Measurement
Measurement helps us find out how long, how heavy, how big, or how much time something takes. It is useful in our daily life and in science. When we measure, we can compare things and talk about them correctly.
For example:
- A ruler helps us measure length.
- A weighing scale helps us measure weight.
- A clock helps us measure time.
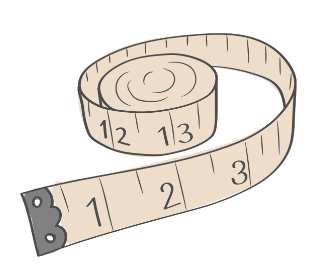
Different Ways to Measure Things
- Length: We use a ruler or a tape measure to find out how long something is.
- Weight: We use a scale to check how heavy something is.

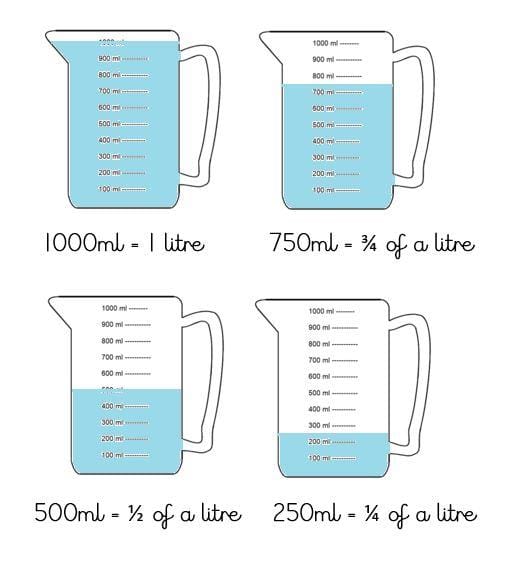
- Volume: We use a measuring cup to see how much liquid something can hold. We measure volume in millilitres (ml) or litres (L).
 Measuring helps us understand the size, weight, and amount of things around us.
Measuring helps us understand the size, weight, and amount of things around us.
Need of Measurement
Measurement is an important part of our daily lives, helping us understand and compare various aspects of the world around us. Whether it’s the length of cloth for a dress or the weight of fruits and vegetables, measuring allows us to make sense of different things correctly.
Examples of Measurement in Daily Life
- The length of cloth required for a dress
- Height and weight to see how much you have grown
- The weight of fruits and vegetables you buy
- The amount of petrol put in a car
- The time taken by you to reach school

 | Get additional INR 200 off today with EDUREV200 coupon. |
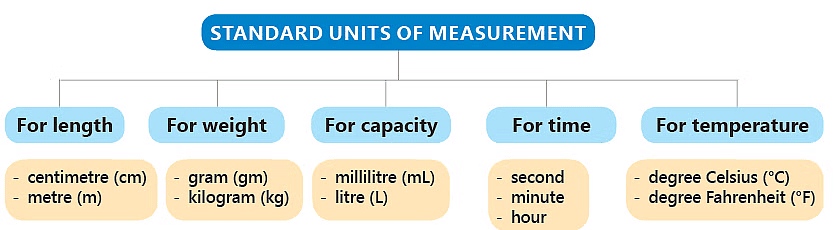
Understanding Measurement Units
- Imagine you ask your tailor to make pants that are 5 handspans long. When you try them on, they turn out to be too long. Can you figure out why?
- Your handspan is different from that of an adult. If everyone uses their own handspan to measure, it can lead to confusion!
- In the past, people used parts of their bodies like handspan, cubit, foot span, and stride length to measure length. These are called non-standard units of measurement.
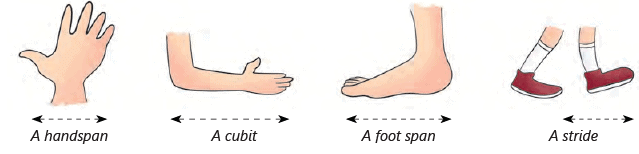
- For example, you might use a mug to measure how much water a bucket can hold, but mugs come in different sizes. So, a mug is also a non-standard unit for measuring liquids.
- To avoid confusion, it is important for everyone to use the same measurement units. This way, measurements will be the same no matter who takes them. Such units are called standard units.
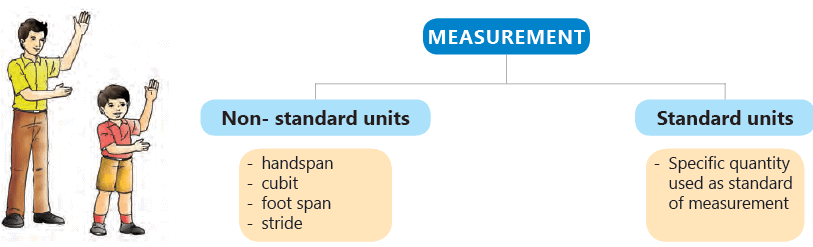
Units of Measurement
What is a Unit?
- A unit is a fixed quantity that is used as a standard for measuring various things.
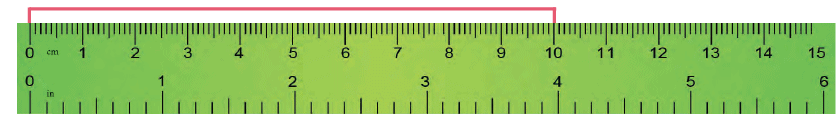
 Measuring Length
Measuring Length
For small lengths, such as those of a pencil or an eraser, we use a standard unit called a centimetre (cm).
To measure the length of a line using a ruler:
- Place the ruler along the line, ensuring one end is at the 0 cm mark.
- Read the length where the other end of the line meets the ruler.
Example: In the given image, the length of the line is measured to be 10 cm.
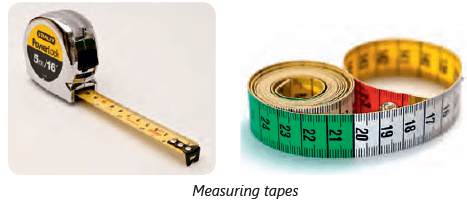
For longer distances, such as the length of a room or the height of a tree, we use a larger unit called a metre (m).
Tools for Measuring Length in Metres:
- Metre Scale:. A metre scale is 1 m or 100 cm long and works similarly to a ruler, allowing for correct measurements in metres.
- Measuring Tape:. A measuring tape can be bent and commonly used for measuring around objects, such as by tailors to measure around the chest. It is also effective for measuring lengths in metres.
| Also read: Worksheet: Measurement |
Measuring Weight
- Weight measurement tells how heavy an object is. The gram (g) and kilogram (kg) are the standard units for measuring weight.
- Grams are used for lighter items, while kilograms are used for heavier objects, such as the weight of fruits or for measuring body weight.
- Shopkeepers usually use balances or electronic weighing scales to measure the weight of products.
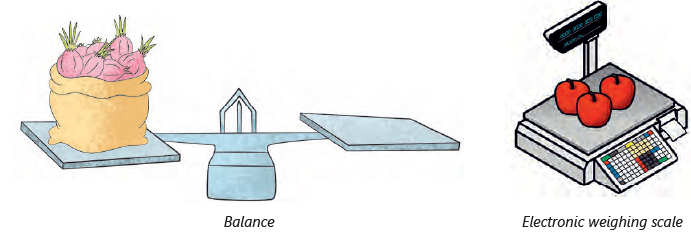
Measuring Capacity
- Capacity refers to the amount of liquid a container can hold. For instance, a bucket can hold more liquid than a mug, so the bucket’s capacity is larger.
- The standard unit for measuring capacity is the litre (L). Smaller quantities of liquid are measured in millilitres (mL).
- One teaspoon is approximately 5 mL, while a glass can hold around 250 mL of liquid. A normal medium-sized mineral water bottle has a capacity of 1 litre.

- We use tools like measuring cylinders, beakers, spoons, and cups to measure capacity correctly.

Measuring Time
The period between two events is called time. In ancient times, people used sundials to measure time.

- Nowadays, we mainly use clocks to measure time, which is expressed in hours and minutes. An hour consists of 60 minutes, and a minute is made up of 60 seconds.
- It is easier to read the time on a digital clock.

Temperature Measurement
| Also read: Worksheet: Measurement |
What is Temperature?
- Temperature is a basic concept in science that tells us how hot or cold something is.
- It is measured in degrees Celsius (°C) or degrees Fahrenheit (°F).
- The normal body temperature is 37°C.
Measurement of Temperature?
- Being able to measure temperature is really important in our everyday lives.
- Temperature measurement is also helpful in various scientific fields.
Try yourself:
Which unit is commonly used to measure the weight of fruits or body weight?
- A.Grams (g)
- B.Kilograms (kg)
- C.Litres (L)
- D.Millilitres (mL)
Conclusion
Measurement helps us in many ways. It tells us how long, heavy, big, or hot something is. It also helps us know how much time something takes. Using the same units for measurement makes sure that everyone understands things the same way. Whether we are buying fruits, checking the time, or measuring our height, measurement helps us in daily life.
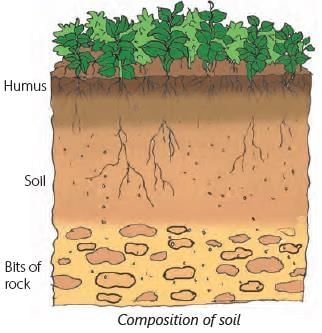
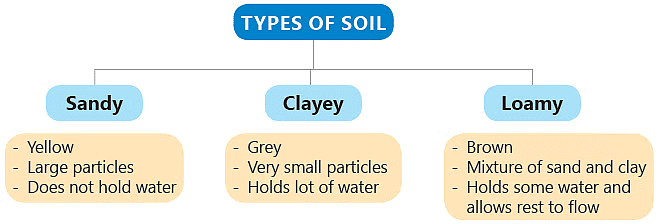
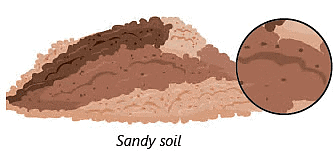
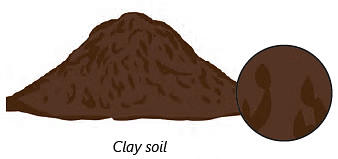
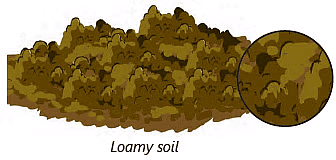
 Soil
Soil
 You provided first aid and made Tina feel better.” Tina, feeling relieved, thanked Aman, saying, “Thank you, Aman! I’m feeling much better now.” Aman’s heart swelled with happiness as he realized the importance of knowing first aid and how it can help others in times of need.
You provided first aid and made Tina feel better.” Tina, feeling relieved, thanked Aman, saying, “Thank you, Aman! I’m feeling much better now.” Aman’s heart swelled with happiness as he realized the importance of knowing first aid and how it can help others in times of need.



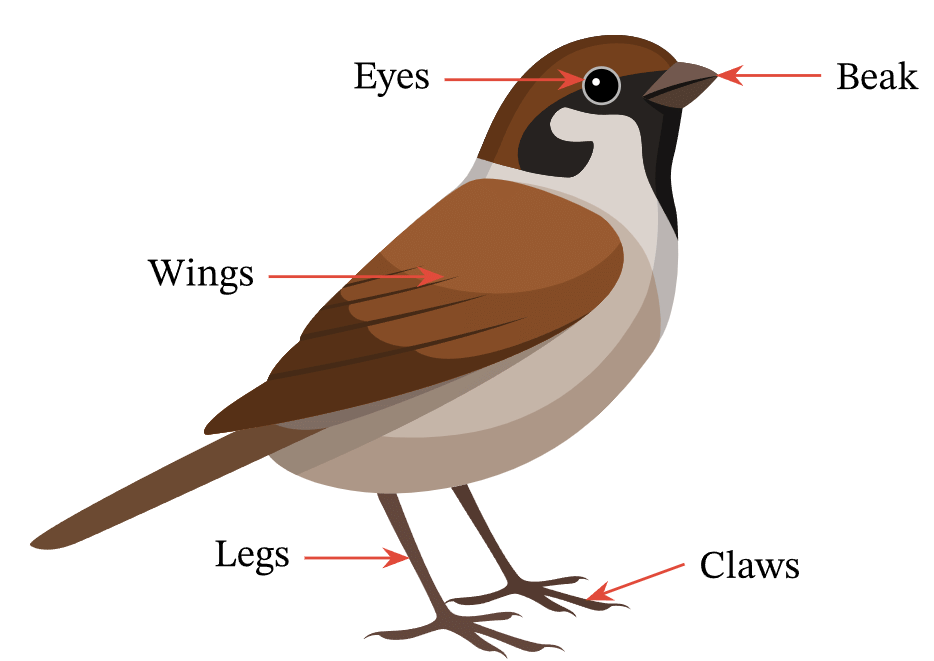 Body parts of a bird
Body parts of a bird


 Crane
Crane Peacock
Peacock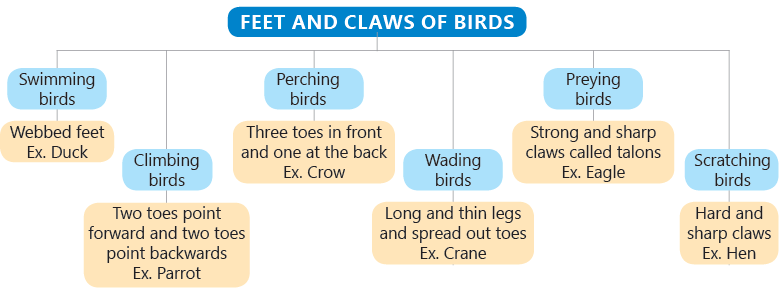
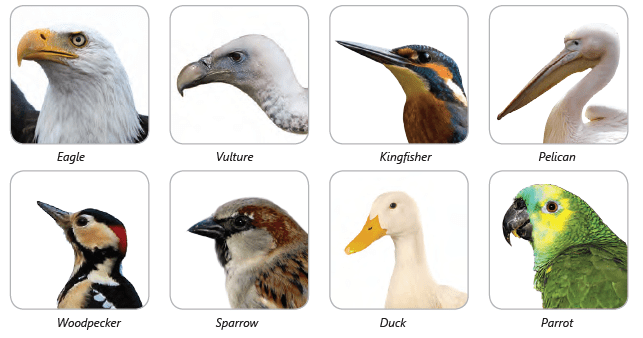 Different types of beaks
Different types of beaks
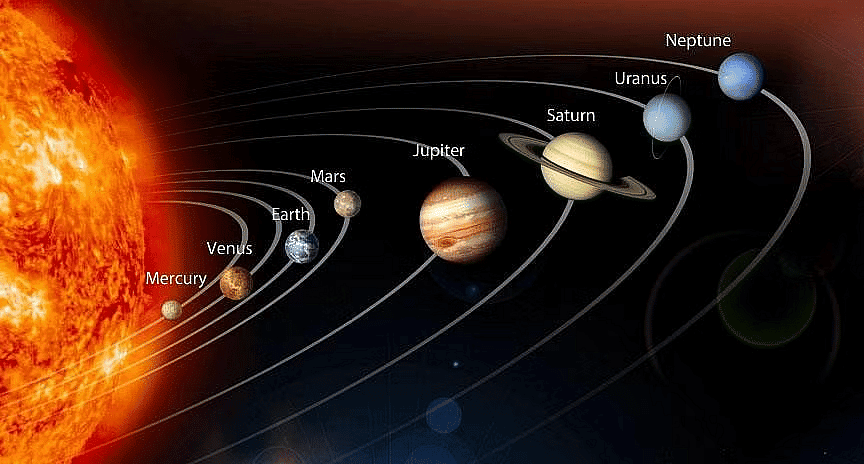 Solar System
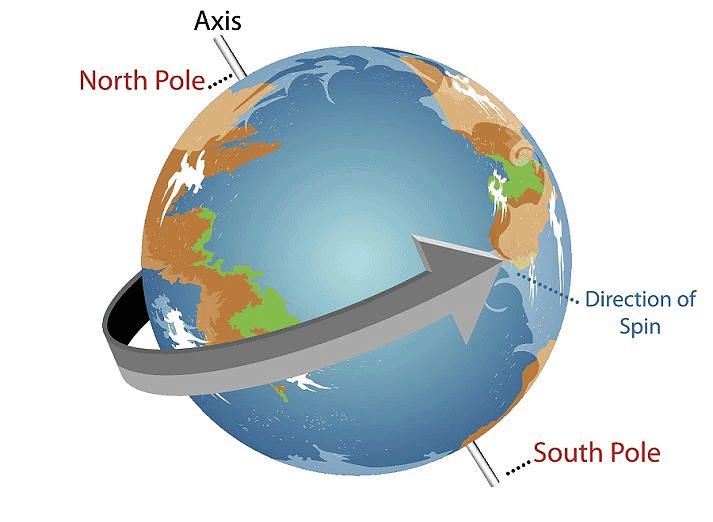
Solar System EarthBut what does Earth look like? Is it perfectly round? Let’s find out!
EarthBut what does Earth look like? Is it perfectly round? Let’s find out!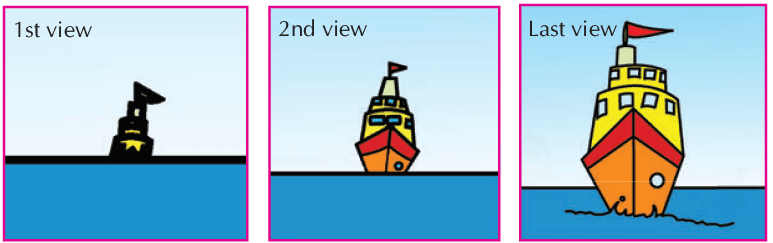 Viewing of ship
Viewing of ship
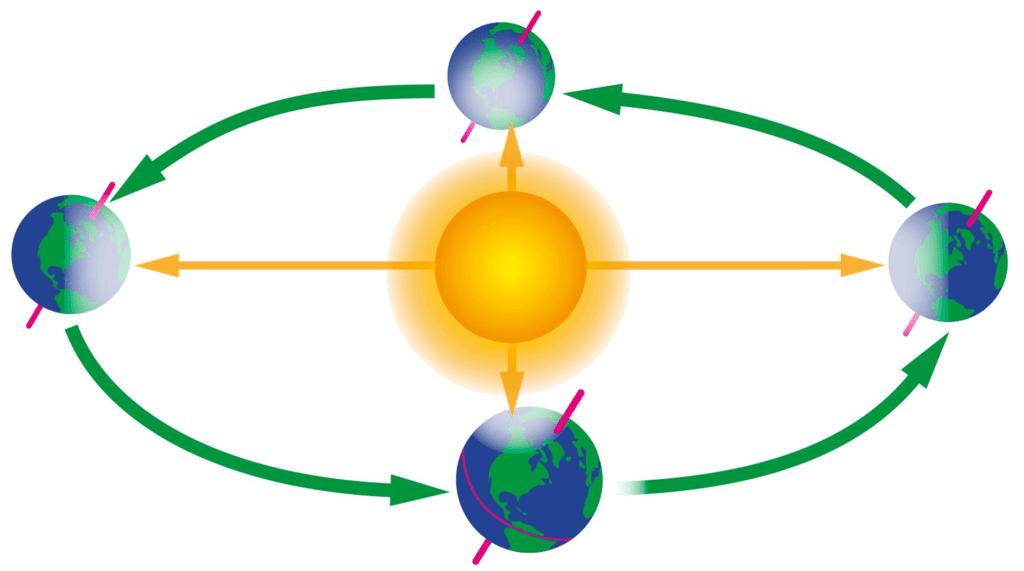 Revolution of the Earth
Revolution of the Earth





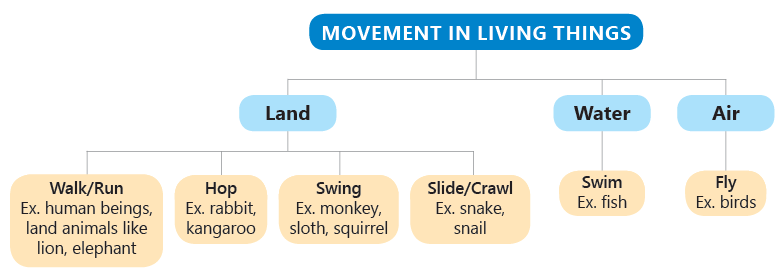


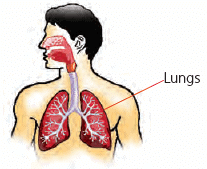
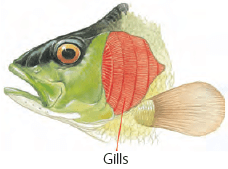
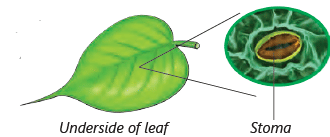

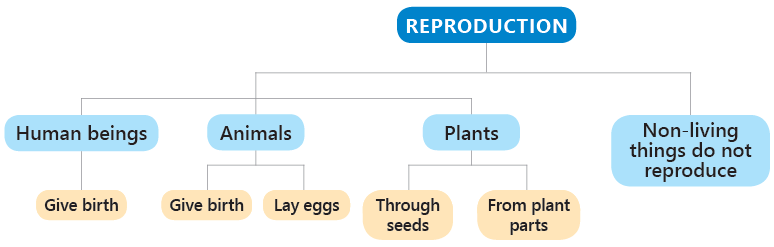


 Plants are very important to us
Plants are very important to us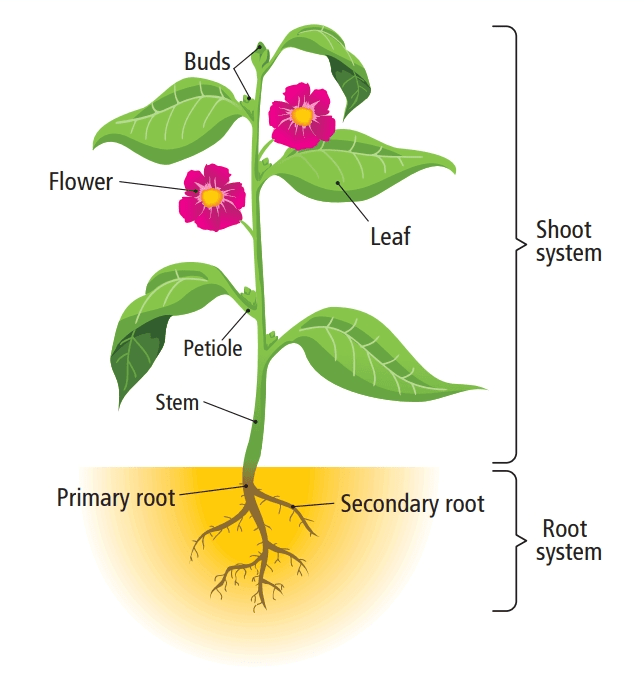
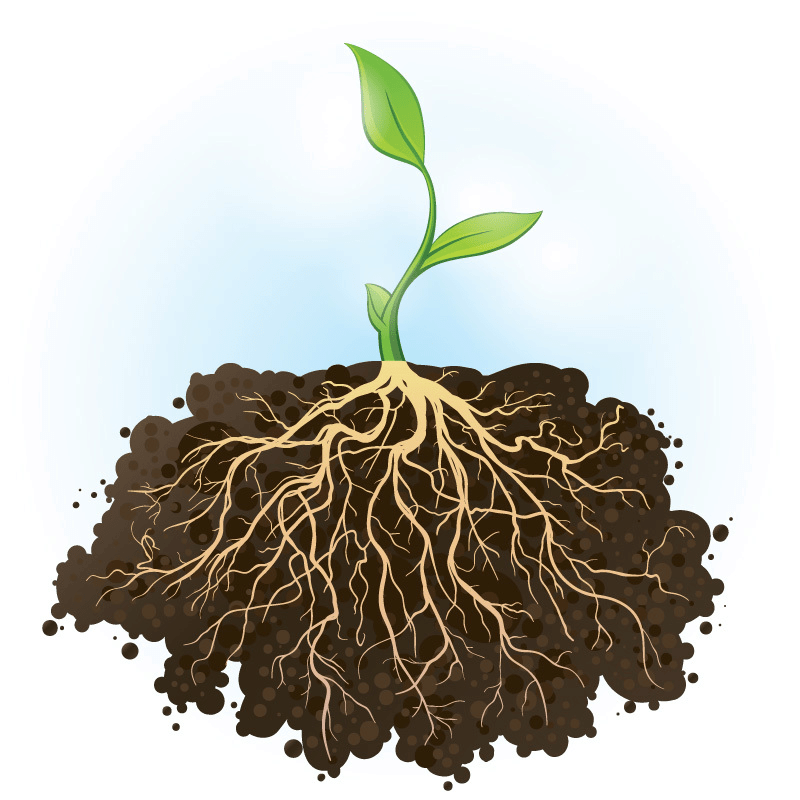 Roots of a Plant
Roots of a Plant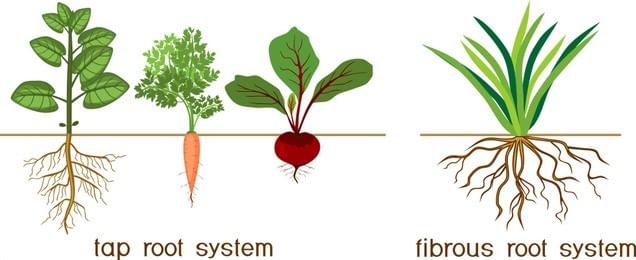
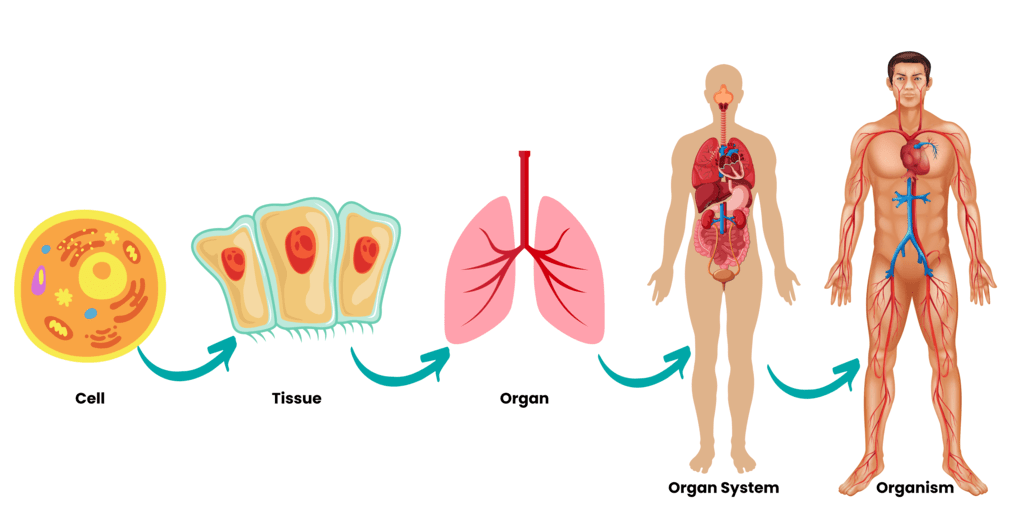
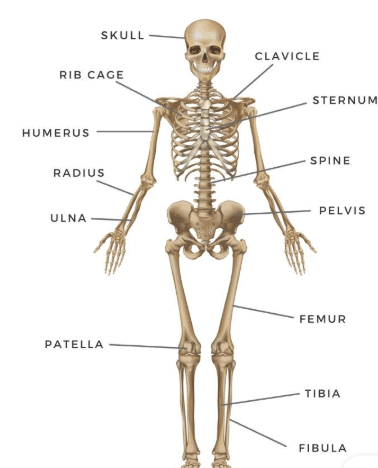
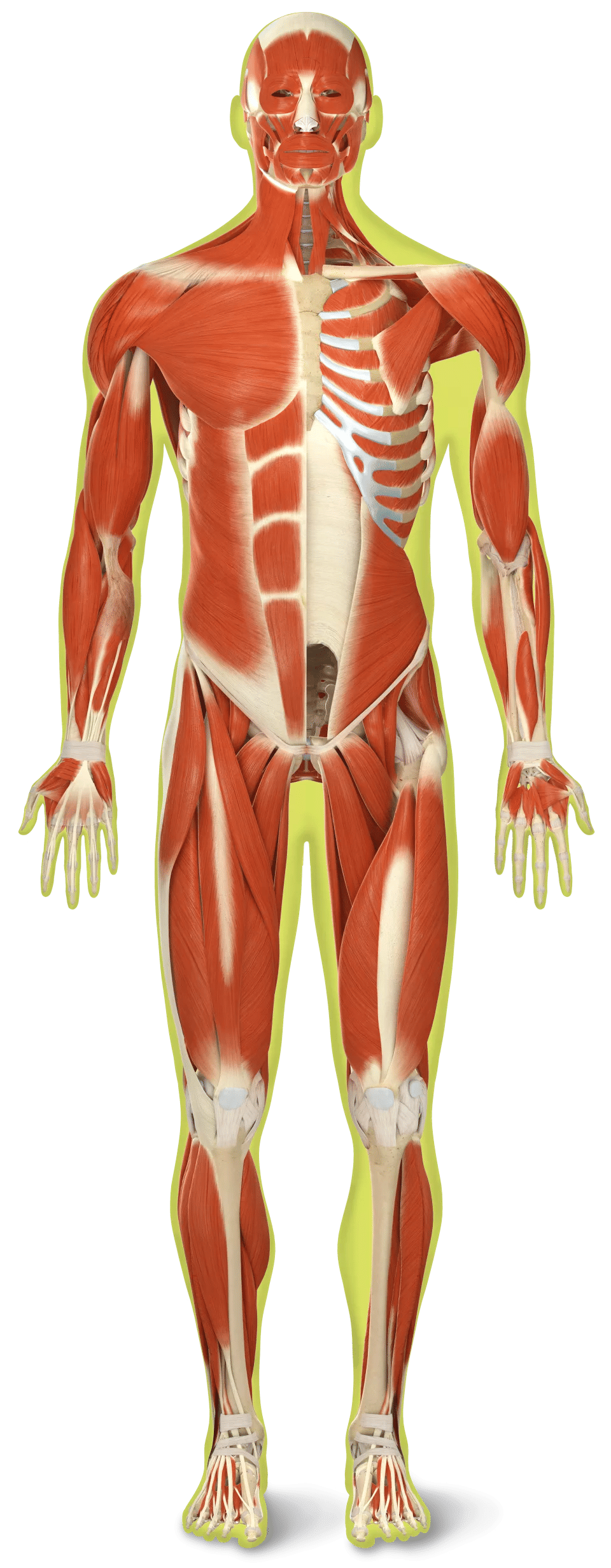 Muscular System
Muscular System