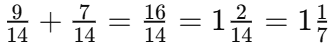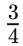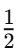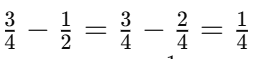Q1: At what age does adolescence typically begin?
Ans: Around the age of 10.
Q2: What causes pimples to appear during adolescence?
Ans: Pimples appear due to an increase in oily secretions from the skin during adolescence.
Q3: What are secondary sexual characteristics?
Ans: Secondary sexual characteristics are signs that the body is preparing for adulthood, like voice changes and body hair growth.
Q4: What marks the onset of adolescence?
Ans: The onset of adolescence is marked by rapid growth and development.
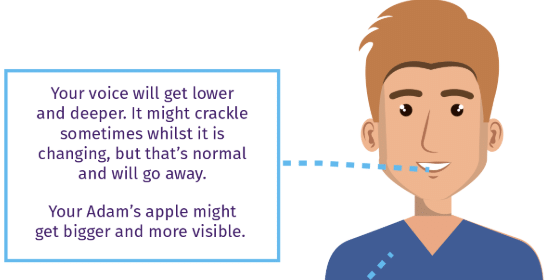
Q5: What happens to boys’ voices during adolescence?
Ans: Boys’ voices become hoarse due to the growth of the voice box, leading to the appearance of an Adam’s apple.
Q6: What is the growth of facial hair in boys a sign of?
Ans: The growth of facial hair in boys is a sign of puberty and the transition to adulthood.
Q7: What is menstruation, and when does it start?
Ans: Menstruation is the discharge of blood from the body, starting around puberty in girls.
Q8: How often does the menstrual cycle typically occur?
Ans: The menstrual cycle generally occurs every 28-30 days.
Q9: What are the two main emotional changes during adolescence?
Ans: Mood swings and increased sensitivity.
Q10: What is a common health issue faced by girls during adolescence?
Ans: Acne, caused by increased oily secretions from the skin.
Q11: What are some examples of secondary sexual characteristics in girls?
Ans: Development of breasts and widening of hips.
Q12: What can help improve reproductive health in adolescent girls?
Ans: A balanced diet, proper hygiene, and the use of sanitary pads during menstruation.
Q13: What should be avoided to ensure good health during adolescence?
Ans: Harmful substances such as tobacco, alcohol, and drugs.
Q14: What is the role of hormones in adolescence?
Ans: Hormones regulate physical and emotional changes and control growth and development.
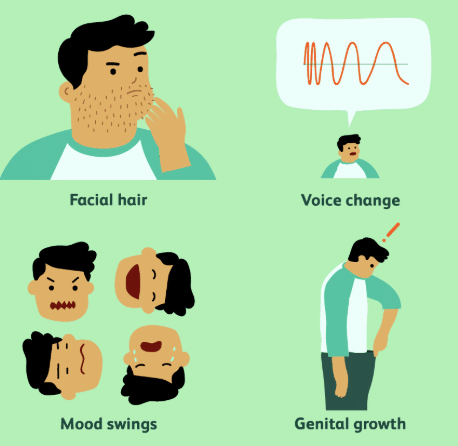
Q15: What physical change occurs in boys’ bodies that is different from girls?
Ans: The development of a moustache and beard.
Q16: What is the importance of exercise during adolescence?
Ans: Regular exercise helps maintain physical and mental health, builds stamina, and boosts mood.
Q17: What is a good source of calcium for adolescents?
Ans: Milk, cheese, and paneer.
Q18: What is the significance of iron in adolescent girls’ diet?
Ans: Iron is important for the formation of blood and to prevent anaemia.

Q19: What is the ?
Ans: It is a campaign to raise awareness about avoiding substance abuse.
Q20: How can adolescents ensure responsible social media use?
Ans: By being respectful, protecting privacy, and avoiding sharing personal photos with strangers.