Short Q&A:
Q1: What is litmus and how is it used to identify acids and bases?
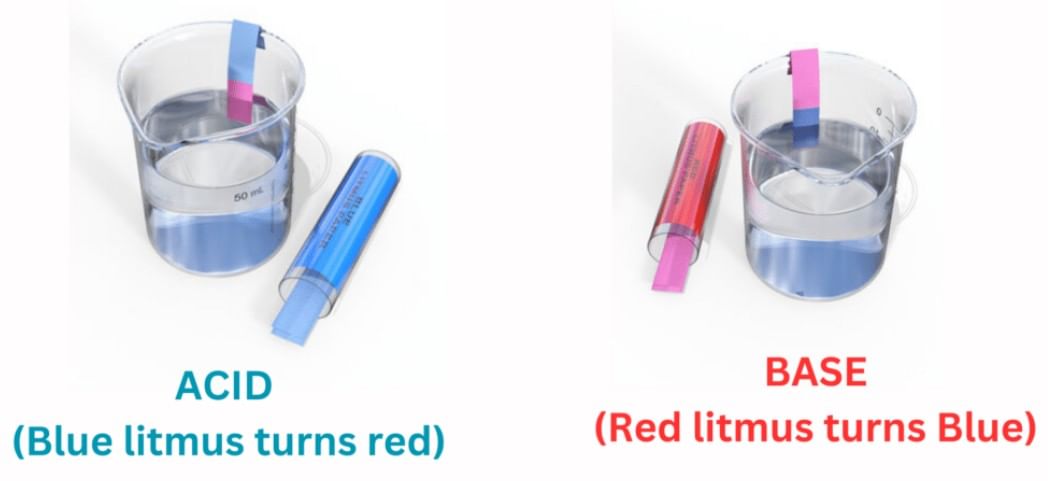
Ans: Litmus is a natural material made from lichens and comes as blue and red paper strips. It helps identify substances: acids turn blue litmus paper red, and bases turn red litmus paper blue.

LitmusQ2: How is red rose extract prepared and how does it act as an indicator?
Ans: Red rose extract is made by crushing fresh rose petals, soaking them in hot water, and filtering the liquid. It changes color to red in acidic substances and green in basic substances, helping to identify them.

Red Rose Petas immersed in Hot WaterQ3: What color change does turmeric paper show when it comes in contact with a base?
Ans: Turmeric paper, which is yellow, turns red when it touches a basic substance. It does not change color with acidic or neutral substances.
Q4: What are olfactory indicators and give an example?
Ans: Olfactory indicators are substances whose smell changes when mixed with acids or bases. For example, a cloth soaked in onion juice loses its smell when put in acidic tamarind water or basic baking soda solution.
Q5: Name two other natural indicators besides litmus and red rose extract.
Ans: Beetroot and purple cabbage are natural indicators. They change color when mixed with acidic or basic substances.
IndicatorsQ6: Red litmus paper is dipped in a solution; it remains red, what is the nature of the solution?
Ans : Red litmus paper when dipped in a solution, if it remains red then the nature of the solution is neutral.
Q7: What are salts? Give examples.
Ans : Salts are the ionic compounds generally formed by neutralisation of an acid with base. They can be acidic, basic as well as neutral. Example acidic salts: sodium bicarbonate, basic salts: magnesium chloride, neutral salt: sodium chloride.
Q8: Give examples of some acids and bases
Ans : Curd, lemon juice, vinegar, orange juice etc. are acids and baking soda, lime water etc. are bases.
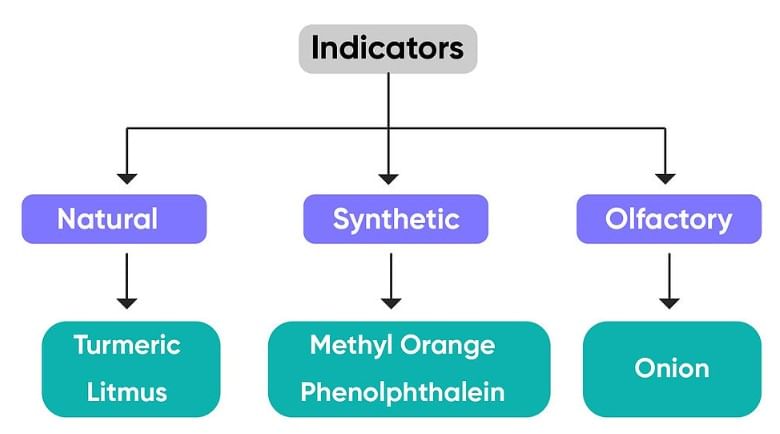
Q9: Define indicators along with examples.
Ans : Indicators are special type of substance that are used to taste whether a substance is acidic or basic in nature. It change the colour of acidic or basis substances when added into it. Turmeric, litmus, etc. are some natural indicators.
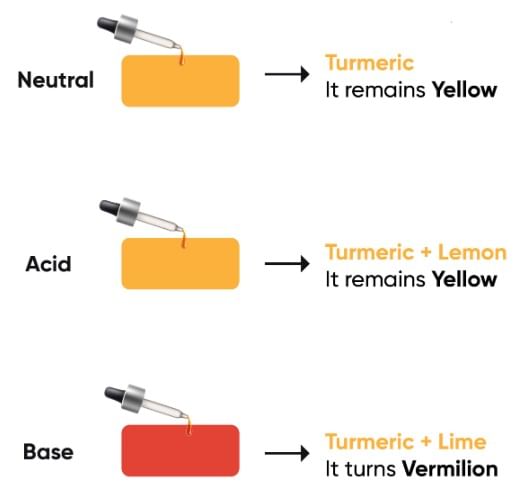
Turmeric as IndicatorQ10: What do you mean by neutral substance, explain with examples?
Ans : The substances which are neither acidic, nor basic are called neutral substance. These substances neither turn blue litmus red nor red litmus blue, for example distilled water, sugar solution etc.
Q11: Rena is trying to wash turmeric stain on her cloth with soap, she noticed the stain colour changed to red, explain why?
Ans : Turmeric is a natural indicator which when reacts with bases turns it into red colour; here soap solution is basic so it turns red.
Q12: Explain why factory waste should be neutralised before disposing it into the water bodies.
Ans : The wastes of many factories contain acids. If they are allowed to flow into the water bodies, the acids will kill fish and other organisms. The factory wastes are, therefore, neutralised by adding basic substances into it.
Long Q&A:
Q1: State few properties of acids.
Ans : Acids are substances known for their sour taste (though tasting them is not safe). The word “acid” is derived from the Latin word ‘ACERE’, meaning sour.
Properties of Acids:
- Sour in taste.
- Turn blue litmus paper red.
- Turn China rose solution dark pink or magenta.
Examples of acidic substances include curd, vinegar, lemon, and orange juice, which all contain natural acids.

Citrus Fruits are Acidic in Nature
Q2: State few properties of bases.
Ans : Bases are substances with a bitter taste and a slippery feel.
Properties of Bases:
- Bitter in taste.
- Turn red litmus paper blue.
- Turn turmeric paper reddish-brown.
- Turn China rose solution green.
Some common examples of bases include baking soda, milk of magnesia, and soap. The chemical nature of these substances is referred to as basic.
Q3: What are the differences between acids and bases?

Ans :
Q4: Describe the process of neutralisation with the help of an example.
Ans :
Neutralisation is a process in which an acid solution when mixed with base solution, react with each other to produce a salt and water along with generation of heat. Salt so produced, may be acidic, basic or neutral in nature. In this process the acidic nature of the acid and the basic nature of the base are destroyed.
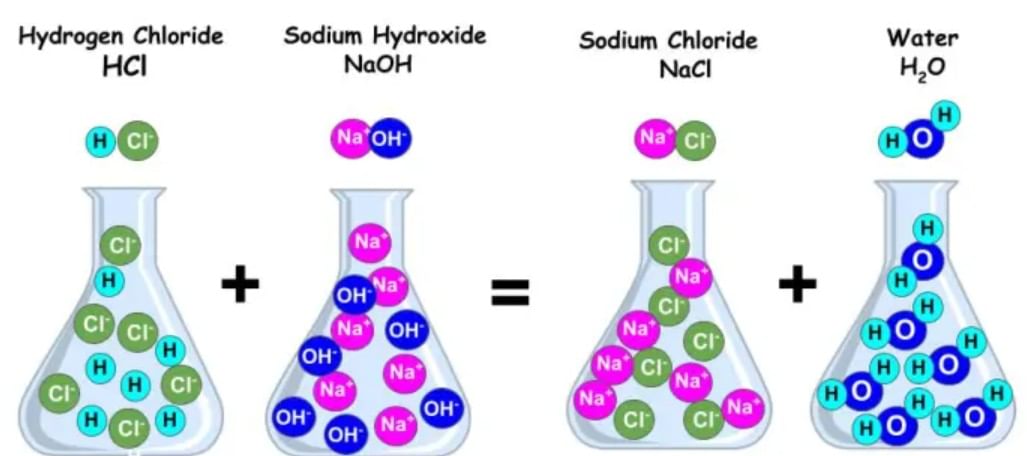
NeutralizationAcid + base → salt + water. (heat is evolved)
For example: HCl + NaOH→ NaCl + H2O.
Hydrochloric acid + Sodiumhydroxide → Sodium chloride + Water
Q5: Explain the process and treatment of an ant bite.
Ans: When an ant bites, it injects an acidic liquid called formic acid into the skin, causing burning pain, redness, and irritation. The effect of the acid can be neutralized by applying a mild base to the affected area.
Two common treatments are:
- Baking soda solution: Baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) neutralizes the acid and reduces the pain and irritation.
- Calamine solution: Calamine contains zinc carbonate, which also neutralizes the acidic effect and provides relief.
Applying either of these substances helps neutralize the acid and reduce the discomfort caused by the ant bite.