Q1: Choose the correct option for each question.
(i) Who was the first Indian in space?
A. Wing Commander Rakesh Sharma
B. Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla
C. DIGIPIN
D. None of the above
(ii) What does DIGIPIN help with?
A. Assigning names to schools
B. Helping postmen locate addresses
C. Identifying plants
D. None of the above
(iii) What ancient Indian practice is celebrated on International Day of Yoga?
A. Meditation
B. Dance
C. Yoga
D. Painting
(iv) From where did chillies originally come?
A. India
B. Europe
C. South America
D. Africa
(v) What unique feature do Indian cows in Brazil have?
A. They are used for transportation
B. They are depicted on stamps and coins
C. They are larger than Brazilian cows
D. None of the above
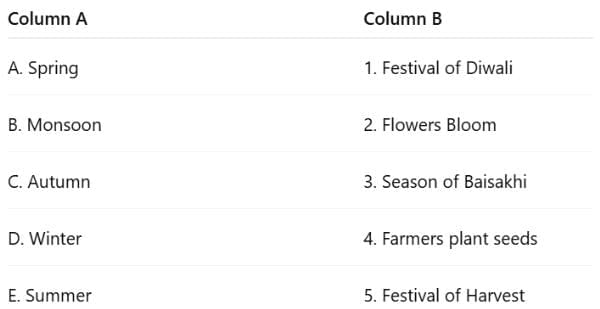
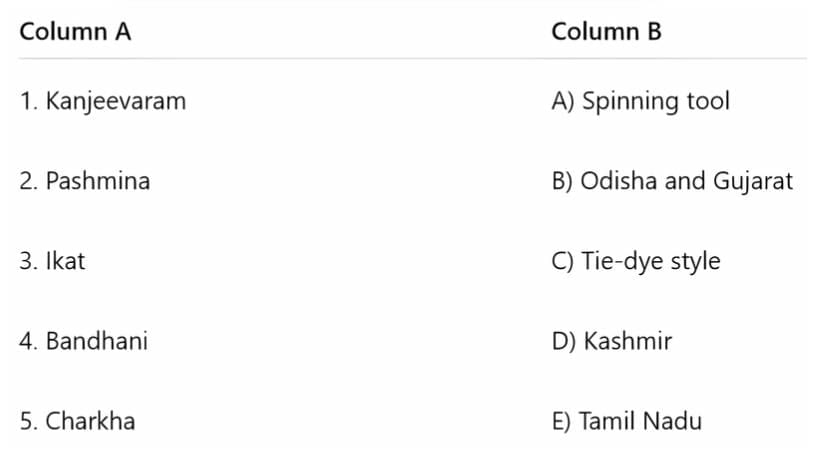
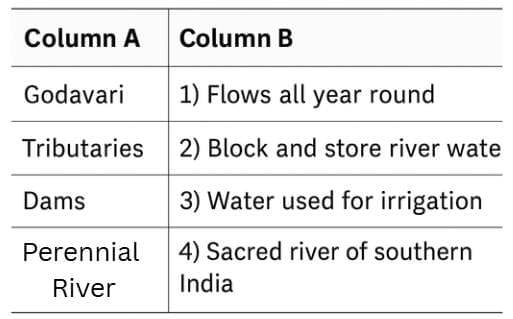
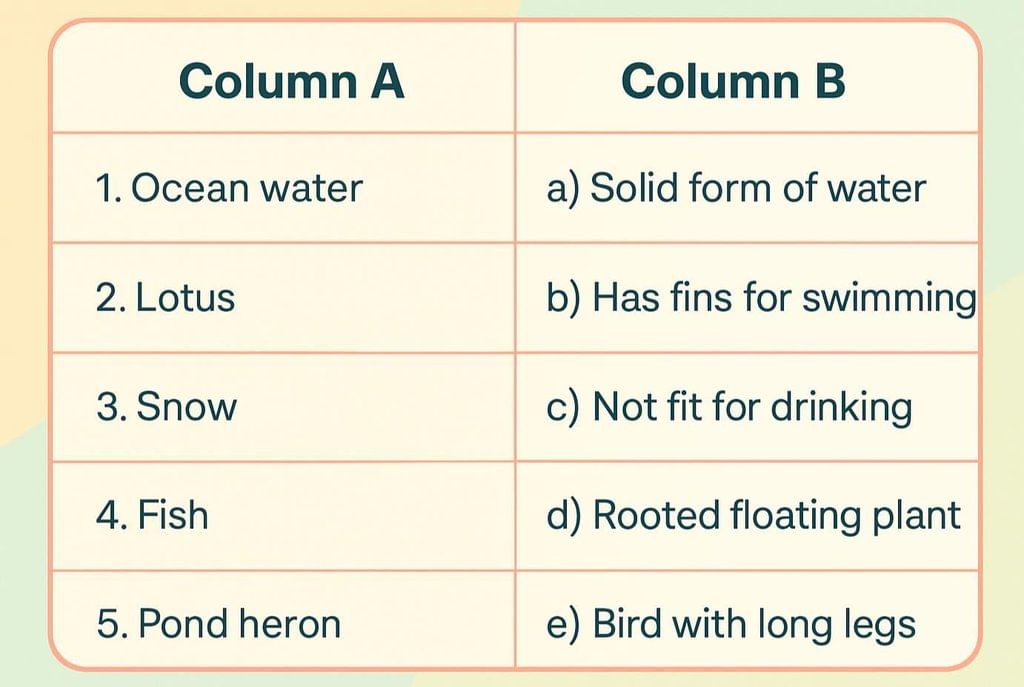
Q2: Match the items in Column A with the correct descriptions in Column B.

Q3: Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the chapter.
(i) The Earth looks like one big home with no visible __________.
(ii) Yoga has been practised in India for more than __________ years.
(iii) The Ministry of __________, Forest and Climate Change logo shows the connection between humans and nature.
(iv) Chillies were brought to India by __________ travellers.
(v) The saying ‘Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’ means __________ is one family.
Q4: State whether the following statements are True or False. Correct the false statements.
(i) The shape of land and sea is visible from space, but no political boundaries.
(ii) The marigold flower originally comes from India.
(iii) The first Indian in space said India looked “Saare Jahaan Se Achcha” from space.
(iv) Yoga was first shared with the world in the 21st century.
(v) The chillies we grow in India were once a staple item in European kitchens.
Q5: Answer the following questions in 2-3 sentences each.
(i) What does the Earth look like from space?
(ii) How do rosy starlings help farmers in India?
(iii) Why is yoga special and important?
(iv) Where did chillies originally come from?
(v) What does “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” mean?
Q6: Answer the following questions in 4-6 sentences each. Use examples from the chapter to support your answers.
(i) Explain how birds like rosy starlings show us that “nature has no boundaries.” What benefits do they provide?
(ii) How did the chilli plant change Indian food culture? Trace its journey from South America to India.
(iii) What does “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” mean? How can we live as one family despite our differences?
(iv) Give examples of how India and other countries have shared culture, food, and ideas with each other.
You can find Worksheet Solutions here: Worksheet Solutions: Earth-Our Shared Home