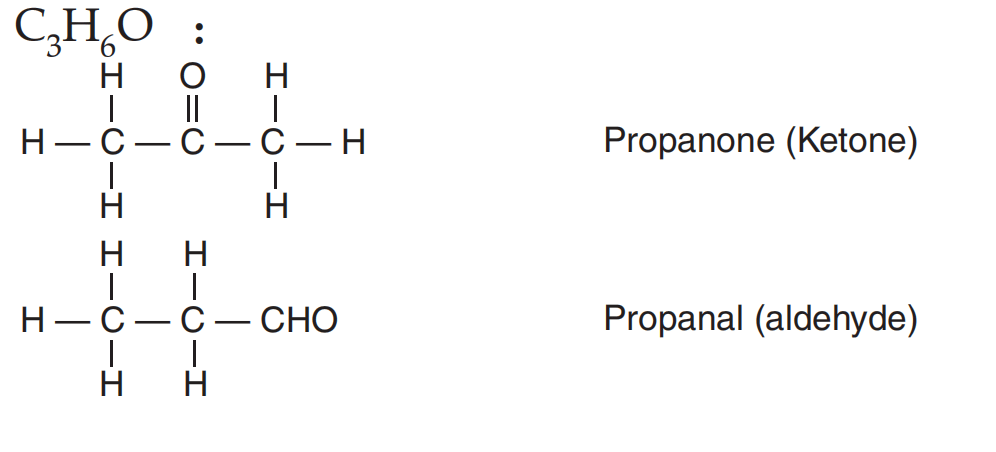
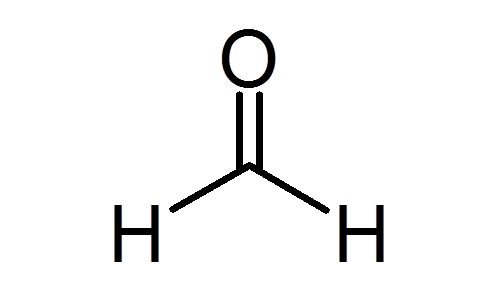
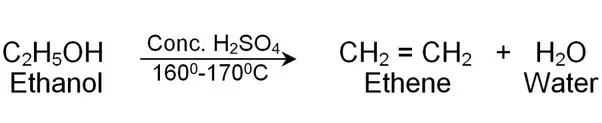
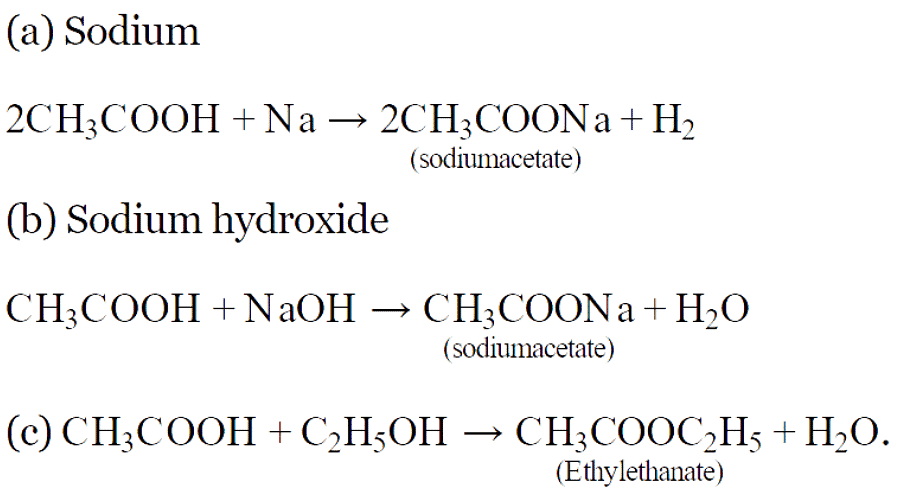Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: Which of the following groups do not constitute a food chain? (1 Mark)
(i) Wolf, rabbit, grass, lion
(ii) Plankton, man, grasshopper, fish
(iii) Hawk, grass, snake, grasshopper, frog
(iv) Grass, snake, wolf, tiger
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (c)
A food chain shows a sequence of organisms where each is eaten by the next one.
In options (ii) and (iii), the order of organisms is incorrect — they do not represent a proper feeding relationship (for example, man does not eat grasshopper or fish directly, and grass cannot be eaten by a hawk).
Hence, (ii) and (iii) do not constitute a food chain.
Q2: The percentage of solar energy which is not converted into food energy by the leaves of green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem is about: (1 Mark)
(a) 1%
(b) 10%
(c) 90%
(d) 99%
Ans: (d)
Only about 1% of the sunlight that falls on green plants is converted into food energy, so 99% of solar energy remains unutilised.
Q3: Two statements are given — one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below
Assertion (A): The amount of ozone in the atmosphere began to drop sharply in the 1980s.
Reason (R): The oxygen atoms combine with molecular oxygen to form ozone. (1 Mark)
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans: (b)Ozone levels dropped sharply in the 1980s due to synthetic chemicals like CFCs, not because oxygen atoms combine with molecular oxygen (which actually forms ozone).
Q4: “Excessive use of chemicals and pesticides in agriculture adversely affects the environment.” Justify this statement. (2 Marks)
Ans: Excessive use of pesticides and chemicals in agriculture leads to their accumulation in soil and water. These chemicals enter the food chain through plants and aquatic organisms and are not degradable. They get progressively accumulated at each trophic level, a process called biological magnification, causing harmful effects on living organisms and the environment.
Q5: Identify from the following a group containing all non-biodegradable substances. (1 Mark)
(a) Leather, Glass, Plastic
(b) Cotton, Wood, Nylon
(c) DDT, Polyester, Glass
(d) Leather, Silk, Wool
Ans: (c)
DDT, polyester, and glass cannot be broken down by biological processes; hence, they are non-biodegradable substances.
Q6: Two statements are given — one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): Animals will not get energy if they eat (consume) coal as food.
Reason (R): Specific enzymes are needed for the breakdown of a particular food.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans: (a)
Animals cannot get energy from coal because enzymes are specific and only break down particular biological substances. Since coal cannot be broken down by these enzymes, it cannot provide energy.
Q7: Some harmful chemicals get accumulated in human bodies through the food chain. Name this phenomenon. Explain the reason for the maximum concentration of these chemicals found in our bodies. (3 Marks)
Ans: This phenomenon is called biological magnification.
Harmful chemicals such as pesticides and fertilizers enter the food chain through soil and water. These chemicals are not degradable and thus accumulate in the tissues of organisms.At each successive trophic level, their concentration increases because they are passed on through food. Since human beings occupy the top level in the food chain, the maximum concentration of these chemicals accumulates in our bodies.
Q8: Other than the abiotic components, which of the given biotic components are not required to make an aquarium with small herbivorous fishes a self-sustaining system? (1 Mark)
(i) Aquatic plants and aquatic animals
(ii) Terrestrial plants and terrestrial animals
(iii) Decomposers as bacteria and fungi
(iv) Consumers as clown fishes and sea urchins
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans: (d)
A self-sustaining aquarium needs aquatic plants (producers), small herbivorous fishes (consumers), and decomposers. Terrestrial plants/animals and large consumers like sea urchins are not required in such an aquatic ecosystem.
Q9: Two statements are given — one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): Use of jute bags for shopping reduces pollution.
Reason (R): Jute is biodegradable and its bag may be reused as and when needed.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans: (a)
- Using jute bags helps reduce pollution because jute is biodegradable and such bags can be reused, reducing non-biodegradable plastic waste.
Q10: In the food chains given below, select the most efficient food chain in terms of energy. (1 Mark)
(a) Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake
(b) Plants → Deer → Lion
(c) Plants → Man
(d) Phytoplankton → Zooplankton → Small Fish → Big Fish
Ans: (c)
The shorter the food chain, the less energy is lost between trophic levels. Since this chain has only two trophic levels, it is the most efficient in terms of energy transfer.
Q11: What are decomposers? Give two examples. State how they maintain a balance in an ecosystem. (3 Mark)
Ans: Decomposers are microorganisms that break down dead plants, animals, and waste materialsinto simple inorganic substances.
Examples: Bacteria and fungi.
Role in maintaining balance:
- They recycle nutrients by converting complex organic matter into simple substances that return to the soil and are used again by plants.
- This process helps in the natural replenishment of the soil and maintains the balance in the ecosystem.
Q12: The examples of natural and manmade (artificial) ecosystems are, respectively: (1 Mark)
(a) Forests and ponds
(b) Crop fields and lakes
(c) Lakes and gardens
(d) Crop fields and forests
Ans: (c)Lakes are natural ecosystems, while gardens are human-made (artificial) ecosystems maintained by people.
Q13: Human activities that are affecting the environment are: (1 Mark)
(a) Minimising the use of chlorofluorocarbons
(b) Excessive use of disposable cups and plates
(c) Maximising the use of reusable utensils for eating food and drinking fluids
(d) Segregating the wastes into biodegradable and non-biodegradable before disposal
Ans: (b)
Using disposable cups and plates increases non-biodegradable waste, leading to environmental pollution and harming ecosystems.
Q14: (a) Why are the organisms of first trophic level important in any food chain?
(b) Justify the following statement: ‘The flow of energy in an ecosystem is unidirectional.’ (2 Marks)
Ans:
(a) The organisms of the first trophic level, known as producers, are very important because they absorb solar energy and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This stored energy in food becomes the source of energy for all other organisms in the food chain such as herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers. Without producers, no other organisms could survive, as they depend directly or indirectly on them for food.
(b) The flow of energy in an ecosystem is unidirectional, meaning it moves in one direction only — from the Sun → producers → consumers → decomposers. The energy captured by producers does not return to the Sun, nor can it go backward in the chain. At each trophic level, some energy is lost as heat, so the energy available to the next level keeps decreasing, making the flow one-way and non-cyclic.
Q15: A gas ‘X’ is found in the upper layer of atmosphere. It is a deadly poison, but still essential for all life forms on earth.
(a) Identify the gas and state the main factor for its depletion in the atmosphere.
(b) How is this gas formed in the upper atmosphere? (2 Marks)
Ans:
(a) The gas ‘X’ is ozone (O₃). It is getting depleted mainly due to synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) used in refrigerants and fire extinguishers.
(b) In the upper atmosphere, ozone is formed when ultraviolet (UV) radiations split some molecules of oxygen (O₂) into free oxygen atoms (O), which then combine with molecular oxygen to form ozone (O₃).
Q16: Study the food web given below:
(a) Identify the food chain(s) in which the eagle receives the highest energy from the producers.
(b) Identify the organism in which a non-biodegradable pesticide will be found in maximum concentration. Name the term used for this phenomenon. (2 Marks)
Ans:
(a) The food chain in which the eagle receives the highest energy from producers is:
Grass → Mouse → Eagle.
This is because the chain is shortest, involving fewer trophic levels, so there is less energy loss between steps, and the eagle receives more energy from the producers.
(b) The organism in which a non-biodegradable pesticide will be found in maximum concentration is the Eagle.
This is due to biological magnification, where harmful chemicals accumulate progressively at each trophic level, reaching the highest concentration in top consumers.
Q17: Consider the following food chain:
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Eagle.
If the amount of energy available at third trophic level is 50 kJ, the available energy at the producer level was: (1 Mark)
(a) 0.5 kJ
(b) 5 kJ
(c) 500 kJ
(d) 5000 kJ
Ans: (d)
According to the 10% law, only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
If the third trophic level (frog) has 50 kJ, then:
Producer → 1st → 2nd → 3rd
Energy at producer level = 50 × 10 × 10 × 10 = 50,000 kJ.
Q18: The incorrect statement about ozone is: (1 Mark)
(a) It is a deadly poisonous gas.
(b) It shields the surface of the Earth from UV radiation from sun.
(c) It is used as a refrigerant and in fire extinguishers.
(d) It is formed by combining an oxygen molecule with a free oxygen atom.
Ans: (c)
Ozone itself is not used as a refrigerant or in fire extinguishers; CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) are.
Ozone protects the Earth from harmful UV radiation.
Q19: Two statements are given – one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below :
Assertion (A): Food web is a network of several food chains operating in an ecosystem.
