं? क्या अपनी कक्षा में आप और समकोण देख सकते हैं?
उत्तर:
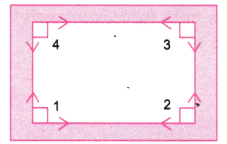
एक खिड़की में 4 समकोण (Right Angles) होते हैं।
ये हैं: ∠1, ∠2, ∠3 और ∠4 — अर्थात चारों कोनों पर।
हाँ, समकोण हमें और भी स्थानों पर देखने को मिलते हैं — जैसे:
- दरवाज़े के कोनों पर
- ब्लैकबोर्ड के कोनों पर
- टेबल, किताब, टाइल्स आदि में भी।
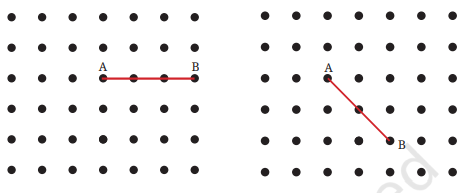
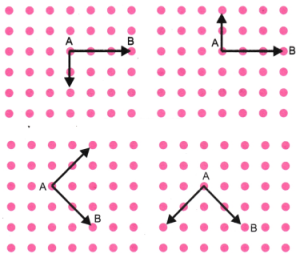
2. बिंदु A को ग्रिड के दूसरे बिंदुओं से एक सरल रेखा में इस प्रकार जोड़ें कि एक सरल कोण प्राप्त हो। इसे करने के विभिन्न तरीके क्या हो सकते हैं?
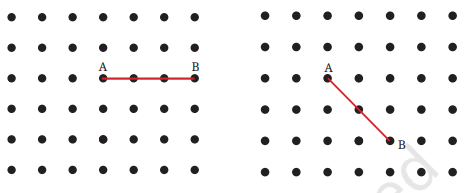
उत्तर:
3. अब बिंदु A को ग्रिड के दूसरे बिंदुओं से एक सरल रेखा में इस प्रकार जोड़ें कि एक समकोण प्राप्त हो। इसे करने के विभिन्न तरीके क्या हो सकते हैं?
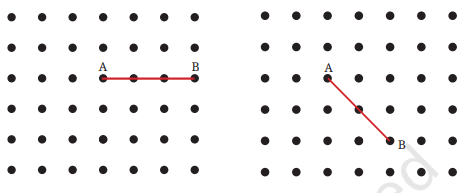
उत्तर:
4. कागज को घुमाकर तिरछा निशान बनाइए। अब एक अन्य निशान बनाइए जो पिछले तिरछे निशान पर लंब हो।
a. अब आपके पास कितने समकोण हैं? तर्क संगत उत्तर दीजिए कि ये कोण पूर्णतया समकोण क्यों हैं?
b. वर्णन कीजिए कि आपने इसे कैसे मोड़ा ताकि जो व्यक्ति इस प्रक्रिया को करना नहीं जानता वह आपकी प्रक्रिया का अनुसरण करके समकोण बना सके।
उत्तर:
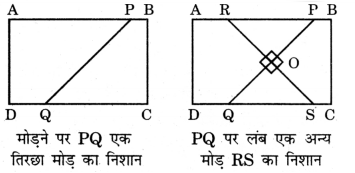
(a) हम चार समकोण ROP, POS, QOS और QOR प्राप्त करते हैं। ये सभी कोण बराबर हैं।
(b) हम कागज को इस प्रकार मोड़ते हैं कि तिरछे मोड़ के निशान का बिंदु P बिंदु Q पर पड़े (गिरे)।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 31,32)
1. पिछली आकृतियों में न्यून कोण, समकोण, अधिक कोण और सरल कोण को पहचानिए।
उत्तर:
2. कुछ न्यून कोण और अधिक कोण भिन्न दशाओं में बनाइए।
उत्तर:
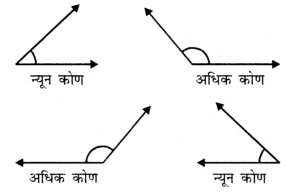
3. क्या आप जानते हैं कि न्यून और अधिक शब्दों का क्या अर्थ है? न्यून का अर्थ नुकीला और अधिक का अर्थ कुंद होता है। आपको क्या लगता है कि इन शब्दों का चयन क्यों किया गया होगा?
उत्तर: “न्यून” का अर्थ है नुकीला, क्योंकि न्यून कोण तेज और छोटा होता है।
“अधिक” का अर्थ है कुंद, क्योंकि अधिक कोण फैला हुआ और चौड़ा होता है।
इन शब्दों का चयन इसलिए किया गया क्योंकि वे उनके आकार और धार को दर्शाते हैं।
4. ज्ञात कीजिए कि नीचे दी गई आकृतियों में कितने न्यून कोण हैं-
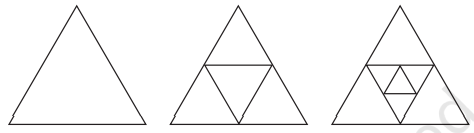
अगली आकृति क्या होगी और उसमें कितने न्यून कोण होंगे? क्या आप संख्याओं में कोई पैटर्न देखते हैं?
उत्तर: a. 3 न्यून कोण
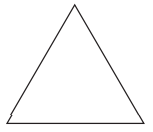
b. 12 न्यून कोण
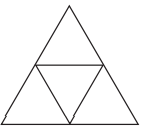
c. 21 न्यून कोण
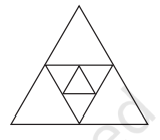
(Page 33)
प्रश्न. एक सरल कोण का डिग्री माप क्या होगा? एक सरल कोण, पूर्ण घुमाव का आधा होता है। क्योंकि पूर्ण घुमाव 360° है तथा पूर्ण घुमाव का आधा 180° होता है। एक समकोण का डिग्री माप क्या होगा? दो समकोण मिलकर एक सरल कोण बनाते हैं। चूँकि एक सरल कोण का माप 180° होता है, तो एक समकोण का माप 90° होगा। 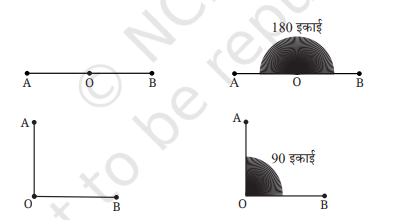
उत्तर: सरल कोण का माप डिग्री में 180° होता है और समकोण का माप डिग्री में 90° होता है।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 35)
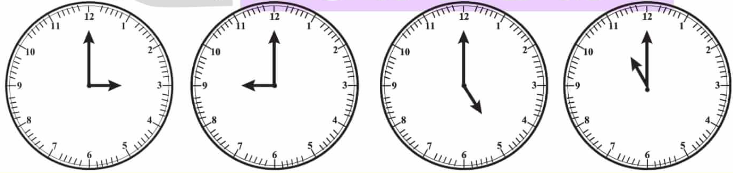
1. निम्नलिखित कोणों के माप लिखिए
a. ∠KAL
ध्यान दीजिए कि इस कोण का शीर्ष बिंदु कोणमापक के केंद्रबिंदु पर संपाती है। अतः KA एवं AL के बीच 1° कोणों की इकाइयों की
संख्या से कोण KAL की माप पता चलती है। गिनने पर, हम पाते हैं-
∠KAL = 30°
क्या मध्यम आकार के चिह्नों एवं बड़े आकार के चिह्नों का उपयोग करते हुए 5 या 10 में इकाईयों की संख्या गिनना संभव है?
b. ∠WAL
c. ∠TAK
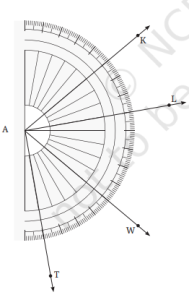
उत्तर: (a) ∠KAL = 30°
(b) ∠WAL = 50°
(c) ∠TAK = 120°
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 40 से 43 तक)
1. चाँदे का प्रयोग करते हुए निम्न कोणों के डिग्री माप ज्ञात कीजिए?
उत्तर: (a) ∠IHJ = 47°
(b) ∠IHJ = 24°
(c) ∠IHJ =110°
2. चाँदे का प्रयोग करते हुए अपनी कक्षा में दिख रहे विभिन्न कोणों के डिग्री माप ज्ञात कीजिए।
उत्तर: ब्लैकबोर्ड के कोने का कोण = 90°
डेस्क (मेज) के कोने का कोण = 90°
3. नीचे दिए गए कोणों के अंश माप ज्ञात कीजिए। जाँच कीजिए की क्या यहाँ कागज के चाँद का प्रयोग कर सकते हैं।
उत्तर: (a) ∠IHJ = 42°
(b) ∠IHJ =116°
यहाँ पर कागज़ का प्रोट्रैक्टर (चाँद) उपयोग नहीं किया जा सकता है।
4. नीचे दिए गए कोण का अंश माप चाँद का प्रयोग करके किस प्रकार निकाला जा सकता है?
उत्तर: हम चाँदे (प्रोट्रैक्टर) की सहायता से पहले छोटे कोण का माप करेंगे।
इसके बाद, वांछित बड़े कोण की माप जानने के लिए उस छोटे कोण के माप को 360° में से घटा देंगे।
यदि छोटे कोण का माप 100° है, तो बड़े कोण का माप होगा:
360° – 100° = 260°
5. निम्न कोणों को मापिए और प्रत्येक का डिग्री माप लिखिए।
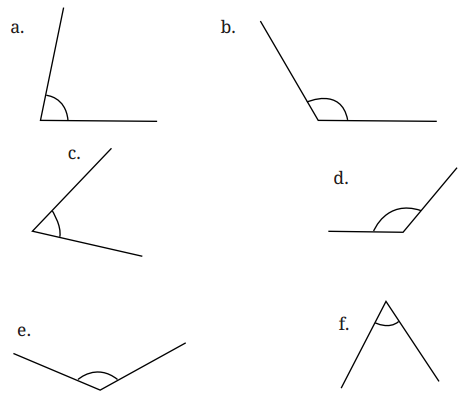
उत्तर: a. कोण = 78°
b. कोण = 120°
(c) कोण = 60°
(d) कोण = 130°
(e) कोण = 130°
(f) कोण = 60°
6. ∠BXE, ∠CXE, ∠AXB और ∠BXC के अंश माप ज्ञात कीजिए।
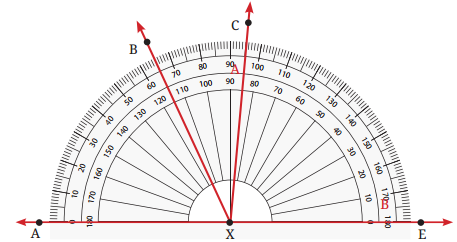
उत्तर: ∠BXE = 115; ∠CXE = 85°; ∠AXB = 65° और ∠BXC = 95° – 65° = 30° है।
7. ∠PQR, ∠PQS और ∠PQT के अंश माप ज्ञात कीजिए।
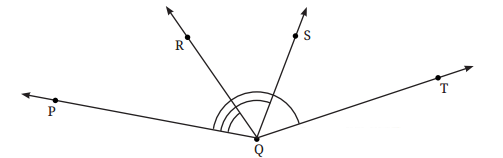
∠PQR = 45°; ∠PQS = 105° और ∠PQT = 152° है।
9. आकृति 2.21 (a) में बने त्रिभज के तीनों कोणों को मापिए और संबंधित कोण के नीचे उसका माप लिखिए। तीनों मापों को जोड़िए। क्या प्राप्त होता है? इस प्रकिया का आकृति 2.21 (b) और (c) के लिए भी प्रयोग कीजिए। अन्य त्रिभुजों पर भी इस प्रकिया का प्रयोग कीजिए। फिर सामान्य तौर पर क्या होता है इसका अनुमान लगाइए। हम आगे की कक्षाओं में जानेंगे कि ऐसा क्यों हुआ।
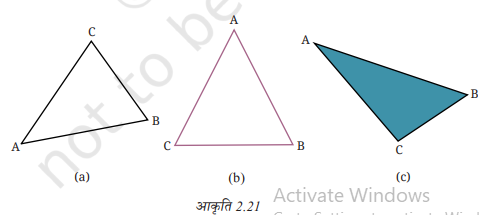
उत्तर: आकृति (a) में, ∠A = 45°; ∠B = 65° और ∠C = 70° है।
आकृति (b) में, ∠A = 50°; ∠B = 65° और ∠C = 65° है।
आकृति (c) में, ∠A = 30°; ∠B = 55° और ∠C = 95° है।
अनुमान इन त्रिभुजों में से प्रत्येक में तीनों कोणों का योग 180° है।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 45, 46)
कोण कहाँ हैं?
