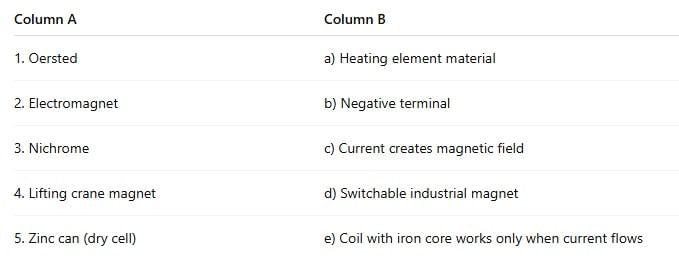
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
- If Earth had never known life, which change in its atmosphere would most likely be true?
a) High oxygen from photosynthesis
b) Thick ozone layer formed naturally without oxygen
c) Very low oxygen and no biologically produced ozone
d) Same composition as today
Answer: c) Very low oxygen and no biologically produced ozone
Without life (photosynthesis), atmospheric O₂ and the ozone layer would not build up. - Which surface feature would most likely be less abundant without life-driven soil formation?
a) Thick, organic-rich soils
b) Basaltic rocks
c) Impact craters
d) Volcanoes
Answer: a) Thick, organic-rich soils
Soils on Earth are greatly enriched and structured by organisms; without life, organic-rich soils would be scarce. - In a lifeless Earth, which gas would most likely be higher due to unbalanced volcanic emissions?
a) Oxygen (O₂)
b) Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
c) Ozone (O₃)
d) Methane (CH₄) from microbes
Answer: b) Carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Without biological carbon sinks, volcanic CO₂ would accumulate more. - Without plants and microbes, the long-term carbon cycle would be mainly controlled by:
a) Photosynthesis and respiration
b) Weathering, volcanism, and ocean chemistry
c) Pollination and seed dispersal
d) Decomposition by fungi
Answer: b) Weathering, volcanism, and ocean chemistry
Abiotic processes would dominate cycles in a lifeless world. - Which color would Earth most likely appear from space without life?
a) Deep blue with green land patches
b) Mostly brown/grey rocks with blue oceans and white clouds
c) Entirely green
d) Mostly white
Answer: b) Mostly brown/grey rocks with blue oceans and white clouds
No vegetation means no green “biosignature” on land. - On a lifeless Earth, the nitrogen cycle would be missing its main conversion by:
a) Lightning only
b) Microbes (nitrogen fixation/denitrification)
c) Volcanoes
d) Wind erosion
Answer: b) Microbes (nitrogen fixation/denitrification)
Biological N-fixation and denitrification are central today; without life they vanish. - Which landform signal would likely be more preserved without life?
a) Rapid soil-covered slopes
b) Stable, sharp rock outcrops and more exposed craters
c) Dense root-bound riverbanks
d) Organic peat bogs
Answer: b) Stable, sharp rock outcrops and more exposed craters
No bioturbation or vegetation cover means less soil, more exposed bedrock/craters. - Absent life, which ocean characteristic would most likely differ?
a) Abundant dissolved oxygen from phytoplankton
b) Strong biological pump transporting carbon to deep ocean
c) No plankton blooms; chemistry set by abiotic processes
d) High biodiversity reefs
Answer: c) No plankton blooms; chemistry set by abiotic processes
No marine life means no biological pump or blooms. - Which protective system would be weaker or absent without life?
a) Planetary magnetic field
b) Ozone layer sustained by O₂ from photosynthesis
c) Plate tectonics
d) Ocean tides
Answer: b) Ozone layer sustained by O₂ from photosynthesis
O₃ depends on O₂; without life, UV shielding by ozone declines strongly. - On a lifeless Earth, seasonal changes would mainly be due to:
a) Migration and leaf fall
b) Tilt-driven insolation patterns only
c) Flowering cycles
d) Plankton blooms
Answer: b) Tilt-driven insolation patterns only
No biosphere responses; only physical solar-angle seasons remain.
Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
- Without photosynthesis, atmospheric __________ would remain very low and ozone would be weak.
Answer: oxygen (O₂)
O₃ forms from O₂; both depend on life today. - In a lifeless world, carbon would build up as __________ from volcanic emissions.
Answer: carbon dioxide (CO₂)
Biological sinks would be absent. - Soils would be thin and largely mineral because there is no input of __________ matter.
Answer: organic
Humus and structure come from life. - Ocean chemistry would lack a biological __________ that moves carbon to the deep sea.
Answer: pump
The biological pump is driven by plankton. - Lightning would be one of the few natural sources converting atmospheric nitrogen, in the absence of __________ fixation by microbes.
Answer: biological (nitrogen)
No N-fixing bacteria means far less bioavailable nitrogen. - Land surfaces would show more visible impact __________ without rapid biological weathering and soil cover.
Answer: craters
Less erosion by roots/biota means more preserved craters. - Without forests and phytoplankton, Earth’s surface would lack the green __________ of life.
Answer: biosignature
Vegetation color is a life indicator. - Climate would be set mainly by orbital position, volcanism, oceans, and the greenhouse effect, not by __________ feedbacks.
Answer: biological
No vegetation or microbial feedback loops. - The atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and magnetosphere would still interact, but the __________ would be missing.
Answer: biosphere
Life is the missing sphere. - Satellite images would show bare rock, deserts, ice, clouds, and oceans, but no __________ patterns from crops or forests.
Answer: vegetation
No green canopies or agricultural mosaics.
Very Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
- What key atmospheric layer would be weaker without life?
Answer: The ozone layer, because it depends on oxygen from photosynthesis. - How would continents look from space without life?
Answer: Mostly brown/grey bare rock and sand, lacking green vegetation. - Which major biogeochemical cycles would be missing their main drivers?
Answer: The carbon and nitrogen cycles would lack biological processes. - Would Earth still have plate tectonics without life?
Answer: Yes; tectonics is driven by internal heat, not biology. - What would replace forests in shaping land surfaces?
Answer: Physical processes like wind, water erosion, volcanism, and impacts.
Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
- Explain why oxygen would be scarce on a lifeless Earth.
Answer: Free O₂ on Earth is mainly produced by photosynthesis. Without life, oxygen would react with rocks and gases and not accumulate, leaving a thin or negligible O₂ atmosphere. - How would oceans differ without marine life?
Answer: No plankton blooms, coral reefs, or biological pump; carbon cycling would be set by chemistry and physics alone, and dissolved oxygen patterns would be purely abiotic. - What visual signatures used by satellites to track ecosystems would disappear?
Answer: Vegetation greenness (NDVI), crop patterns, algal blooms, and deforestation scars would be absent; images would be dominated by rock, sand, ice, water, and clouds. - Would weather and climate still vary in a lifeless world?
Answer: Yes. Seasons, winds, clouds, and rainfall would still occur due to solar heating, rotation, and ocean–atmosphere physics, but without biological feedbacks. - How would the carbon cycle be balanced without photosynthesis and respiration?
Answer: By slow abiotic processes: volcanic outgassing adding CO₂, silicate weathering and ocean chemistry removing CO₂, and carbonate rock formation over geologic timescales.
Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.
- Column A:
1) Ozone layer
2) Biological pump
3) Nitrogen fixation
4) Humus-rich soil
5) Green vegetation signal - Column B:
a) Satellite NDVI/green cover from plants
b) Deep-ocean carbon transport by plankton
c) Thicker, organic topsoil maintained by decomposers
d) UV shield formed from atmospheric O₂
e) Conversion of N₂ to usable forms by microbes
Correct Matches:
- Ozone layer — d) UV shield formed from atmospheric O₂
Explanation: O₃ derives from O₂; both depend on life today. - Biological pump — b) Deep-ocean carbon transport by plankton
Explanation: Marine life moves carbon into the deep sea. - Nitrogen fixation — e) Conversion of N₂ to usable forms by microbes
Explanation: Key biological pathway for bioavailable nitrogen. - Humus-rich soil — c) Thicker, organic topsoil maintained by decomposers
Explanation: Decomposition builds and sustains fertile soils. - Green vegetation signal — a) Satellite NDVI/green cover from plants
Explanation: The “green” biosignature indicates living plant cover.

 Which mirror makes objects appear smaller but gives a wider field of view?
Which mirror makes objects appear smaller but gives a wider field of view?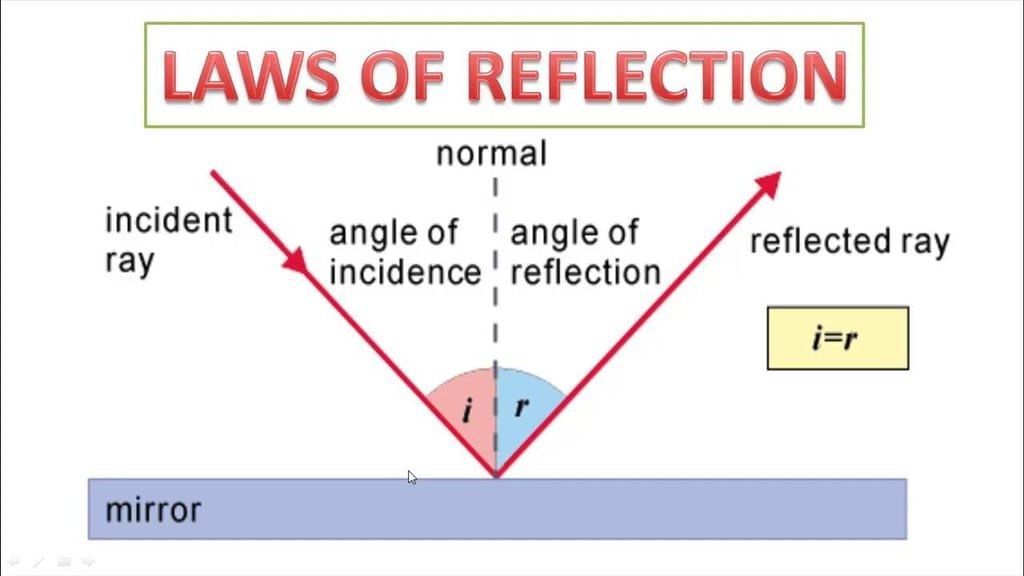
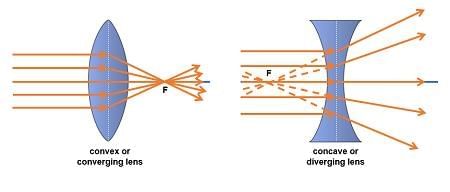

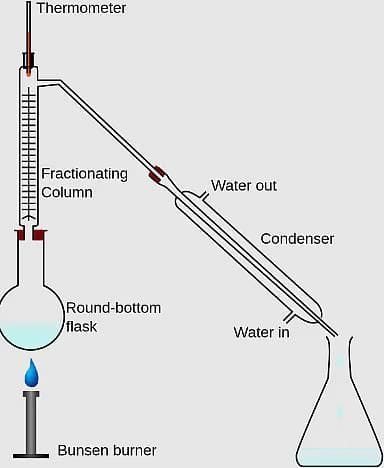
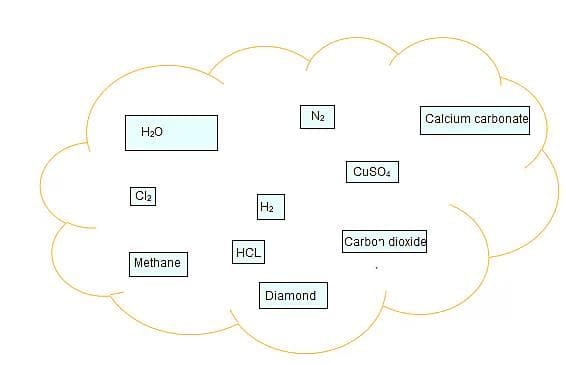
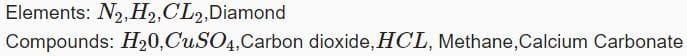
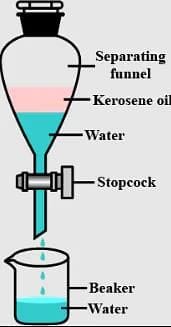
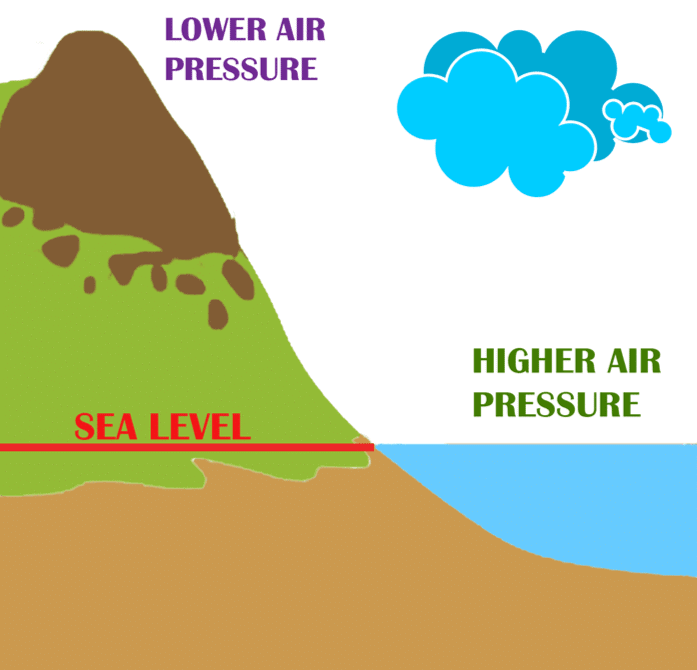 Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by:
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by: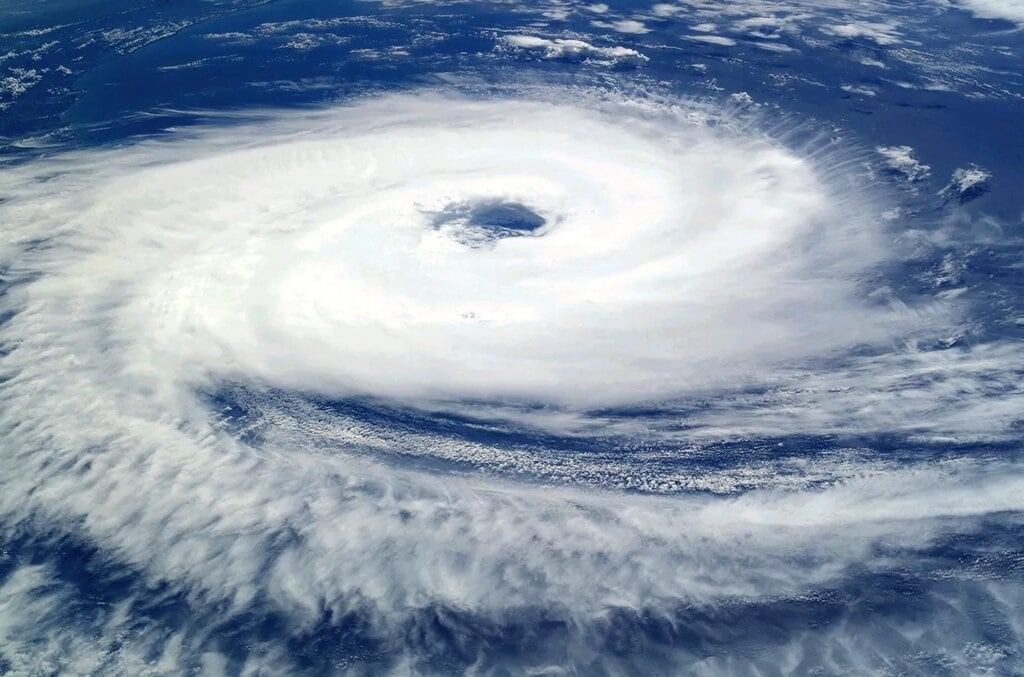
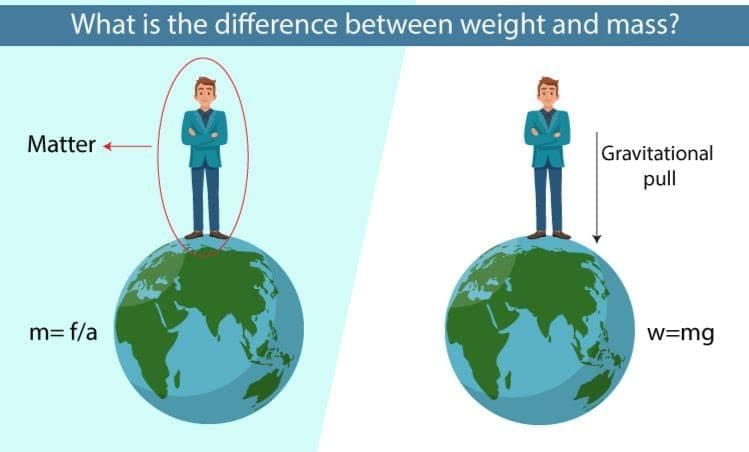
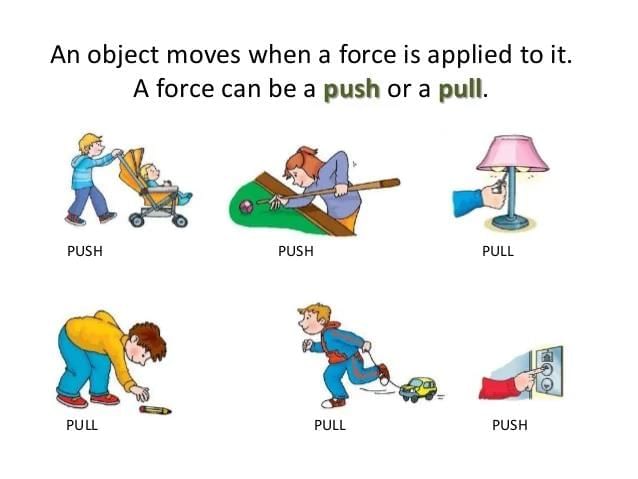 In science, a force is defined as:
In science, a force is defined as: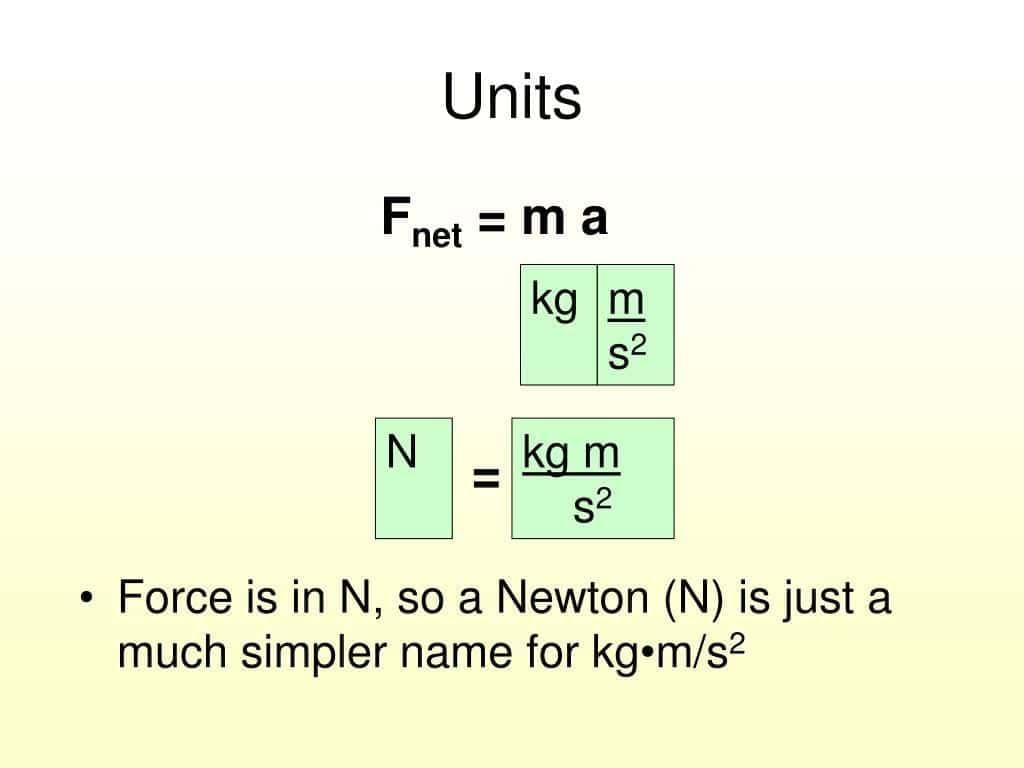 The SI unit of force is:
The SI unit of force is: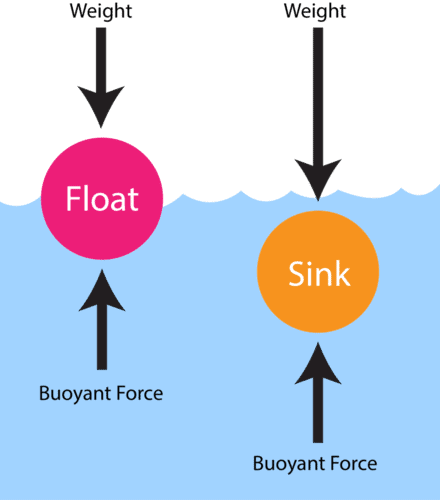
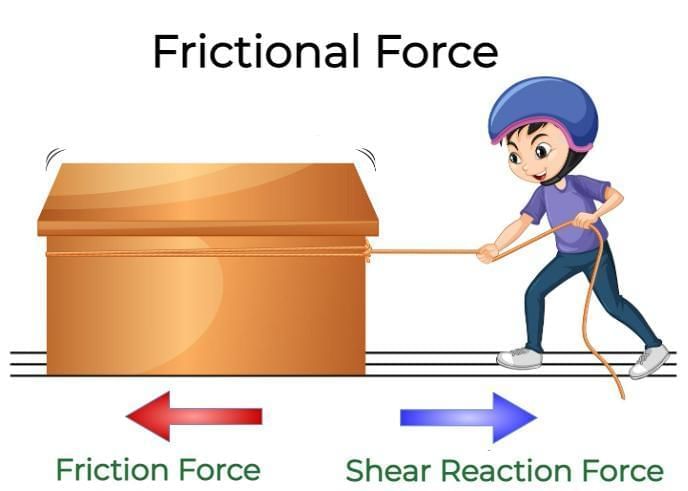 Friction always acts in a direction __________ to motion.
Friction always acts in a direction __________ to motion.


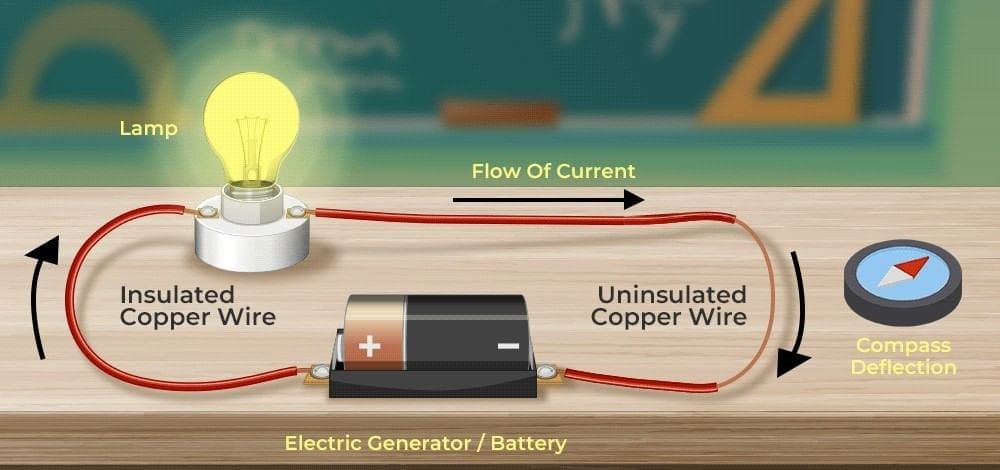 What did Oersted discover in 1820?
What did Oersted discover in 1820?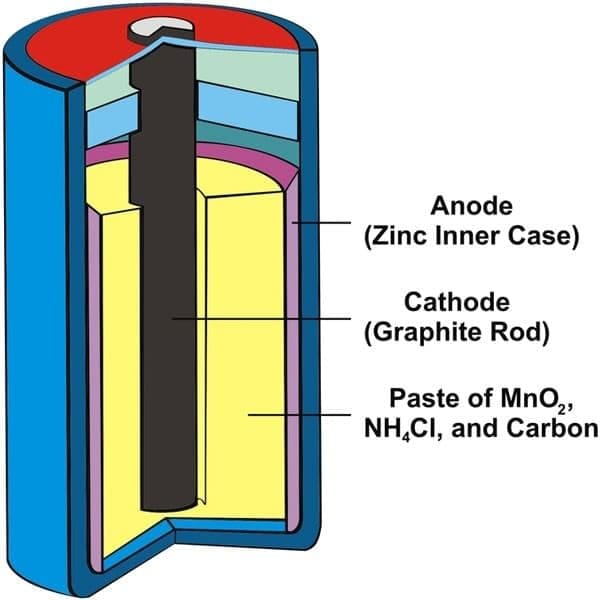 In a simple voltaic (galvanic) cell, electricity is produced by:
In a simple voltaic (galvanic) cell, electricity is produced by:
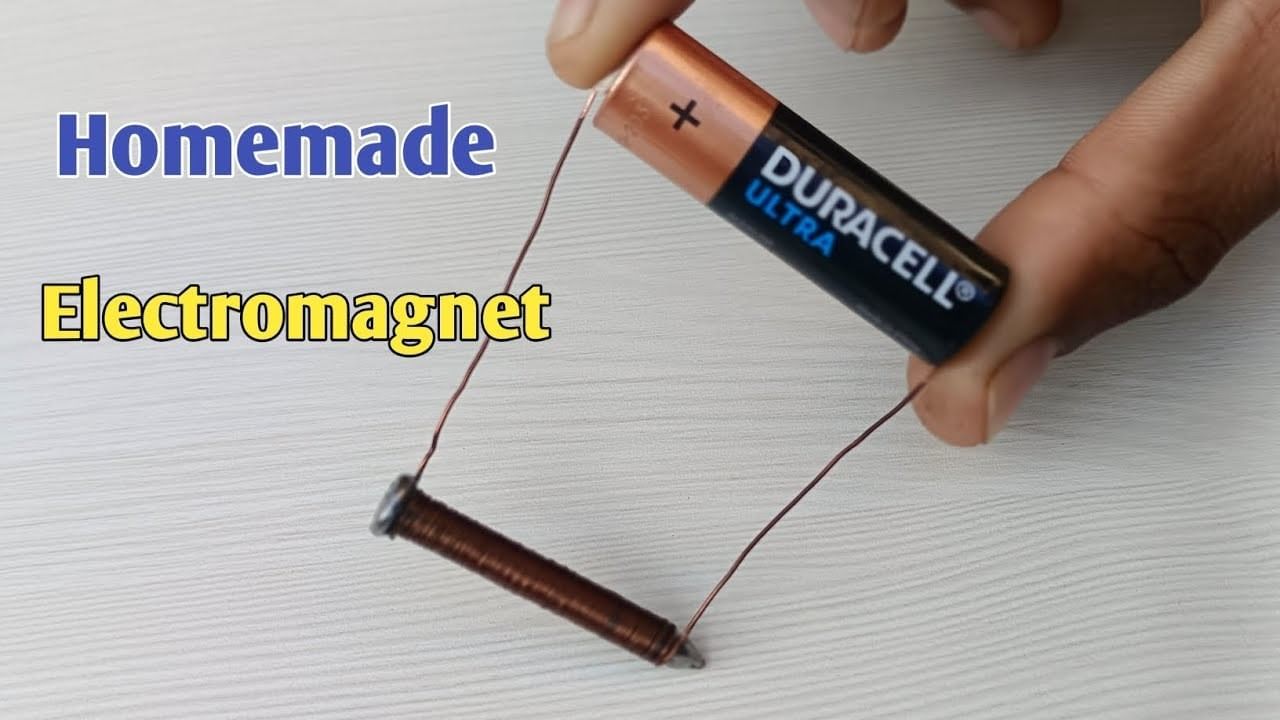 How can you make a simple electromagnet at home?
How can you make a simple electromagnet at home?