Reason (R): Food web decreases the stability of an ecosystem. (1 Mark)
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans: (c)
- A food web is indeed a network of many interconnected food chains, but it actually increases the stability of an ecosystem, not decreases it.
Q20: We do not clean natural ponds or lakes, whereas an aquarium or a swimming pool needs to be cleaned regularly. Why? (2 Marks)
Ans: Natural ponds and lakes are self-sustaining ecosystems that contain producers, consumers, and decomposers. These components interact and maintain a natural balance by recycling nutrients and cleaning the system on their own.
An aquarium or swimming pool, however, is a human-made system that lacks sufficient decomposers and natural processes of purification. Hence, it needs to be cleaned regularly to remove waste and maintain a healthy environment.
Q21: Green plants occupy the first trophic level in every food chain because they: (1 Mark)
(a) exist over a large area.
(b) have very less concentration of harmful chemicals.
(c) have to feed large number of herbivores.
(d) can synthesize food by photosynthesis.
Ans: (d)
Green plants are producers; they make their own food from inorganic substances using sunlight through photosynthesis, so they always occupy the first trophic level in a food chain.
Previous Year Questions 2024
Q1: For Q. Nos., two statements are given – One labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below: (1 Mark) (2024)
Assertion (A): Accumulation of harmful chemicals is maximum in the organisms at the highest trophic level of a food chain.
Reason (R): Harmful chemicals are sprayed on the crops to protect them from diseases and pests.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans: (b)
Harmful chemicals do accumulate in organisms at the highest trophic level due to a process called biomagnification, and these chemicals are often sprayed on crops to protect them. However, the reason does not directly explain why the accumulation is highest at the top of the food chain, so it’s not a correct explanation of the assertion.
Q2: (A) Plants -> Deer -> Lion. (1 to 3 Marks) (2024)
In the given food chain, what will be the impact of removing all the organisms of the second trophic level on the first and third trophic levels? Will the impact be the same for the organisms of the third trophic level in the above food chain if they were present in a food web? Justify.
OR
(B) A gas ‘X’ which is a deadly poison is found at the higher levels of the atmosphere and performs an essential function. Name the gas and write the function performed by this gas in the atmosphere. Which chemical is linked to the decrease in the level of this gas? What measures have been taken by an international organization to check the depletion of the layer containing this gas?
Ans: (A)
- Number of plants/organisms of first trophic level will increase.
- Number of lions/ organisms of third trophic level will decrease.
- No
- As the organisms of that level will find alternative foods and will not starve to death / food web is more stable where other animals as prey may be available.
OR
- Gas ‘X’ is Ozone.
- Ozone shields the surface of the earth from ultra-violet (UV) radiations from the sun.
- CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons)
- Succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels / Manufacturing of CFC free refrigerators
Q3: Name the term used for the materials which cannot be broken down by biological processes. Give two ways by which they harm various components of an ecosystem. (1 to 3 Marks) (2024)
Ans:
- Non-biodegradable substances
- Two ways:
(i) They are inert and persist in the environment for long time and cause pollution.
(ii) Cause Biological magnification
(iii) Affect the fertility of soil
Q4: Use of pesticides to protect our crops affects organisms at various trophic levels especially human beings. Name the phenomenon involved and explain how does it happen. (1 to 3 Marks) (2024)
Ans: Phenomenon – Biological Magnification /Biomagnification:
- Pesticides are washed down into the soil and water bodies.
- From the soil pesticides are absorbed by crop plants along with water and minerals and enter the food chain.
- These chemicals are non-biodegradable and get accumulated progressively at each trophic level.
- As human beings occupy the top level in any food chain, the maximum concentration of these chemicals gets accumulated in our bodies.
Q5: Consider the following statements about ozone: (1 to 3 Marks) (2024)
(A) Ozone is poisonous gas.
(B) Ozone shields the earth’s surface from the infrared radiation from the sun.
(C) Ozone is a product of UV radiations acting on oxygen molecule.
(D) At the lower level of the earth’s atmosphere, ozone performs most essential function.
The correct statements are
(a) (A) and (B)
(b) (A) and (C)
(c) (B) and (C)
(d) (B) and (D)
Ans: (b)
Ozone can be harmful at ground level, making it a poisonous gas. Statement (C) is also correct since ozone is formed when ultraviolet (UV) radiation interacts with oxygen molecules. However, statement (B) is incorrect because ozone protects the Earth from UV radiation, not infrared radiation, and statement (D) is misleading because ozone’s essential functions are primarily in the upper atmosphere, not at lower levels.
Q6: Assertion (A) and Reason (R), answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below: (1 Mark) (2024)
Assertion (A): The waste we generate daily may be biodegradable or non-biodegradable.
Reason (R): The waste generated, if not disposed off properly may cause serious environmental problems.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Ans: (b)
The answer is (b) because both statements are true: waste can be either biodegradable (which can break down naturally) or non-biodegradable (which cannot), and improper disposal of waste can indeed lead to serious environmental issues. However, the reason does not explain why waste is categorized as biodegradable or non-biodegradable, so it’s not a direct explanation of the assertion.
Q7: What are decomposers? List two consequences of their absence in an ecosystem. (1 to 3 Marks) (2024)
Ans: Decomposers are the microorganisms that break-down the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances.
Consequences:
(i) No replenishment of soil
(ii) Foul smell
(iii) Breeding of flies
(iv) Accumulation of dead plants and animals in the environment.
(v) No recycling of nutrients
Q8: We water the soil but it reaches the topmost leaves of the plants. Explain in brief the process involved. (1 to 3 Marks) (2024)
Ans: When water is lost through stomata in the leaves by transpiration, it creates a suction force/transpiration pull, due to which water is pulled up through xylem of the roots to the leaves.
Q9: Some wastes are given below: (1 to 3 Marks) (2024)
(i) Garden waste
(ii) Ball point pen refills
(iii) Empty medicine bottles made of glass
(iv) Peels of fruits and vegetables
(v) Old cotton shirt
The non-biodegradable wastes among these are:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i), (iv) and (v)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Ans: (b)
Non-biodegradable wastes are those that do not break down naturally in the environment. In the given options, ballpoint pen refills (ii) and empty medicine bottles made of glass (iii) are non-biodegradable because they can persist in the environment for a long time. The other items like garden waste, fruit and vegetable peels, and old cotton shirts decompose naturally and are considered biodegradable.
Q10: Two statements are given one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below. (1 Mark) (2024)
Assertion (A): Oxygen is essential for all aerobic forms of life.
Reason (R): Free oxygen atoms combine with molecular oxygen to form ozone.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans: (b)
Assertion (A) correctly states that oxygen is essential for aerobic life forms, while Reason (R) explains a process involving oxygen and ozone formation, which is also true. However, Reason (R) does not explain why oxygen is essential for life, so the correct answer is (b): both are true, but Reason (R) does not explain Assertion (A).
Q11: Which one of the following is not a natural ecosystem? (1 Mark) (2024)
(a) Pond ecosystem
(b) Grassland ecosystem
(c) Forest ecosystem
(d) Cropland ecosystem
Ans: (d)
A natural ecosystem is one that occurs naturally without human interference. Among the options given, a cropland ecosystem (d) is not natural because it is created and managed by humans for farming purposes. In contrast, pond, grassland, and forest ecosystems develop naturally in the environment.
Q12: Differentiate between food chain and food web. In a food chain consisting of deer, grass and tiger, if the population of deer decreases, what will happen to the population of organisms belonging to the first and third trophic levels? (3 Marks) (2024)
Ans:
- Population of grass/ first trophic level will increase.
- Population of tiger/ third trophic level will decrease.
Q13: Identify the food chain in which the organisms of the second trophic level are missing: (1 Mark) (2024)
(a) Grass, goat, lion
(b) Zooplankton, Phytoplankton, small fish, large fish
(c) Tiger, grass, snake, frog
(d) Grasshopper, grass, snake, frog, eagle
Ans: (c)
In a food chain, the second trophic level usually consists of primary consumers that eat producers (like plants). In option (c), tiger, grass, snake, frog, there are no primary consumers (like a herbivore) between the grass (producer) and the snake. Instead, the snake directly feeds on frogs, which means the second trophic level is missing.
Q14: In which of the following organisms, multiple fission is a means of asexual reproduction? (1 Mark) (2024)
(a) Yeast
(b) Leishmania
(c) Paramoecium
(d) Plasmodium
Ans: (d)
Multiple fission is a type of asexual reproduction where an organism divides into many parts at once. In this case, Plasmodium (d), which causes malaria, reproduces through multiple fission in its life cycle, producing many daughter cells simultaneously. The other options like yeast, Leishmania, and Paramecium reproduce differently.
Q15: A food chain will be more advantageous in terms of energy if it has:
(a) 2 trophic levels
(b) 3 trophic levels
(c) 4 trophic levels
(d) 5 trophic levels (1 Mark) (CBSE 2024)
Ans: (a)
In a food chain, energy is lost at each trophic level due to metabolic processes, typically around 90% of energy is lost as heat, while only about 10% is transferred to the next level. Therefore, a food chain with fewer trophic levels will retain more energy available to the organisms at the higher level.
With 2 trophic levels (e.g., producers and primary consumers), there is minimal energy loss compared to longer chains, making it more advantageous in terms of energy efficiency.
Thus, the correct answer is (a) 2 trophic levels.
 | Get additional INR 200 off today with EDUREV200 coupon. | Avail Offer |
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q1: Use of several pesticides which results in excessive accumulation of pesticides in rivers or ponds, is a matter of deep concern. Justify this statement. (3 Marks) (2023)
Ans: The use of several pesticides results in accumulation of pesticides in rivers and ponds. These chemicals are either washed down into the soil or into the water bodies. From the soil, these are absorbed by the plants along with water and minerals, and from the water bodies these are taken up by aquatic plants and animals and enters the food chain. As these chemicals are not degradable, these get accumulated progressively at each trophic level. As human beings occupy the top level in any food chain, the maximum concentration of these chemicals get accumulated in our bodies i.e., biological magnification. Our food grains such as wheat and rice, vegetables and fruits, and even meat, contain varying amounts of pesticide residues cannot always be removed by washing or other means and causes health hazards.
Q2: How is ozone formed in the higher levels of the atmosphere? “Damage to the ozone layer is a cause of concern.” Justify this statement. (3 Marks) (2023)
Ans: Ozone (O3) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. It is formed in the stratosphere layer of atmosphere when high energy UV rays act on O2 molecule splitting it into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with molecular oxygen (O2) to form ozone (O3).
Q3: “Although gardens are created by man but they are considered to be an ecosystem.” Justify this statement. (2 Marks) (2023)
Ans: In a garden, various plants like grasses, trees, flower bearing plants such as jasmine, sunflower, rose, and animals like insects, frogs and birds are found. All these living organisms interact with each other and their growth, reproduction and other activities are affected by the abiotic components such as light, water, wind, soil, minerals, etc. of ecosystem. Thus, a garden is considered to be an ecosystem.
Q4: What is the difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances? List two methods of safe disposal of biodegradable domestic waste. (2 Marks) (2023)
Ans: Differences between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances are as follows :
Domestic waste can be safely disposed off by composting. In composting, biodegradable domestic wastes, such as left-over food, fruit, vegetable peels, etc., can be buried in pit, dug into ground. They are converted into compost and used as manure.
In landfill a huge pit is made in an open low lying area and wastes are dumped into the pits. Once the pits are full, they are covered with soil and left for decomposition.
Q5: How do harmful chemicals get accumulated progressively at each trophic level in a food chain? (3 Marks) (CBSE 2023)
Ans: The process by which harmful substances enter the food chain and becomes concentrated at each trophic level is known as biomagnification.
Example: Biomagnification of DDT in an Aquatic Food Chain
Biomagnification of DDT in an Aquatic Food Chain
Q6: (A) Why does a kitchen garden called an artificial ecosystem while a forest is considered to be a natural ecosystem?
(B) While designing an artificial ecosystem at home, write any two things to be kept in mind to convert it into a selfsustaining system. Give reason to justify your answer. (3 Marks) (CBSE 2023)
Ans: (A) Kitchen gardens are referred to as artificial ecosystems because they are man-made and contain adjusted abiotic and biotic components. It is an ecosystem where plants are produced, including fruits and vegetables, whereas a forest is a place where various creatures live in harmony and rely on one another for food and other necessities. As a result, a forest creates an ecosystem that can support itself.
(B) Two things to keep in mind while designing an artificial ecosystem:
(1) Balance between biotic and abiotic factors.
(2) Recycling of nutrients and wastes.
Reason: Abiotic factors include elements like temperature, light, water, and nutrients, whereas biotic factors are things like plants, animals, fungus, and microorganisms. Due of their interdependence, any changes to one of these components can have an impact on the ecosystem as a whole. To support the development and survival of all organisms within the ecosystem, it is crucial to maintain a balance between various components in the ecosystem. Recycling is essential for maintaining the health and sustainability of the ecosystem.
Q7: (A) Construct a food chain of four trophic levels comprising the following:
Hawk, snake, plants, rat
(B) 20,000 J of energy was transferred by the producers to the organism of second trophic level. Calculate the amount of energy that will be transferred by organisms of the third trophic level to the organisms of the fourth trophic level. (3 Marks) (2023)
Ans: (A) The flow of nutrients and energy from one organism to another at different trophic levels forms a food chain.
Plants → Rat → Snake → Hawk
(B) Only 10% of energy will be transferred to the next trophic level, according to the 10% law of energy transfer, and 90% will be wasted as heat and incomplete digestion. According to this law,
(1) Energy is transferred from producers to the second trophic level = 20,000 J.
(2) Energy moved from the second to the third trophic level: 10% of 20,000 J = 2,000 J.
(3) Energy moved from the third to the fourth trophic level is equal to: 10% of 2,000 J = 200 J
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q1: (i) Why are crop fields considered as artificial ecosystems?
(ii) Write a common food chain of four steps operating in a terrestrial ecosystem. (2022 C)
Ans:
(i) Crop fields are the artificial ecosystems because in crop fields, both biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components are manipulated by human beings. Humans can change edaphic factors by adding fertilisers, water, etc. Biotic components may be changed using biocides or adding useful organisms like earthworms etc.
(ii) A food chain consists of various organism at various trophic levels. In terrestrial ecosystem, a common food chain is
Grass Grasshopper→ Frog→ Snake
Q2: (i) List two human-made ecosystems.
(ii) “We do not clean a pond in the same manner as we do in an aquarium.” Give reason to justify this statement. (Term II, 2021-22)
Ans:
(i) The two human made ecosystems are aquarium and garden.
(ii) We do not clean pond as we do in an aquarium because the waste generated in a pond is acted upon by the decomposers which convert them into simple soluble substances, whereas, in aquarium, the waste gets mixed with water and left untreated due to absence of decomposers.
Q3: In the following food chain, only 2J of energy was available to the peacocks. How much energy would have been present in Grass? Justify your answer. Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake Peacock (Term II, 2021-22)
Ans: In the given food chain, 20,000 J of energy must have been present in grass. This is because, as per the 10% law of energy transfer, only 10% of energy is transferred to the next trophic level.
Q4: What are human-made ecosystems? Give an example. Can a human-made ecosystem become a self-sustaining ecosystem? Give reason to justify your answer. (2022)
Ans: Artificial ecosystems area unit human-made structures wherever organic phenomena and abiotic elements area unit created to act with one another for survival. it’s not self-sufficient and might decrease while not human facilitated. samples of artificial ecosystems embrace aquariums, agriculture fields, zoos, etc.
- A system, that is formed and maintained by mortals, is named synthetic | a synthetic} or man-made system. Some samples of artificial ecosystems area unit aquariums, gardens, agriculture, apiary, poultry, piggery, etc.
- Man-made ecosystems don’t seem to be self-sufficient as a result they rely on naturally created ecosystems just like the water bodies. just like the crop fields that could be an artificial system that depends on water bodies like rivers, and groundwater for water and life. Same approach gardens conjointly rely on nature for their property.
- All organisms like plants, animals, microorganisms, and mortals further because the physical surroundings act with one another and maintain a balance in nature. All interacting organisms in a locality in conjunction with the non-living constitute the setting kind associate degree system.
- All the organic phenomenon elements comprising living organisms and abiotic elements comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, soil, etc create an associate degree system.
- An artificial system could be a variety of systems created by man by artificial means and not present sort of a forest, ponds, lakes, etc. samples of artificial ecosystems area unit crop fields and gardens.
- Man-made ecosystems don’t seem to be self-sufficient as a result they rely on naturally created ecosystems just like the water bodies. just like the crop fields that could be an artificial system that depends on water bodies like rivers, and groundwater for water and life. Same approach gardens conjointly rely on nature for their property.
Hence, artificial ecosystems don’t seem to be self-sufficient.
Q5: (a) Name the group of organisms which form in the first trophic level of all food chains. Why are they called so?
(b) Why are the human beings most adversely affected by biomagnification?
(c) State one ill-effect of the absence of decomposers from a natural ecosystem. (2022)
Ans: (a) Producers form the first trophic level of all food chains. They are called producers because they are autotrophic organisms which alone are able to manufacture organic food from inorganic raw materials by the process of photosynthesis. They capture sun’s energy and convert it into chemical energy. The chemical energy is used in combining raw materials into organic food. This food is used up by themselves and rest enters the food chains as food for consumers.
(b) Human beings are most adversely affected by biomagnification because they occupy the highest trophic level in any food chain. As in biomagnification, successive concentration of non-biodegradable substances increases in the trophic level of food chains, so, it leads to most toxicity at highest trophic level. Hence, maximum concentration of chemicals get accumulated most in their body.
(c) Absence of decomposers will lead to the accumulation of dead remains and waste products of organisms in our natural ecosystem. The decomposers breakdown complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances, so, that it can go into the soil and can be used up by plants.
Q6: What is ozone? How is it formed in the upper layers of the earth’s atmosphere? How does ozone affect our ecosystem? (2022)
Ans: Ozone (O3) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen. It is formed in the stratosphere layer of atmosphere when high energy U V rays act on O2 molecule splitting it into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with molecular oxygen (O2) to form ozone (O3).
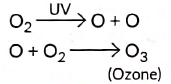
Ozone shields the surface of the earth from U V radiations from the sun. The depletion of ozone layer will lead to global warming and some serious health issues such as damage of skin cells that leads to skin cancer, snow blindness or inflammation of cornea, increased fatality of young animals, mutations and reduced immunity.
Q7: (a) We do not clean ponds or lakes, but an aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly. Why?
(b) Why is ozone layer getting depleted at the higher levels of the atmosphere? Mention one harmful effect caused by its depletion. (2022)
Ans: (a) We do not clean pond as we do in an aquarium because the waste generated in a pond is acted upon by the decomposers which convert them into simple soluble substances, whereas, in aquarium, the waste gets mixed with water and left untreated due to absence of decomposers.
(b) The ozone layer is getting depleted at the higher levels of the atmosphere due to use of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) which are used in refrigerator. Other ozone depleting substances include carbon tetrachloride, hydrofluorocarbons used in fire extinguisher, air i conditioners, etc.
Due to the ozone layer depletion, humans will be directly exposed to the ultraviolet radiations of sun. This will result in serious health issues like skin cancer, sunburns, quick ageing, mutations and weak immune system.
Q8: Kulhads (disposable cups made of day) and disposable paper cups both a re used as an alternative For disposable plastic cups. Which one of these two can be considered as a better alternative to plastic cups and why? (2022)
Ans: Kulhad:
- Kulhad is a cup that is made using clay or soil.
- This is usually used for serving tea/coffee.
- This was brought in use to replace the plastic cup in trains.
- Plastic is a nonbiodegradable harmful substance that does not decompose in nature and affects the ecosystem or environment negatively.
- Kulhads are made of biodegradable soil, therefore, this was used to replace the plastic and protect the environment and health of humans.
Discontinuation of kulhads:
- Since kulhads are made using clay, it is a practice of harming the environment too.
- The clay is fertile soil and kulhads were discontinued to avoid its reduction.
- Making of kulhad on a large scale to serve tea passengers in the train was leading to the loss of this top fertile soil.
Q9: (a) What is meant by garbage? List two classes into which garbage is classified.
(b) What do we actually mean when we say that “enzymes are specific in their action”? (2022)
Ans: (a) Garbage is the waste material (rubbish) especially of domestic refuse. The two classes into which garbage is classified are
(i) Biodegradable
(ii) Non-biodegradable.
(b) Enzymes are specific in their action. For example, enzyme maltase acts on sugar maltose but not on lactose or sucrose. Different enzymes may act on the same substrate but give rise to different products. Similarly an enzyme may act on different substrates producing different end products.
| Also read: Garbage, Waste Management & Depletion of the Ozone Layer |
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q1: What are consumers? Name the four categories under which the consumers are further classified. (2021 C)
Ans: Consumers are the organisms which are unable to synthesise their own food. Therefore, they utilise materials and energy stored by the producers or eat other organisms. They are known as the heterotrophs. The consumers are of following categories:
(i) Primary or first-order consumers: These include the animals which eat plants or plant products. They are called herbivores or primary (first order) consumers. E.g., Cattle, deer, goat, rabbit, hare, rats, mice, grasshoppers etc
(ii) Secondary or second order consumers: These include the animals which depend on primary consumers for their food. They are called primary carnivores or secondary (second order) consumers. Secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. E.g., Cats, dogs, foxes, small fish, etc.
(iii) Tertiary or third order consumers: These are large carnivores (or top carnivores) which feed on primary and secondary consumers. These are termed as secondary carnivores or tertiary (third order) consumers. Common examples include shark and crocodile, wolves, lion, etc. (iv) Quaternary or fourth order consumers: These are even larger carnivores which feed on secondary carnivores (tertiary consumers). E.g., Tigers, lions and eagles/hawks etc.
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q1: How is ozone layer formed? State its importance to all life forms on earth. Why the amount of ozone in the atmosphere dropped sharply in the 1980s? (2020)
Ans: When high energy ultraviolet radiations react with oxygen present in stratosphere (the higher level of atmosphere) it splits into its constituent atoms. Since these atoms produced are very reactive, they react with molecular oxygen (O2) to form ozone (O3).
Ozone shields the surface of the earth from UV radiations from the sun. The depletion of ozone layer will lead to global warming and some serious health issues such as damage of skin cells that leads to skin cancer, snow blindness or inflammation of cornea, increased fatality of young animals, mutations and reduced immunity. In 1980s, the production of CFCs increased which releases active chlorine in the atmosphere. The active chlorine then reacts with ozone molecules present there to convert them to oxygen. This results in thinning of ozone layer. CFCs are used as refrigerants and in fire extinguishers. That is why, amount of ozone in the atmosphere dropped sharply.
Q2: (a) Write two harmful effects of using plastic bags on the environment. Suggest alternatives to the usage of plastic bags. (b) List any two practices that can be followed to dispose off the waste produced in our homes. (2020)
Ans:
(a) Two harmful effects of using plastic bags on the environment:
(i) Plastic bags are non-biodegradable substances which are not acted upon by microbes. So, they cannot be decomposed and therefore persist in the environment for a long time causing harm to the soil fertility and quality.
(ii) Plastic bags choke drains which result in waterlogging, that allows breeding of mosquitoes and hence leads to various diseases. Jute bags and cloth bags are the alternatives to the polyethene bags.
(b) Practices that can be followed to dispose off the waste produced in our homes:
(i) Separation of biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes.
(ii) The biodegradable waste can be converted to manure.
(iii) Non-biodegradable waste should be disposed off at suitable places from where municipal authorities can pick them up and dispose properly and scientifically.
(iv) Use discarded bottles and jars to store food items.
Q3: (A) Construct a terrestrial food chain comprising four trophic levels.
(B) What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
(C) Calculate the amount of energy available to the organisms at the fourth trophic level if the energy available to the organisms at the second trophic level is 2000 J. (CBSE 2020)
Ans: (A) A terrestrial food chain comprising of four trophic levels:
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake
(B) If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level then the transfer of food energy to next level will stop. Organisms of previous trophic level will also increase. For Example: If all herbivores in an ecosystem are killed, there will be no food available for the carnivores of that area. Consequently, they will also die or will shift to other areas. Populations of producers will also increase in absence of herbivores causing an imbalance in the ecosystem.
(C) Consider the same food chain that we have made i.e., (A),
Grass → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake
In this food chain, organism at the second trophic level is grasshopper and the energy available at this trophic level is 2000 J. According to 10% law, 10% of energy will be available to frog (Third trophic level) which is 200 J. The energy available to the snakes will be available as 10% of 200 J. Thus, the energy available to the snake is 20 J.
The 10% law states that during transfer of energy from one trophic level to the next trophic level, only about 10% of energy is available to the higher trophic level.
To summarise:
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q1: (a) A food chain generally has three or four trophic levels. Explain.
(b) What is biological magnification? Explain. (2019 C)
Ans:
(a) The number of trophic levels in a food chain are limited because at each trophic level only 10% of energy is utilised for the maintenance of organism which occur at that trophic level and the remaining large portion is lost as heat. As a result, organisms at each trophic level pass on lesser energy to the next trophic level, than they receive. The longer the food chain, the lesser is the energy available to the final member of food chain.
(b) Biological magnification is characterised by the increase in the non-biodegradable substances (DDT, Hg, etc.) in successive trophic levels of a food chain. The level of such toxic substances will be different in different trophic levels of a food chain because these substances are accumulated more in higher trophic levels.
Q2: Define an ecosystem. Draw a block diagram to show the flow of energy in an ecosystem. (Delhi 2019)
Ans: An ecosystem is defined as a structural and functional unit of the biosphere. It comprises of living organisms and their non-living environment that interact by means of food chains and biogeochemical cycles resulting in energy-flow, biotic diversity and material cycling to form stable self-supporting system. Green plants capture about 1% of the solar energy incident on the earth to carry out the process of photosynthesis.
A part of this trapped energy is used by plants in performing their metabolic activities and some energy is released as heat into the atmosphere. The remaining energy is chemical energy stored in the plants as photosynthetic products. When these green plants are eaten up by herbivores, the chemical energy stored in the plants is transferred to these animals. These animals (herbivores) utilise some of this energy for metabolic activities and some energy is released as heat while the remaining energy is stored in their body. This process of energy transfer is repeated till top carnivores. In an ecosystem, transfer of energy follows 10 per cent law, i.e., only 10 per cent of the energy is transferred to each trophic level from the lower trophic level. The given block diagram shows unidirectional flow of energy at different trophic levels in a freshwater ecosystem:
Q3: (a) How can we help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Suggest any three methods. (Delhi 2019)
(b) Distinguish between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable wastes. (DoE, A1 2011)
Ans: (a) The three methods of waste disposal are:
- Recycling: solid, wastes like paper, plastics, metals can be sent to processing factories where they are remoulded or reprocessed to new materials.
- Production of compost: Biodegradable wastes like fruit and vegetable peels, plant products, left over food, grass clippings, human and animal waste can be converted into compost by burying this waste into grund and can be used as manure.
- Incineration: Burning dawn many household waste, chemical waste and biological waste into ash is known as incineration. A large amount of waste can be easily converted into ash which can be disposed off in landfill.
(b) Differences between:
Previous Year Questions 2017
Q1: (a) What is an ecosystem? List its two main components.
(b) We do not clean ponds or lakes, but an aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly. Explain. (CBSE 2013,2017)
Ans:
(a) A self-sustaining functional unit consisting of living and non-living components is called an ecosystem.
Components: Biotic components like plants and animals. Non-biotic components like soil, wind, light etc.
(b) A pond is a complete, natural and self-sustaining ecosystem whereas an aquarium is an artificial and incomplete ecosystem, without decomposers therefore it needs regular cleaning for proper running.
Q2: You have been selected to talk on “ozone layer and its protection” in the school assembly on ‘Environment Day.’ (Delhi 2017)
(a) Why should ozone layer be protected to save the environment?
(b) List any two ways that you would stress in your talk to bring in awareness amongst your fellow friends that would also help in protection of ozone layer as well as the environment.
Ans: (a) Ozone layer at the higher levels of the atmosphere, acts as a shield to protect earth from the harmful effects of the ultraviolet (UV) radiations; hence, it should be protected.
(b)
- Urging the people to not to buy aerosol products with CFC that are available in the market.
- Conducting poster making competition or street plays presenting the importance of ozone layer on earth.
Q3: Your mother always through that fruit juices are very healthy for everyone. One day she read in the newspaper that some brands of fruit juices in the market have been found to contain certain level of pesticides in them. She got worried as pesticides are injurious to our health. (Foreign 2017)
(а) How would you explain to your mother about fruit juices getting contaminated with pesticides?
(b) It is said that when these harmful pesticides enter our body as well as in the bodies of other organisms they get accumulated and beyond a limit cause harm and damage to our organs. Name the phenomenon and write about it.
Ans:
(a)
- Pesticides are the chemicals used to protect our crops from diseases and pests.
- These chemicals are washed down either into the soil or into water bodies.
- From the soil, they are absorbed by the terrestial plants along with water and minerals.
- From the water bodies, they are absorbed by the aquatic plants.
- When the fruits of these plants are used to prepare fruit juices, they are contaminated with the pesticides.
(b)
- The phenomenon is called biomagnification. It is the phenomenon in which certain harmful chemicals enter the food chain and get accumulated and increase in concentration at successive trophic levels.
- It is because they are not degradable.
- The maximum concentration of these chemicals is found in the top level consumers.
Q4: In the following food chain, 100 J of energy is available to the lion. How much energy was available to the producer? (AI 2017)
Ans: Plants → Deer → Lion
1,000,000 J of energy was available to the producer.
Q5: Why should biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes be discarded in two separate dustbins? (AI 2017(C); Delhi 2013,15)
Ans: The biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes must be discarded in two different dustbins because biodegradable wastes gets decomposed by the microorganisms whereas non-biodegradable wastes can be recycled and reused.
