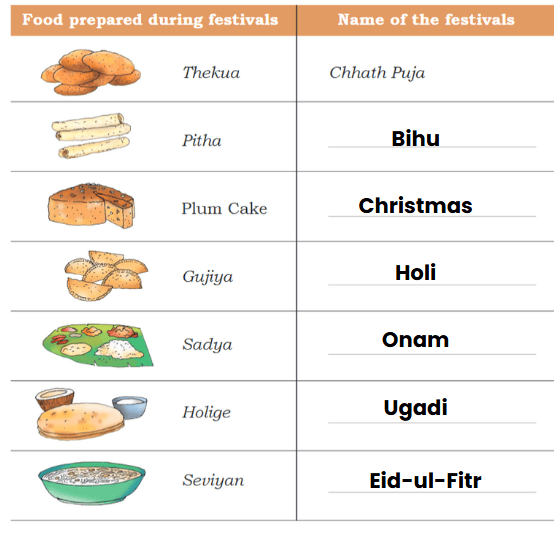
Let’s Take A Look Around Us! (Page 125)
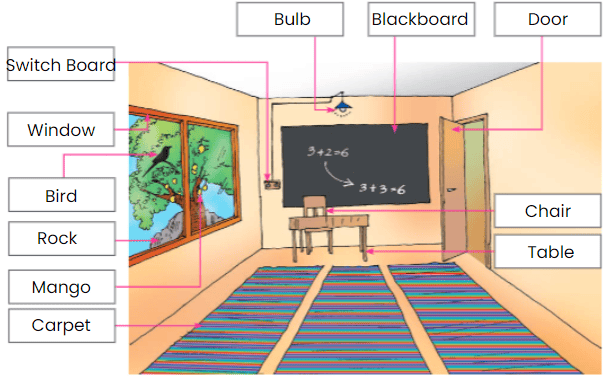
Q: Can you name the things that Khushi has drawn ? Write in the boxes given.
Ans:
Activity 1 (Page 124)
Understand your Classroom
Draw a picture of your classroom in your notebook. Label the things that you have drawn.
Khushi is curious, “Where have all these things come from? Who has made them? What are they all made of?” she thought.
Let us help Khushi find out.
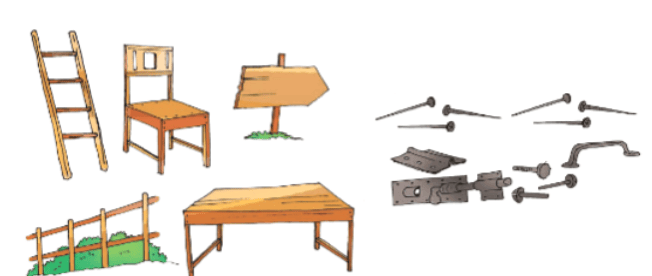
The table and chair are made of wood. Where do we get wood from?
The hinges, nails and latches of the door are made of some metals.
Ans: Students are encouraged to attempt it on their own.
Activity 2 (Page 125)
Spot the Metals
Find as many things or parts of things, that are made of metals. Which metals do you recognise around you? If you do not know the name of the metal, ask your friends or an elder. Make a list of these metals in your notebook.
Ans: I looked around and found many things made of metals. Some of the items I found include:
Door hinges – made of iron
Spoon – made of stainless steel
Water tap – made of brass
Coins – made of copper or nickel
Scissors – made of steel 
Activity 3 (Page 126)
Seeing through things
Collect a few small objects of different materials from your surroundings like bottles, papers, cloth, and utensils, etc. Look at a light bulb or a candle flame through them. You can see through some objects very clearly, you can partially see through some others, while you cannot see through some objects at all. Order these objects from those you can see through very clearly, to those you cannot see through at all.
