Q1. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
- According to WHO, health means:
a) Only absence of disease
b) Physical fitness only
c) Complete physical, mental, and social well-being
d) Ability to work hard - Which is a sign, not a symptom?
a) Pain
b) Tiredness
c) Dizziness
d) Fever - Which disease is non-communicable?
a) Typhoid
b) Dengue
c) Diabetes
d) Chickenpox  Which habit helps prevent communicable diseases?
Which habit helps prevent communicable diseases?
a) Skipping breakfast
b) Sharing towels
c) Washing hands with soap
d) Sleeping very late- Which statement about antibiotics is correct?
a) They kill viruses like flu
b) They treat protozoan diseases
c) They kill bacteria
d) They are safe to take without prescription - Who discovered the first antibiotic, penicillin?
a) Edward Jenner
b) Alexander Fleming
c) Robert Koch
d) Louis Pasteur - Vaccines protect by:
a) Killing pathogens directly in the body
b) Teaching the immune system to recognize germs
c) Giving energy to white blood cells
d) Replacing antibiotics - Which factor commonly increases risk of NCDs?
a) Playing outdoors
b) Balanced diet
c) Longer lifespans and less physical activity
d) Handwashing - Which practice from Ayurveda supports holistic health?
a) Variolation
b) Dinacharya and ritucharya
c) Overuse of antibiotics
d) Skipping meals - AQI is used to measure:
a) Water purity
b) Body temperature
c) Air quality
d) Sleep quality
Q2. Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
- Health includes physical, mental, and ______ well-being.
- Headache is a ______ experienced by the patient.
- A measurable change like a rash or swelling is called a ______.
- Diseases that spread from person to person are called ______ diseases.
- Diseases like cancer and asthma that do not spread are ______ diseases.
- The body’s ability to fight diseases is called ______.
- Using weakened or inactive germs to train the body’s defense is called a ______.
- Taking antibiotics without need can lead to antibiotic ______.
- Building and using toilets helps prevent diseases spread through contaminated ______.
- Practising ______, like deep breathing, supports mental health in Ayurveda.
Q3. Very Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in one line.
- What does WHO say about health?
- Name one vector that spreads communicable diseases.
- What is the term for the body’s natural defense system?
- Which discovery led to modern antibiotics?
- What does AQI stand for?
Q4. Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.
- How did screen time and loneliness affect student’s health?
- How do communicable diseases spread through air?
- Why should we finish a full course of antibiotics?
- How does community sanitation improve health?
- Why are relationships important for health?
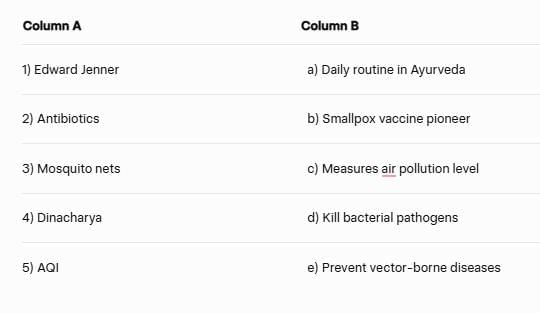
Q5. Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.
Check the worksheet solutions here.

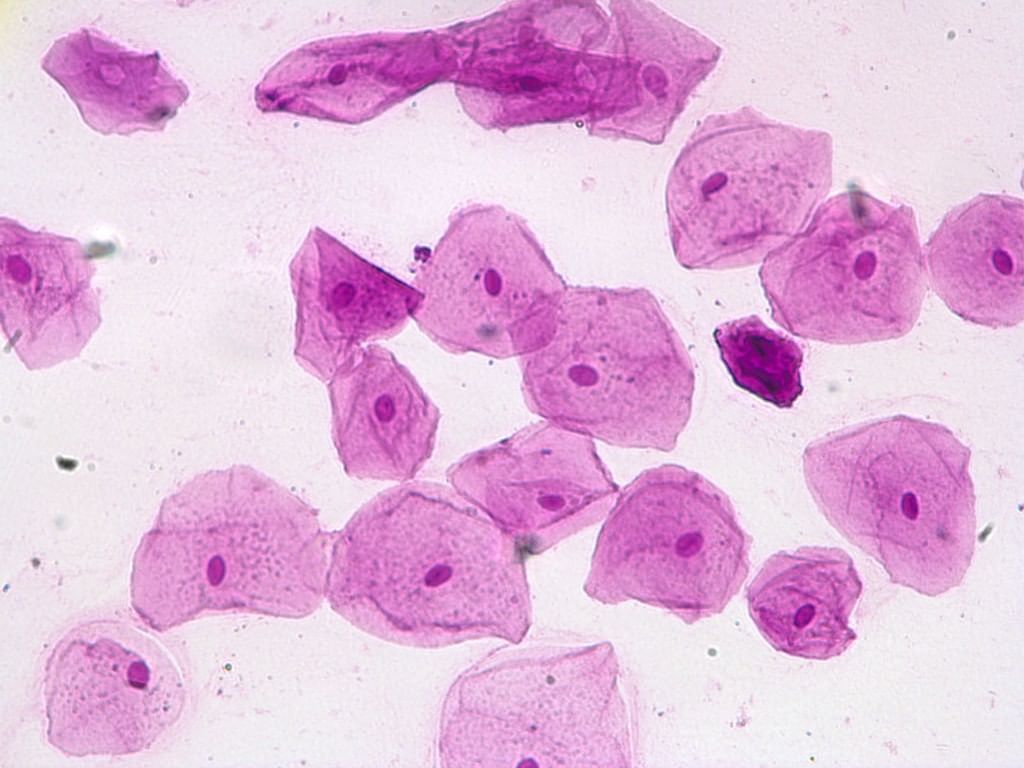 Cheek cells are commonly stained with ______ ______.
Cheek cells are commonly stained with ______ ______.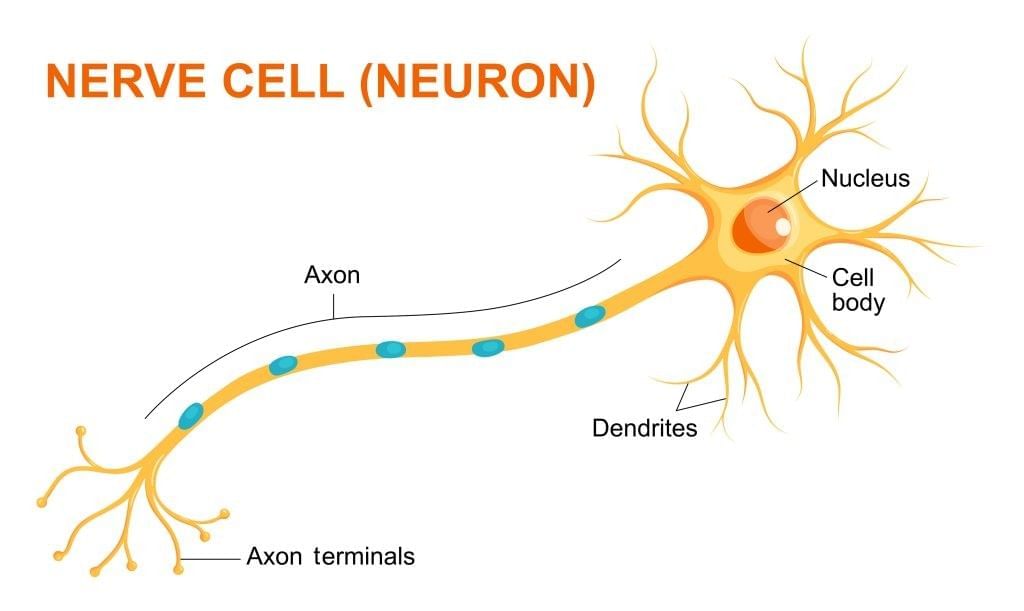 How do nerve cells (neurons) suit their function?
How do nerve cells (neurons) suit their function?
 In the “roots and kites” symbol, roots mainly remind us to:
In the “roots and kites” symbol, roots mainly remind us to: