Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1. Which of the following is not a factor of production?
(a) Land
(b) Labour
(c) Money
(d) Entrepreneurship
Ans: (c) Money
Money alone is not considered a factor; instead, it is part of capital when used for production.
Q2. In economics, “land” refers to—
(a) Only soil and ground
(b) All natural resources used for production
(c) Only forests
(d) Only minerals
Ans: (b) All natural resources used for production
Land includes soil, forests, minerals, water, sunlight, air, etc.
Q3. Human effort, both physical and mental, used in the production process is called—
(a) Capital
(b) Labour
(c) Entrepreneurship
(d) Technology
Ans: (b) Labour
Labour means human physical and mental effort in production.
Q4. The knowledge, skills, and expertise of workers are called—
(a) Land
(b) Human capital
(c) Physical labour
(d) Entrepreneurship
Ans: (b) Human capital
Human capital makes labour more productive.
Q5. Which two main facilitators help build strong human capital?
(a) Wealth and inheritance
(b) Education and healthcare
(c) Minerals and forests
(d) Elections and democracy
Ans: (b) Education and healthcare
Education increases skills, and healthcare ensures productivity.
Q6. Capital in production refers to—
(a) Only money
(b) Durable assets like machinery, tools, and buildings plus money
(c) Only human resources
(d) Only natural resources
Ans: (b) Durable assets like machinery, tools, and buildings plus money
Capital includes machines, tools, offices, and money used in production.
Q7. The person who takes risk, combines resources, and creates businesses is called—
(a) Worker
(b) Capitalist
(c) Entrepreneur
(d) Educator
Ans: (c) Entrepreneur
Entrepreneurs create businesses, innovate, and take risks.
Q8. Which Indian business leader founded India’s first airline in 1932?
(a) Dhirubhai Ambani
(b) J.R.D. Tata
(c) Ratan Tata
(d) Verghese Kurien
Ans: (b) J.R.D. Tata
He founded Tata Airlines, later known as Air India.
Q9. Which of the following shows how technology helps production?
(a) Pulleys and wheelbarrows in ancient times
(b) UPI for faster payments today
(c) Drones spraying fertilizers
(d) All of these
Ans: (d) All of these
Technology improves production in both traditional and modern ways.
Q10. India became the first country in 2014 to pass a law requiring companies to spend part of their profits on—
(a) Exports
(b) Corporate Social Responsibility
(c) Workers’ salaries
(d) Import duties
Ans: (b) Corporate Social Responsibility
Companies must spend 2% of profits on CSR activities.
Match the Following
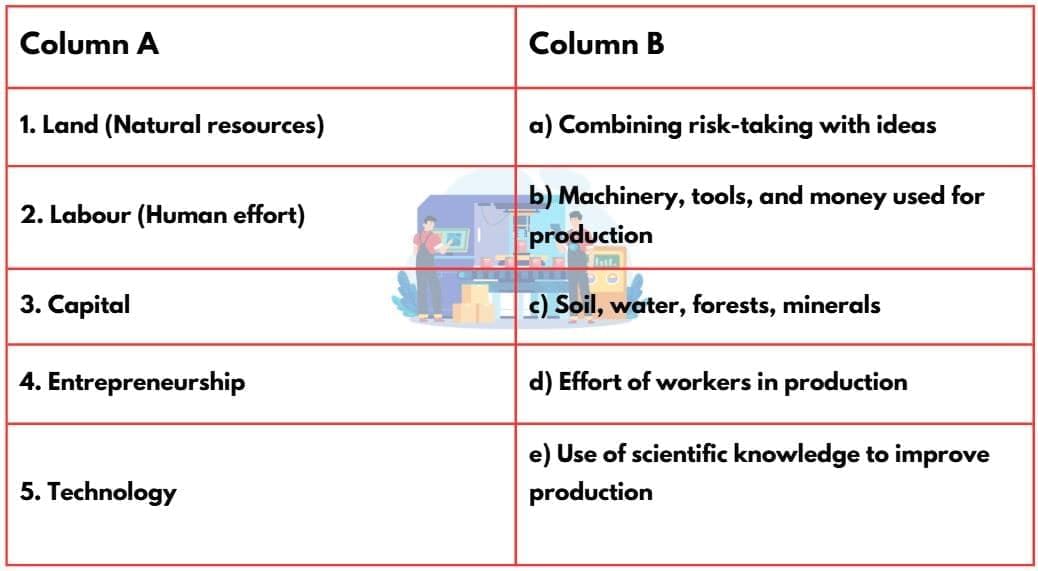
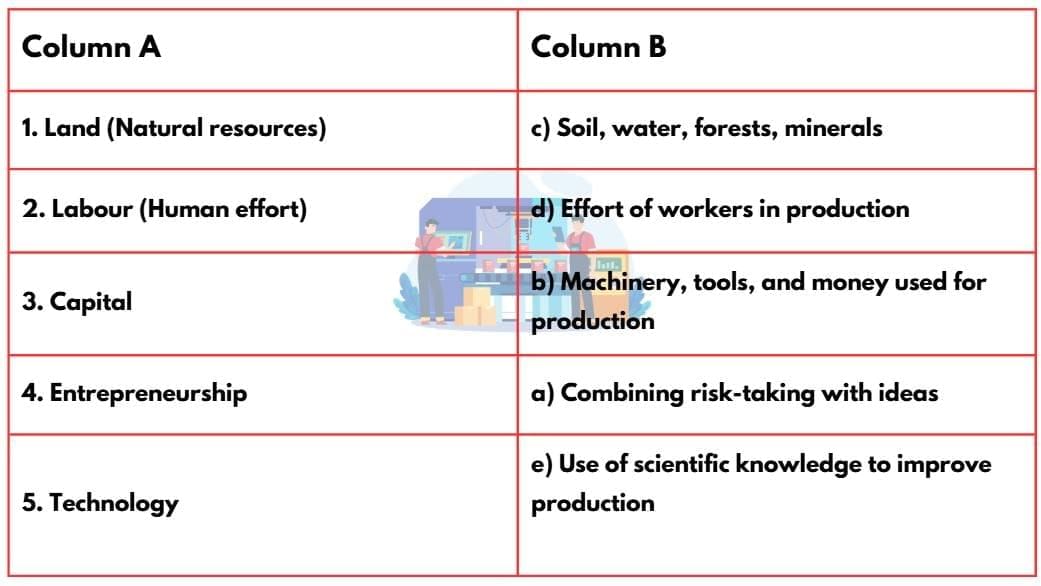
Ans:
True or False
Q1. Human capital is the same as human labour.
Ans: False
Human capital adds skills and knowledge, making labour more effective.
Q2. Education and training improve the productivity of workers.
Ans: True
They equip workers with skills and expertise.
Q3. J.R.D. Tata started the first steel plant in India.
Ans: False
He founded India’s first airline, not the first steel plant.
Q4. Technology reduces barriers to learning and jobs.
Ans: True
Technology enables online courses and wider job access.
Q5. In economics, capital also includes buildings, tools, and machinery.
Ans: True
Capital covers both money and durable production assets.
Q6. CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) means ignoring society’s welfare and focusing only on profits.
Ans: False
CSR is about companies spending on social welfare and sustainability.
Fill in the Blanks
Q1. The four main factors of production are land, labour, capital, and ______.
Ans: Entrepreneurship
Q2. Knowledge and skills that make labour more effective are called ______ capital.
Ans: Human
Q3. Good ______ helps workers be healthy and productive.
Ans: Healthcare
Q4. The concept of kaizen, meaning continuous improvement, comes from ______.
Ans: Japan
Q5. J.R.D. Tata founded ______ Airlines in 1932.
Ans: Tata (later Air India)
Q6. Money borrowed from a bank must be repaid with ______.
Ans: Interest
Q7. In 2014, India made CSR spending by companies ______ under law.
Ans: Mandatory
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1. Define factors of production.
Ans: Factors of production are resources like land, labour, capital, and entrepreneurship used to produce goods and services.
Q2. Give two examples of natural resources used in production.
Ans: Water and minerals.
Q3. What is the difference between labour and human capital?
Ans: Labour is physical and mental effort, while human capital refers to skills and knowledge that increase productivity.
Q4. Name two ways societies can build human capital.
Ans: Education and healthcare.
Q5. What is capital? Give one example.
Ans: Capital includes man-made resources like machines or money; example: a sewing machine.
Q6. Who is called an entrepreneur?
Ans: A person who takes risks, organizes factors of production, and creates businesses.
Q7. Mention one contribution of J.R.D. Tata to India.
Ans: He founded India’s first airline (Tata Airlines/Air India).
Q8. Give two examples of technology used in modern production.
Ans: Drones in farming and UPI for payments.
Q9. What does CSR stand for?
Ans: Corporate Social Responsibility.
Q10. Why should factors of production be used responsibly?
Ans: To protect the environment, ensure fair treatment of workers, and secure resources for future generations.