Ans:
See through clearly : Clear glass bottle , Clear Plastic Bottle , Clean Water
See through Partially : Frosted glass, Butter Paper, Thin Fabric
Cannot see through at all : Wooden door , Book, Metal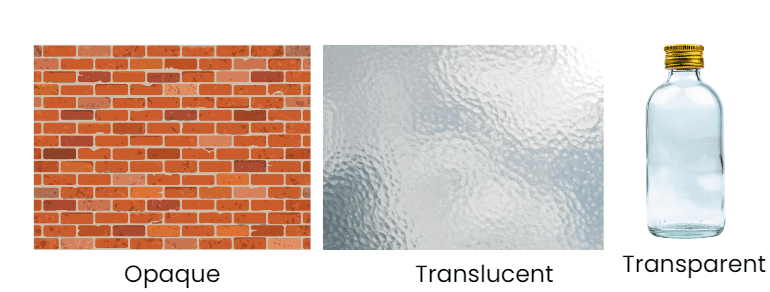
Activity 4 (Page 127)
Let us colour the world!
Collect two or three see-through bags, bottles or thin cloth of different colours. Look at a sheet of white paper through them.
- Does the colour of the paper appear to change?
- Does white paper appear different when you look at it through thin blue plastic or glass? Or, thin yellow plastic or glass?
- Do the colours of different objects appear to change? How did a blue object look through thin yellow plastic?
- Have you earlier experienced looking through coloured transparent objects? Try to recall such experiences.
Ans: Students are encouraged to attempt it on their own.

Write (Page 128)
Chain Game
In the table below, Khushi has grouped objects according to the materials that they are made of. Her list of objects is in the first column of the table. The names of the materials are in the second column. The third column of the table is for you to complete. Here write the names of some objects you have seen that are made from that material. Some objects around you may be made from materials not in this list, e.g., clay and rubber are missing in Khushi’s list. Use one of these to add an additional row in the table.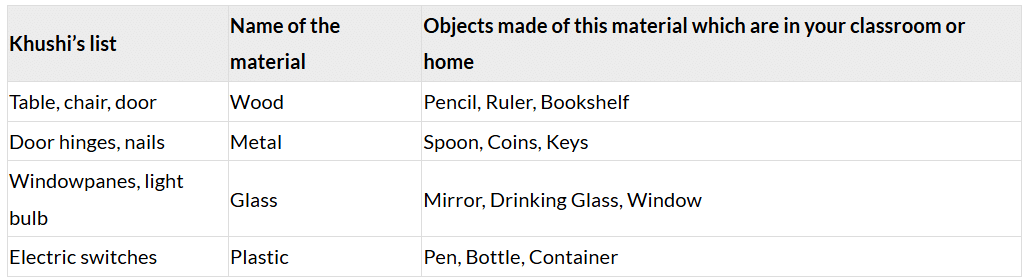
Q: Where do all these materials come from ? Can you locate their source ?
For Example, Wood – Tree
Metals – ____________
Cloth – ______________
Ans:
Metals — Metals are extracted from ores, which are found in the Earth.
Cloth — Cloth is made from natural fibers like cotton (from plants) or wool (from animals) or synthetic materials such as polyester.
Find out (Page 129)
Talk to your Grandparents
- In their childhood, were these things made of the same materials?
- Are there new materials now that they might not have seen before?
- Are there any materials that they saw in their childhood that are not in use now? Why?
Ans: Yes, materials can differ in various ways, not just how they look. For example, texture, weight, etc.
Find out
- What material is your spoon made of?
Ans: My spoon is made up of Steel.
- Is it made of metal, wood or some other material? Can you guess?
Ans: Steel is an Alloy.
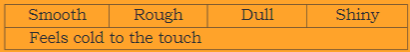
- Which of these words or phrases describes the spoon?
Ans: The Spoon is Smooth and Shiny.
Activity 5 (Page 130)
Knock on it and it will speak to you! Orchestra
Take a metal spoon and at least five objects made up of different materials-wood, metal, plastic, cloth and glass. Gently tap the spoon on each of them. Listen to the sound that each of them makes. Make your own words to describe all these different sounds.
Ans: Students are encouraged to attempt it on their own.
Write (Page 130)
Odd Pairs
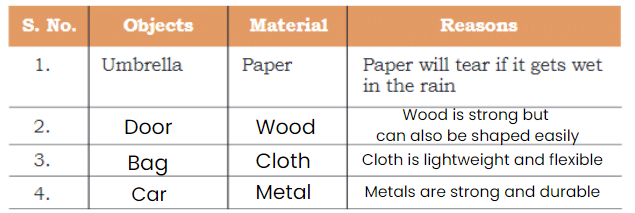
Q: List five objects and pair them with a material that is not suitable for it! Explain why these materials will not work to make these objects. One example is done for you.
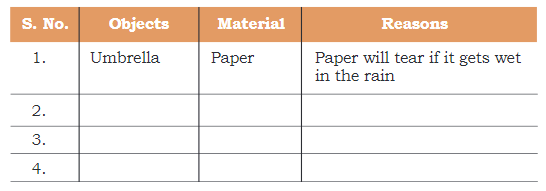
Ans:
Activity 6 (Page 132)
Let’s group them another way!
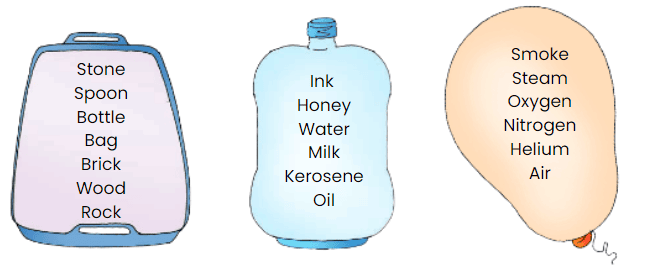
Here are the names of some objects: ink, a stone, smoke, ice, steam, a spoon, honey, a bottle, a bag, and water.
If it is a solid, write its name on the tray; if it is a liquid, write it in the bottle; if it is a gas, write it in the balloon.
Add some of your objects in the tray, bottle, and balloon.
Ans:
Q: Some objects could be confusing, such as sand sponge, or clay. Identify more such objects and write the names of at least three of them.
Ans: Cotton Candy , Silica Gel and Pumice Stone
Natural — Artificial (Page 133)
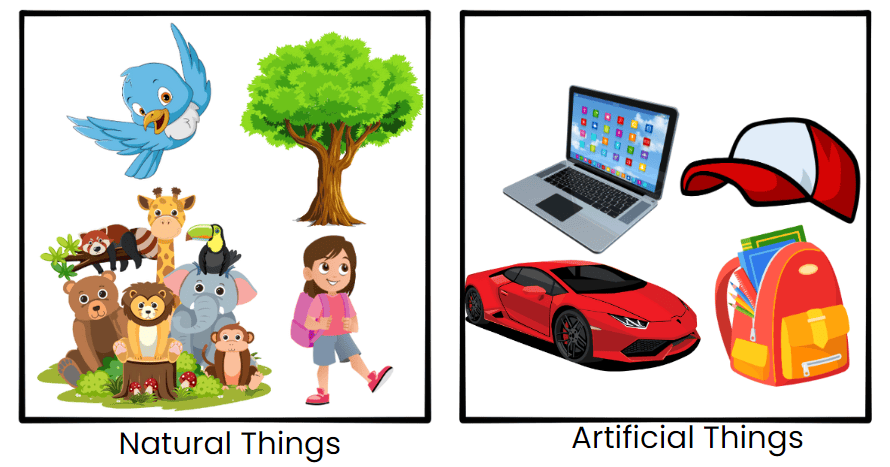
Q: List out five things in each group.
Ans:
- Natural: Tree, Mango, Bird, Rock, Water
- Artificial: Clothes, Shoes, Table, Car, Book

Find Out
- Have you seen trees around you that bear flowers and fruits at special times of the year?
Ans: Yes, I have seen trees that bear flowers and fruits at special times of the year. For example:
(i) Mango trees have flowers in February-March and fruits in June-July.
(ii) Guava trees give fruits in winter (November-December).
(iii) Apple trees grow fruits in summer (July-August).
Different trees have different seasons for flowers and fruits!
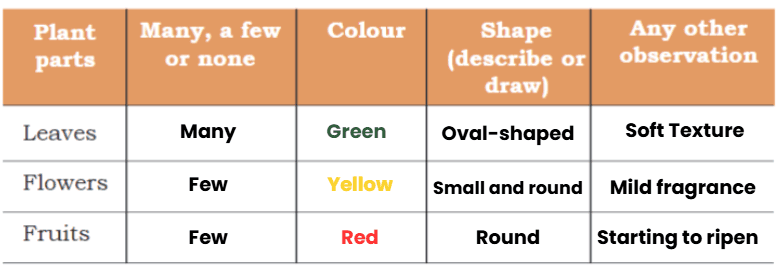
- If you have ever eaten a ripe mango or seen mangoes in the market or watched a mango tree through the year, try to guess— at what time of the year did Khushi draw her picture?
Ans: Khushi most likely drew her picture in June, because mangoes ripen during the summer season. During this time, mango trees are full of ripe mangoes, and we can see them in the markets.
- Could it be around January or around June?
Ans: It could be around June because mangoes ripen in the summer season. During this time, mango trees are full of ripe mangoes, and we can see them in the market. In January, mango trees usually have flowers but not ripe fruits.
Let us Reflect (Page 134)
A. Write
Q: Things around us are made of different types of materials. Write down the names of three materials we commonly see around us.
Ans:
- Wood
- Metal
- Plastic
B. Discuss
Q: Suppose you find a shining spoon. You don’t know if it is made of metal or whether it is made of some other material and then painted with shiny paint. How would you find out?
Ans: I would tap the spoon on a hard surface and listen to the sound it makes. A metal spoon would make a distinct ringing sound. I could also check the weight and feel of the spoon, as metal spoons are generally heavier and feel cooler to the touch than painted plastic spoons.
C. Draw
Q: Draw three natural and three artificial things.
Ans:
D. Do it
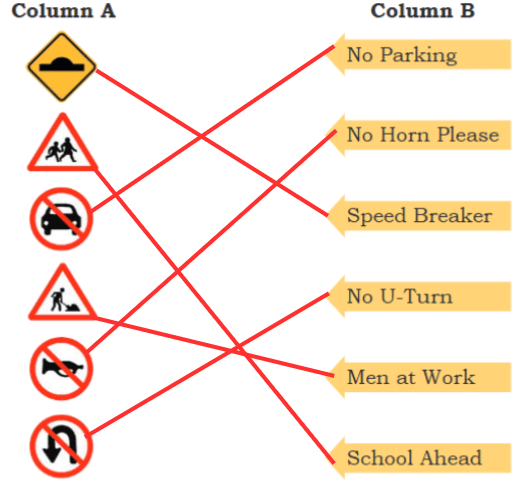
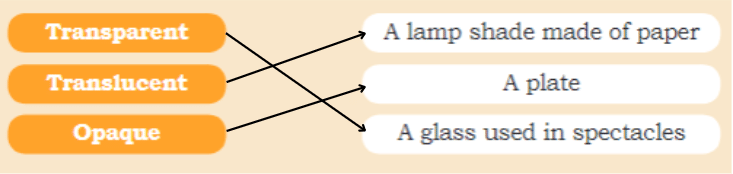
Q: Match the pairs
Ans:





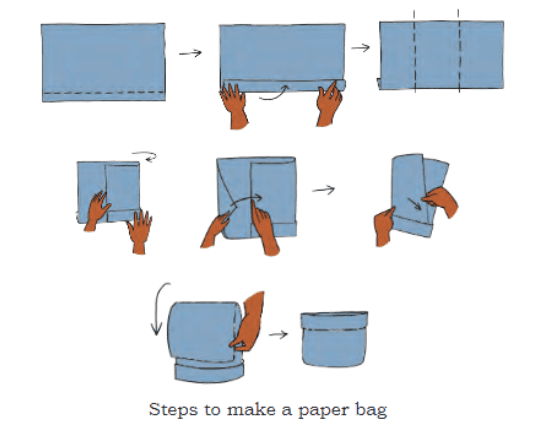











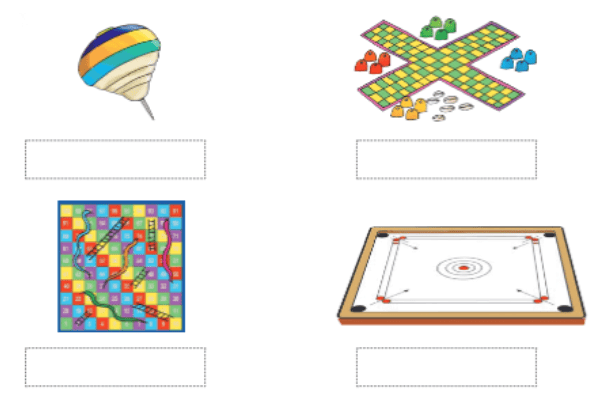
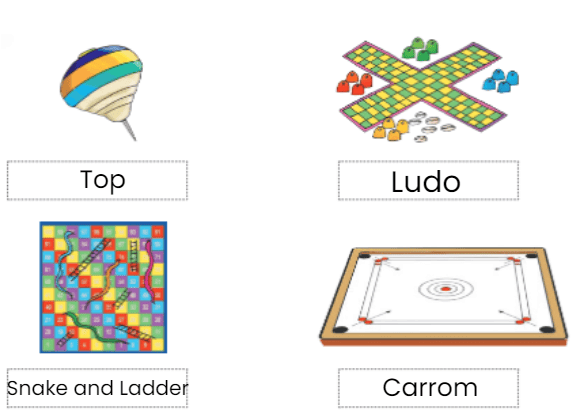

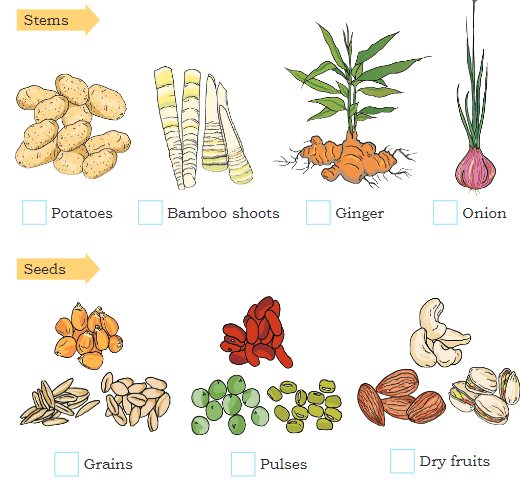
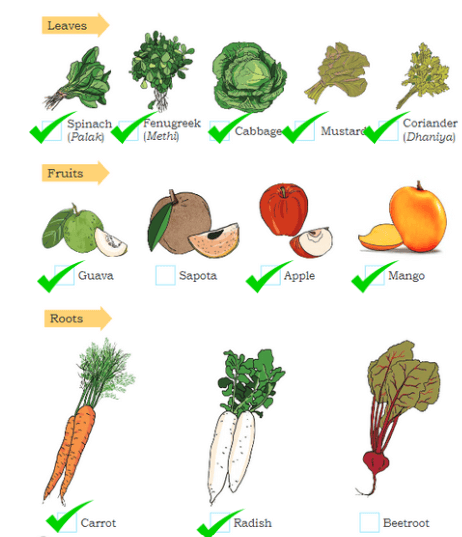
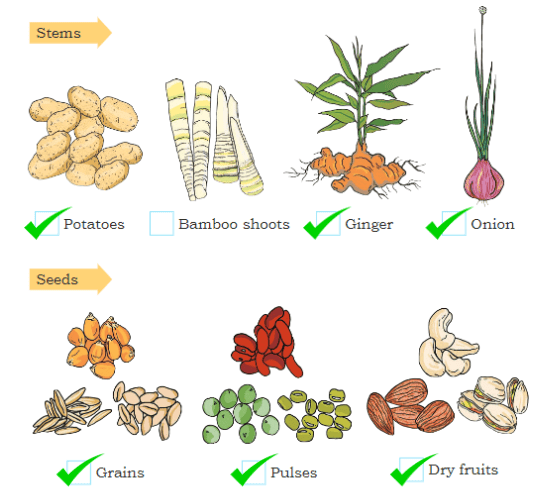









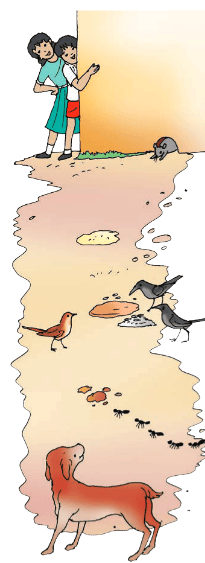 Make a Guess:
Make a Guess: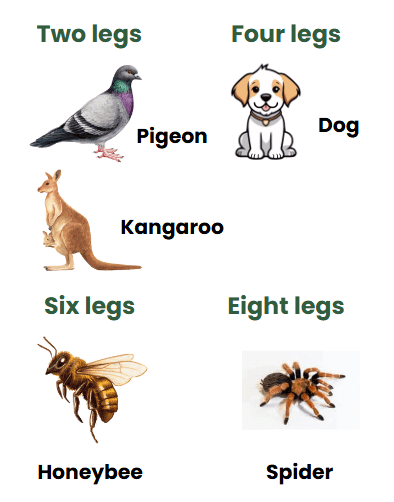

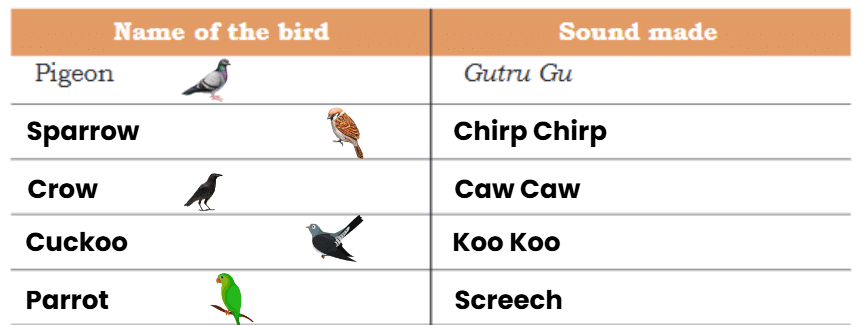
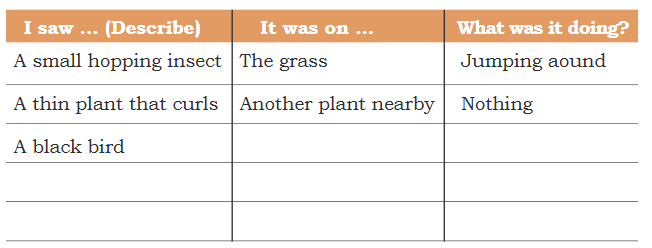


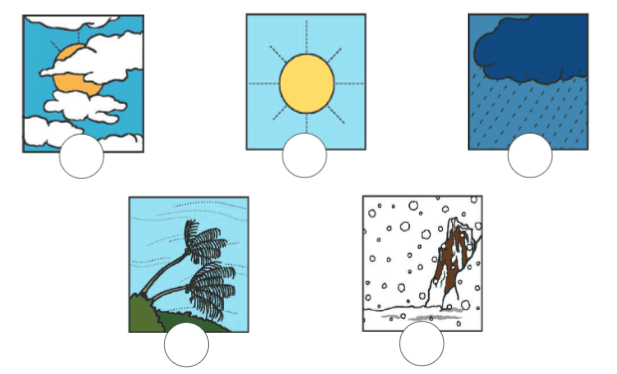

 Ans:
Ans: