Q1. What does WHO say health means beyond just not being sick?
Answer: Health means complete physical, mental, and social well-being.
Q2. Which three areas make up overall health?
Answer: Physical, mental, and social health.
Q3. What is one sign that a person is physically healthy?
Answer: They can do daily tasks efficiently.
Q4. What habit can improve mental health in students?
Answer: Limiting screen time and managing stress.
Q5. Which traditional system teaches balance through dinacharya and ritucharya?
Answer: Ayurveda.
Q6. What is one good daily habit for health?
Answer: Eating a balanced diet.
Q7. What is one bad habit that harms health?
Answer: Spending too much time on mobile phones.
Q8. Why is outdoor play good for health?
Answer: It keeps the body active and strong.
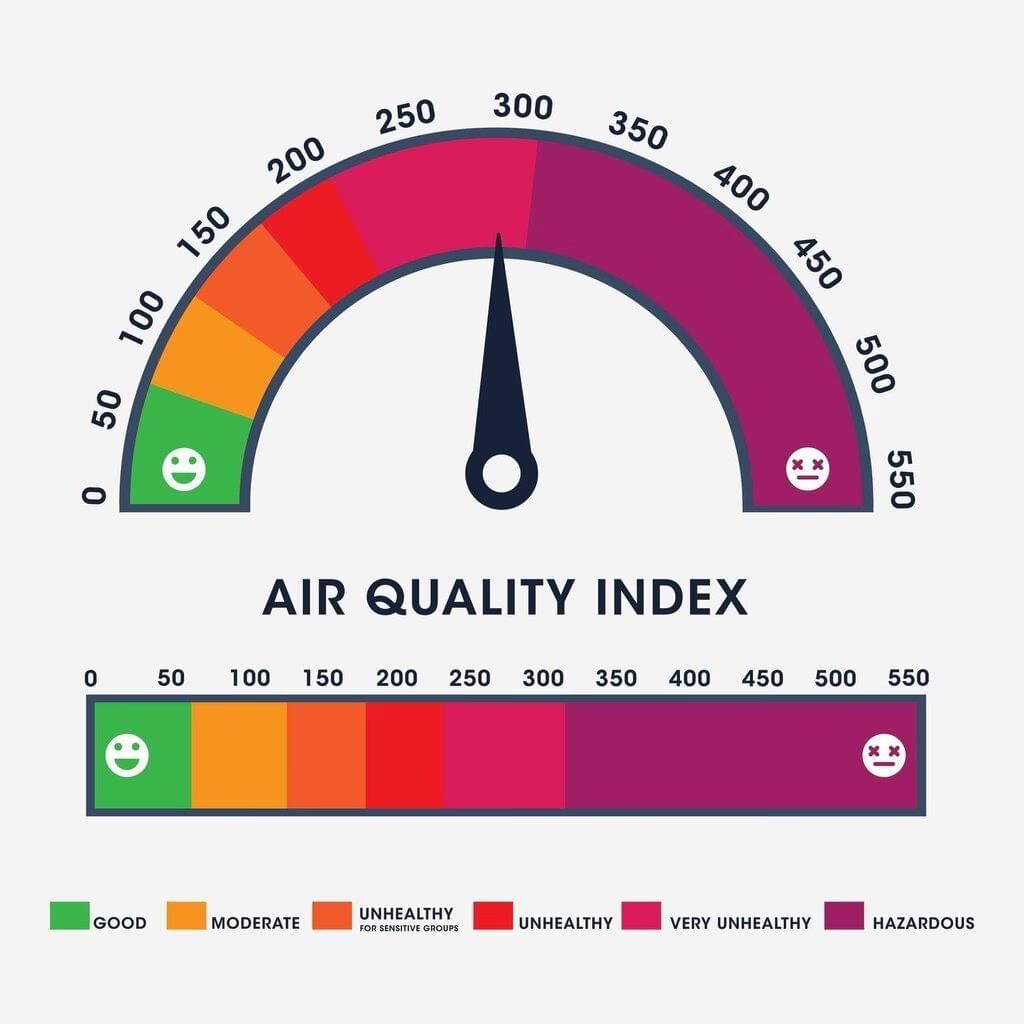
Q9. What does the Air Quality Index (AQI) tell us?
Answer: It shows how clean or polluted the air is.
Q10. What is a symptom?
Answer: A symptom is what we feel, like pain or dizziness.
Q11. What is a sign?
Answer: A sign is what others can observe or measure, like fever.
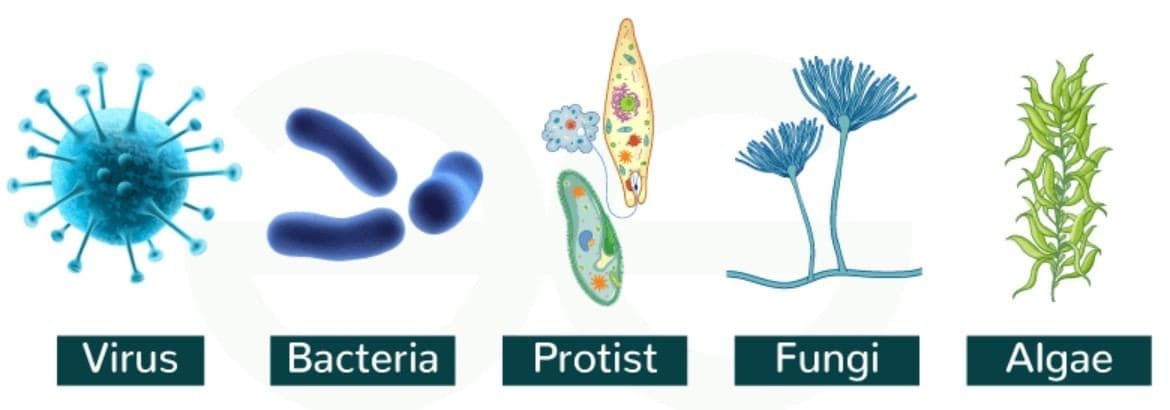
Q12. What causes communicable diseases?
Answer: Pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protozoa.
Q13. Name one way communicable diseases spread?
Answer: Through air by coughing or sneezing.

Q14. What is a non-communicable disease?
Answer: A disease that does not spread from person to person.
Q15. Give one example of a deficiency disease.
Answer: Anaemia.
Q16. What simple practice helps prevent many infections?
Answer: Washing hands with soap.
Q17. What is immunity?
Answer: The body’s ability to fight diseases.
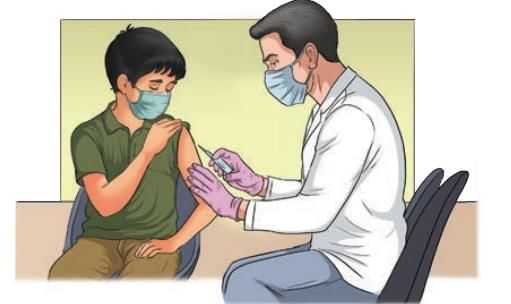
Q18. How do vaccines protect us?
Answer: They train the immune system to fight specific germs.
Q19. Who developed the first smallpox vaccine?
Answer: Edward Jenner.
Q20. What do antibiotics kill?
Answer: Bacteria.
Q21. Do antibiotics work on viruses?
Answer: No, antibiotics do not work on viruses.
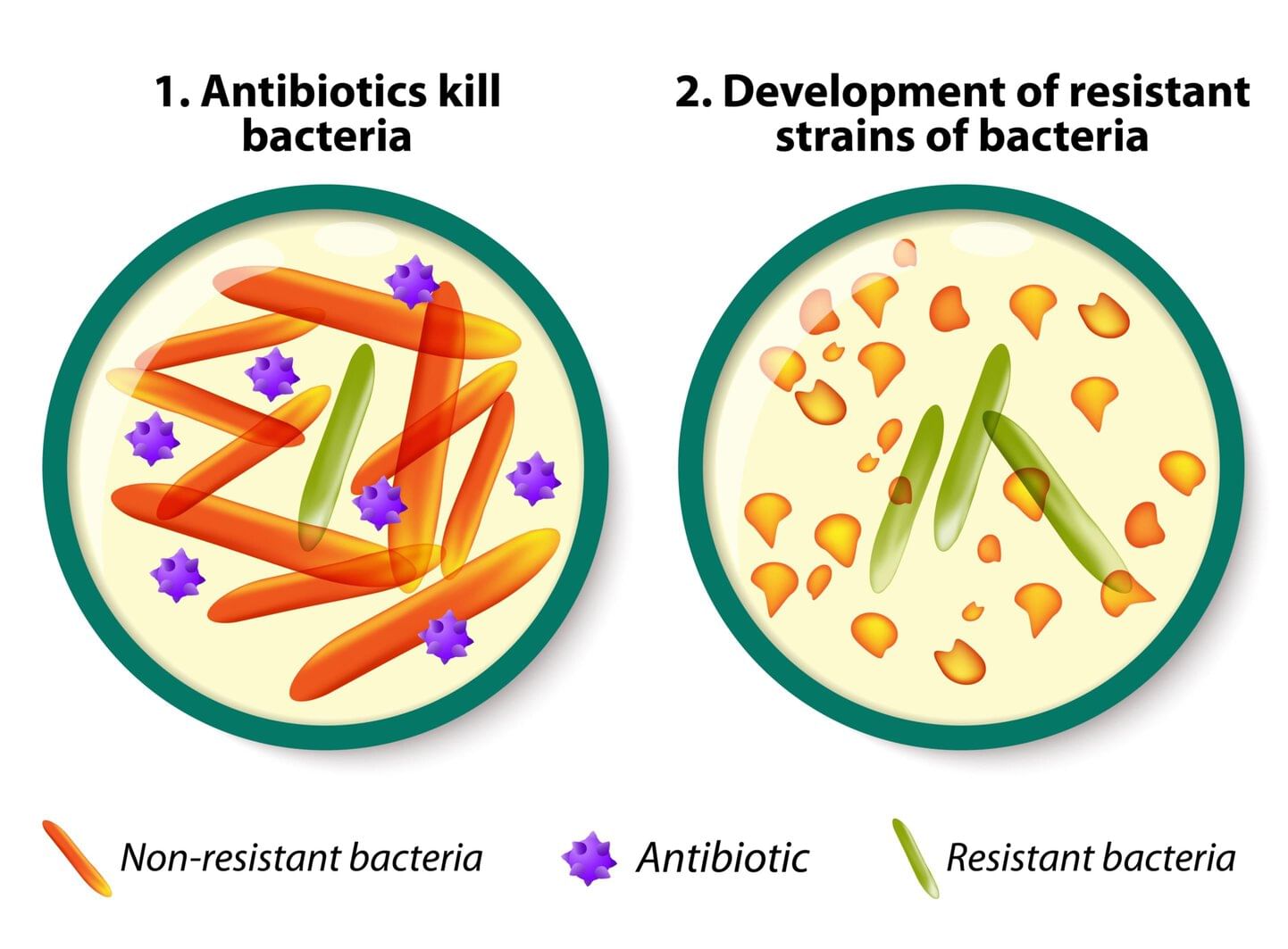
Q22. What is antibiotic resistance?
Answer: When bacteria change and stop being killed by antibiotics.
Antibiotic Resistance
Q23. How can we prevent antibiotic resistance?
Answer: Take antibiotics only as prescribed and finish the full course.
Q24. What lifestyle change helps prevent NCDs?
Answer: Regular exercise.
Q25. Why is “prevention better than cure”?
Answer: Because stopping disease early is easier and safer than treating it later.