1. घड़ी में कोण-
a. घड़ी की सूईयाँ अलग-अलग समय पर भिन्न कोण बनाती हैं। 1 बजे सूईयों के बीच 30° का कोण होता है। क्यों?
b. 2 बजे कोण कितना होगा? और 4 बजे? 6 बजे?
c. घड़ी की सूईयों द्वारा बने अन्य कोणों को ढूँढिए।
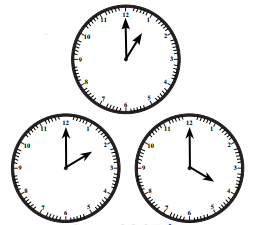
उत्तर: a. क्योंकि घड़ी का पूरा गोल चक्र 360° होता है
और उसमें 12 घंटे होते हैं।
इसलिए हर घंटे के बीच का कोण =
360° ÷ 12 = 30°
इसलिए 1 बजे, घंटे और मिनट की सुईयों के बीच का कोण = 30°
b. अन्य समयों पर कोण:
2 बजे = 2 × 30° = 60°
4 बजे = 4 × 30° = 120°
6 बजे = 6 × 30° = 180° (यह सरल कोण है)
c.
2. एक दरवाजे का कोण-
क्या ऐसा संभव है कि कोण का प्रयोग कर यह बताया जा सके कि दरवाजा कितना खुला है?
कोण का शीर्ष और कोण की भुजाएँ क्या होंगी?

उत्तर: हाँ, दरवाज़े के खुलने की स्थिति को कोण के माध्यम से बताया जा सकता है।
जब दरवाज़ा खुलता है, तो वह दीवार से एक कोण बनाता है। जितना ज़्यादा दरवाज़ा खुलेगा, उतना ही बड़ा कोण बनेगा।
3. विद्या झूले पर अपना समय आनंद से बिता रही है। उसने ध्यान दिया कि जब उसने झूलना शुरू किया तो जितना बड़ा कोण है, उतनी ही अधिक गति वह झूले पर अर्जित कर रही है। लेकिन यहाँ कोण है कहाँ? क्या आप यहाँ पर किसी कोण को देख सकते हैं?

उत्तर: जैसा कि आकृति में दर्शाया गया है, कोण पेड़ की शाखा तथा विद्या द्वारा थामी (पकड़ी) डोरी या रस्सी द्वारा बन रहा है।

4. यहाँ एक खिलौने के दोनों ओर तिरछे तख्ते (slanting slab) लगे हैं, जितना अधिक कोण या तख्ते का झुकाव होगा उतनी ही तेजी से गेंद लुढ़कती है। क्या कोणों का प्रयोग तख्तों के झुकाव के वर्णन में किया जा सकता है? प्रत्येक कोण की भुजाएँ क्या होंगी? कौन-सी भुजा दिखाई देगी और कौन-सी नहीं?

उत्तर: हाँ। इन कोणों में से प्रत्येक में एक भुजा खिलौने का ऊर्ध्वाधर किनारा होगा तथा दूसरी भुजा तिरछा तख्ता होगा। तिरछा तख्ता दिखाई देगा, जबकि खिलौने का ऊर्ध्वाधर किनारा दिखाई नहीं देगा।
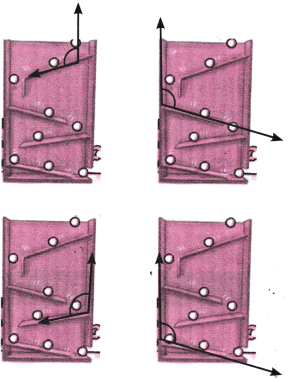
5. नीचे दिए गए चित्रों का अवलोकन कीजिए जिनमें एक कीट एवं उसकी घुमायी गई स्थितयाँ दी गई हैं। क्या घूर्णन (घुमाव ) की मात्रा बताने के लिए कोणों का उपयोग किया जा सकता है? यदि हाँ, तो कैसे? कोण का शीर्ष-बिंदु एवं उसकी भुजाएँ कौन-सी होंगी? [संकेत-कीट को छूकर जाती हुई क्षैतिज रेखा को देखिए।]

उत्तर: हाँ, दी हुई प्रत्येक आकृति में एक-चौथाई घूर्णन एक समकोण के बराबर घूर्णन को बताता है। दोनों आकृतियों में क्षैतिज और ऊर्ध्वाधर रेखाएँ कोण की भुजाएँ हैं। साथ ही, प्रत्येक कीट का आधार इस कोण का शीर्ष-बिंदु है।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 49, 50)
1. आकृति 2.23 में दर्शाए सभी संभव कोणों की सूची बनाइए। क्या आप उन सभी को ढूँढ़ पाए? अब सभी कोणों के माप का अनुमान लगाइए। इसके पश्चात् चाँदे की सहायता से कोणों का माप देखिए। अपनी सभी संख्याओं (डिग्री माप) को एक सारणी में अंकित कीजिए। देखिए आपके अनुमानित उत्तर सही माप के कितने समीप हैं।
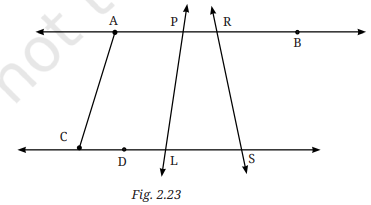
उत्तर: कोणों की सूची (List of Angles):
∠PAC
∠APD
∠DPS
∠LPR
∠PLS
∠ARP
∠PRS
∠RSL
∠ALC
डिग्री में अनुमानित माप:
∠PAC: 120°
∠APD: 90°
∠DPS: 120°
∠LPR: 60°
∠PLS: 90°
∠ARP: 30°
∠PRS: 150°
∠RSL: 90°
∠ALC: 120°
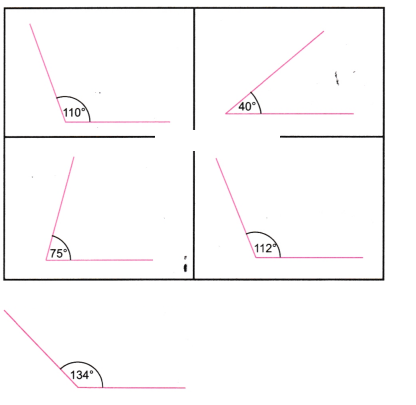
2. चाँदे की सहायता से निम्न डिग्री माप के कोण बनाइए-
(a)110°, (b) 40°, (c) 75°, (d)112°, (e) 134°
उत्तर:
3. एक कोण बनाइए जिसका डिग्री माप नीचे दिए गए कोण के समान हो।
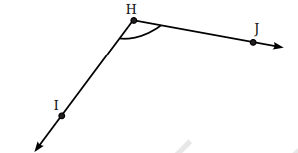
इस कोण को बनाने में प्रयुक्त सभी चरणों को भी लिखिए।
उत्तर: चरण 1: दिए गए कोण को मापिए (∠IHJ = 120°)
चरण 2: प्रोटेक्टर का उपयोग करके ∠ABC = 120° कोण बनाइए।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 51, 52)
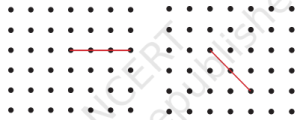
1. नीचे दिए गए प्रत्येक ग्रिड में, बिंदु A को ग्रिड के दूसरे बिंदुओं से एक सरल रेखा से इस प्रकार मिलान कीजिए कि हमें:
(a) एक न्यून कोण प्राप्त हो।
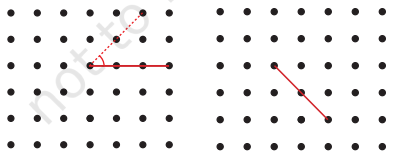
उत्तर:
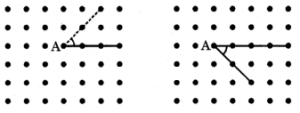
(b) एक अधिक कोण प्राप्त हो।
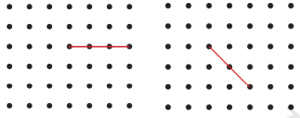
उत्तर:

(c) एक प्रतिवर्ती कोण प्राप्त हो।
उत्तर:

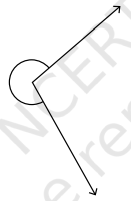
2. चाँदे की सहायता से प्रत्येक कोण का माप निकालिए। प्रत्येक कोण को न्यून कोण, अधिक कोण, समकोण या प्रतिवर्ती कोण में वर्गीकृत कीजिए।
(a) ∠PTR, (b) ∠PTQ, (c) ∠PTW, (d) ∠WTP
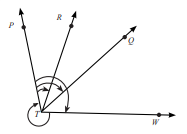
उत्तर: (a) ∠PTR = 30°; न्यून कोण है।
(b) ∠PTQ = 60°; न्यून कोण है।
(c) ∠PTW = 100°; अधिक कोण है।
(d) ∠WTP = 260°; प्रतिवर्ती कोण है।
आइए, पता लगाएँ (Page 53, 54)
1. निम्न अंश माप वाले कोणों को बनाइए-
(a) 140°, (b) 82°, (c) 195°, (d) 70°, (e) 35°
उत्तर:
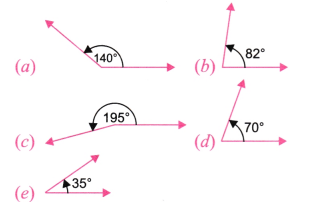
2. प्रत्येक कोण के माप का अनुमान लगाइए और फिर चाँदे से मापिए-
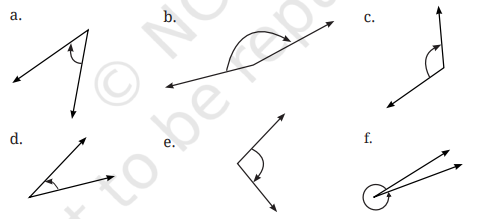
इन कोणों को न्यून कोण, अधिक कोण, समकोण और प्रतिवर्ती कोणों में वर्गीकृत कीजिए।
उत्तर: (a) 45°; न्यून कोण है।
(b) 170°; अधिक कोण है।
(c) 120°; अधिक कोण है।
(d) 30°; न्यून कोण है।
(e) 100° अधिक कोण है।
(f) 350°; प्रतिवर्ती कोण है।
3. एक आकृति बनाइए जिसमें तीन न्यून कोण, एक समकोण और दो अधिक कोण हों।
उत्तर:
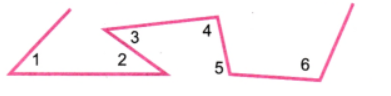
कोण 1, 2 और 3 तीव्र कोण हैं, कोण 4 समकोण है, और कोण 5 तथा 6 स्थूल कोण हैं।
4. अक्षर M को इस प्रकार बनाइए कि दोनों ओर के कोण 40° के हों और मध्य में कोण 60° का हो।
उत्तर:
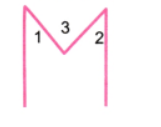
∠1 = 30°, ∠2 = 30°, ∠3 = 60°
5. अक्षर Y को इस प्रकार बनाइए कि 150, 60° और 150° के तीन कोण बनें।
उत्तर:
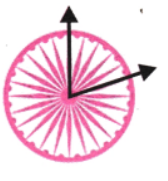
6. अशोक चक्र में 24 तीलियाँ होती हैं। दो संलग्न तीलियों के बीच कितने अंश माप का कोण होगा? दो तीलियों के बीच सबसे बड़ा न्यून कोण क्या होगा?
उत्तर:

दो लगातार तीलियों के बीच का कोण = 360 ÷ 24 = 15°
सबसे बड़ा तीव्र कोण = 5 × 15° = 75°

 Ans:
Ans: 
 Ans:
Ans: 




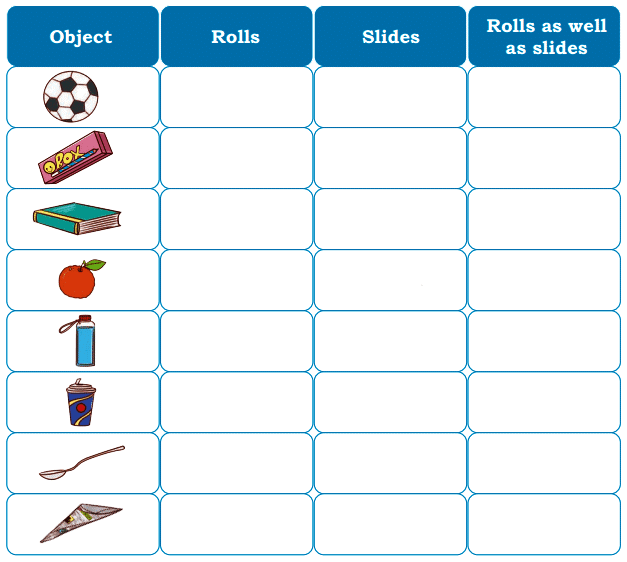
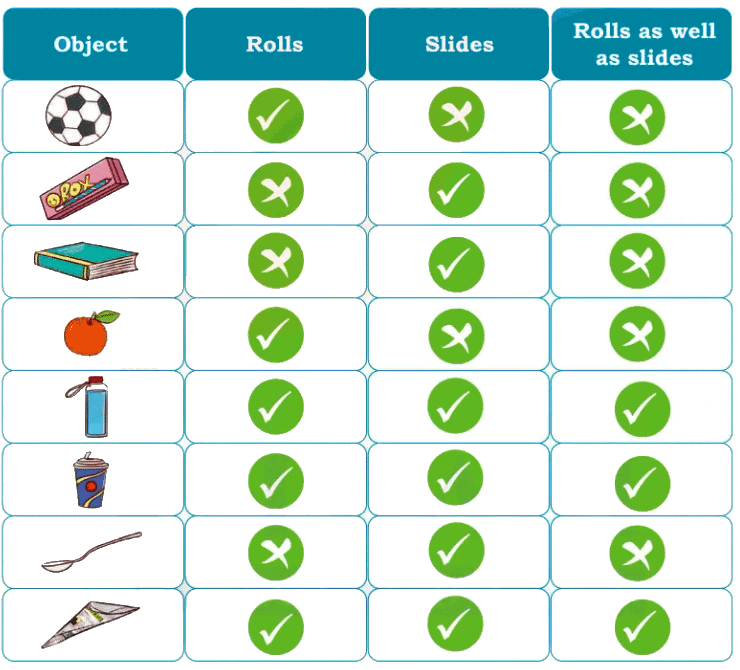

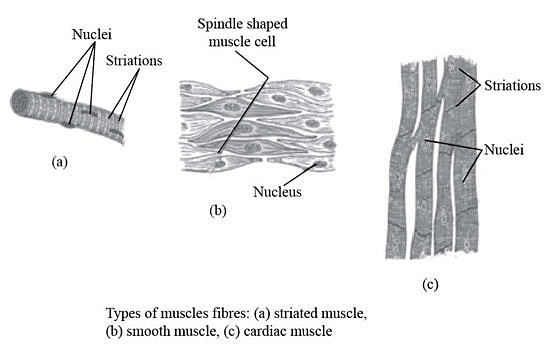
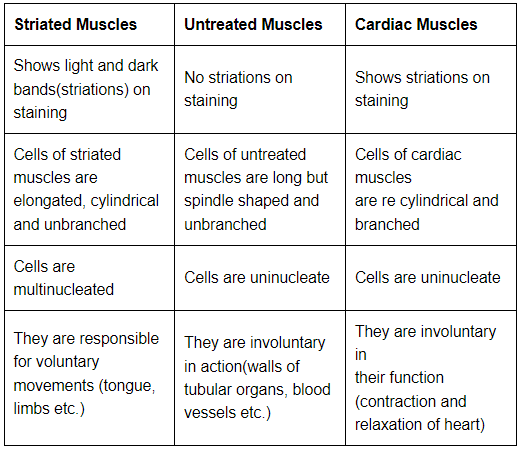
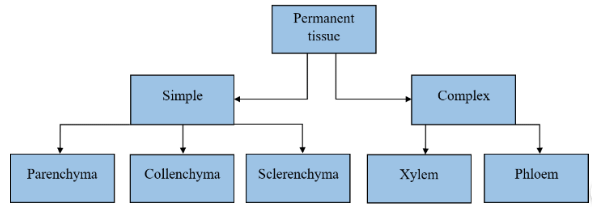
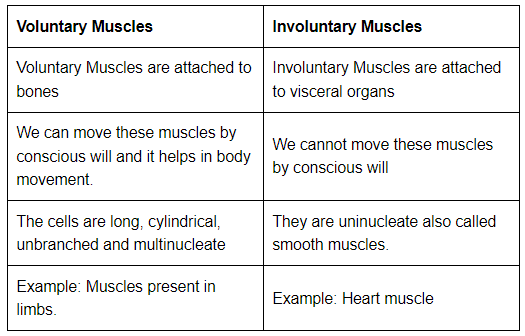
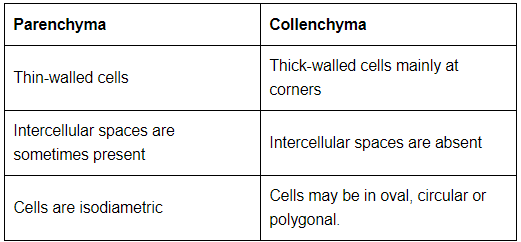
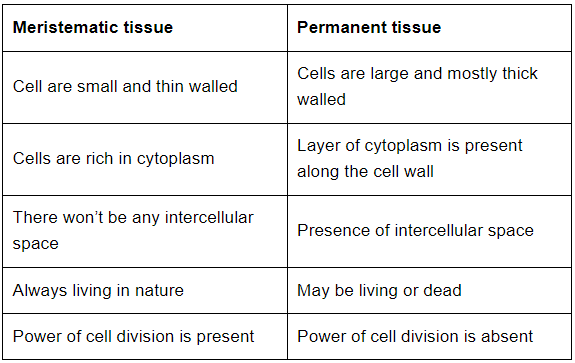
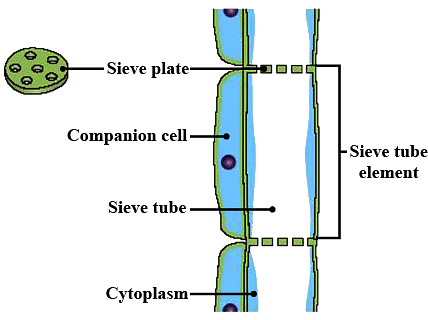 Q3: Name types of simple tissues.
Q3: Name types of simple tissues.