Q6: Name any two man-made ecosystems. (Foreign 2017)
Ans: Agricultural/crop fields, aquaria, gardens,
| Also read: Garbage, Waste Management & Depletion of the Ozone Layer |
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q1: Name two natural ecosystems. (CBSE 2016-17 C)
Ans: Some natural ecosystems are:
- Temperate forest
- Tropical forest
- Grassland
- Ocean
- Lake
 Types of Natural Ecosystem
Types of Natural Ecosystem
Q2: What are decomposers? Write the role of decomposers in the environment. (CBSE 2016-17 C)
Ans: Decomposers are microorganisms that derive their nutrition from dead remains and waste products of organisms.
They play a vital role in our environment by breaking down the complex organic substance into simple inorganic substance which is made available for plants and other organisms. Hence they act as scavengers and not only keep the environment clean but also replenish the minerals.
Q3: We often use the word environment. What does it mean? (Foreign 2016)
Ans: It is the sum total of all external conditions and influences that affect the life and development of an organism, i.e. the environment includes all the physical or abiotic and biological or biotic factors.
Q4: Why are green plants called producers? (Delhi 2016)
Ans: Green plants can produce their own food by photosynthesis from inorganic compounds and hence are called producers.
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q1: What is ten per cent law? Explain with an example how energy flows through different trophic levels. (Delhi 2015)
Ans: Energy available at each successive trophic level of food chain is ten per cent of that at the previous level.
This is called ten per cent law. Thus, 90 per cent energy is lost to the surroundings at each trophic level. However, plants absorb only one per cent of radiant energy of the Sun during photosynthesis. This is explained as under :
Q2: What is ozone? How and where is it formed in the atmosphere? Explain how does it affect ecosystem. (Foreign 2015)
Ans: Ozone is an isotope of oxygen, i.e. it is a molecule formed by 3 atoms of oxygen.
Ozone exists in the ozone layer of stratosphere. At higher level o f atmosphere, O2 molecule breaks down to 2 oxygen atom. The oxygen atom then combines with the oxygen molecule to form ozone.
Ozone layer in the atmosphere prevents UV rays from reaching earth. Exposure to excess UV rays causes skin cancer, cataract and damages eye and immune system. It also decreases crop yield and reduces population of phytoplankton, zooplankton and certain fish larvae which are an important constituent of aquatic food chain. It also disturbs rainfall, causing ecological disturbance and reduces global food production. Thus, it affect the ecosystem.
Q3: “Energy flow in food chains is always unidirectional.” Justify this statement. Explain how the pesticides enter a food chain and subsequently get into our body. (Foreign 2015)
Ans: The energy flow through different steps in the food chain is unidirectional. The energy captured by autotrophs does not revert back to the solar input and it passes to the herbivores, i.e. it moves progressively through various trophic levels. Thus energy flow from sun through producers to omnivores is in single direction only.
Pesticides are sprayed to kill pests on food plants. The food plants are eaten by herbivores and alongwith the food, pesticides are also eaten by the herbivores. Herbivores are eaten by carnivores and alongwith the herbivore animal, pesticide also enters the body of the carnivore. Man eat both plants and animals and pesticide alongwith food enters the body of human. Concentration of pesticides increases as we move upward in the food chain and the process is called bio-magnification.
Q4: What is an ecosystem? List its two main components. We do not clean natural ponds or lakes but an aquarium needs to be cleaned regularly. Why is it so? Explain. (AI 2015)
Ans: Ecosystem: It is the structural and functional unit of biosphere, comprising of all the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment. Thus, an ecosystem is a self-sustaining system where energy and matter are exchanged between living and non-living components.
Main components of ecosystem:
(i) Biotic Component: It means the living organisms of the environment-plants, animals, human beings and microorganisms like bacteria and fungi, which are distinguished on the basis of their nutritional relationship.
(ii) Abiotic Component: It means the non-living part of the environment-air, water, soil and minerals. The climatic or physical factors such as sunlight, temperature, rainfall, humidity, pressure and wind are a part of the abiotic environment.
An aquarium is an artificial and incomplete ecosystem compared to ponds or lakes which are natural, self-sustaining and complete ecosystems where there is a perfect recycling of materials. An aquarium therefore needs regular cleaning.
Q5: Write the full name of the group of compounds mainly responsible for the depletion of ozone layer. (Foreign 2015)
Ans: CFC → Chloroflurocarbon
Q6: Which of the following are always at the second trophic level of the food chains?
Carnivores, Autotrophs, Herbivores [AI 2015]
Ans: Herbivores are always at the 2nd trophic level.
Q7: The following organisms form a food chain. Which of these will have the highest concentration of nonbiodegradable chemicals? Name the phenomenon associated with it. Insects, Hawk, Grass, Snake, Frog. (Foreign 2015)
Ans: Hawk will have highest concentration of non-biodegradable chemicals. The phenomenon is called biomagnification.
Q8: The first trophic level in a food chain is always a green plant. Why? (AI 2015)
Ans: Only green plants can make their own food from sunlight. Green plants, therefore, always occupy the 1st trophic level in a food chain.
Q9: What will be the amount of energy available to the organism of the 2nd trophic level of a food chain, if the energy available at the first trophic level is 10,000 joules? (AI 2015)
Ans: 100 Joules of energy will be available to the organism of the 2nd trophic level.
Q10: (a) What is biodiversity? What will happen if biodiversity of an area is not preserved? Mention one effect of it. (AI 2015)
(b) With the help of an example explain that a garden is an ecosystem.
(c) Why only 10% energy is transferred to the next trophic level?
Ans: (a) Biodiversity is the existence of a wide variety of species of plants, animals and microorganisms in a natural habitat within a particular environment or existence of genetic variation within a species. Biodiversity of an area is the number of species or range of different life forms found there. Forests are ‘biodiversity hotspots’. Every living being is dependent on another living being. It is a chain. If biodiversity is not maintained, the links of the chain go missing. If one organism goes missing, this will affect all the living beings who are dependent on it.
(b) A garden comprises of different kind of flora and fauna such as grasses, flowering and nonflowering plants, trees, frogs, insects, birds, etc. All these living organisms depend and interact with each other and their growth, reproduction and other vital biological activities depend upon the abiotic component comprising of physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals. Therefore, we can say that a garden is an ecosystem.
(c) Only 10% energy is transferred to the next trophic level because other 90 per cent is used for things like respiration, digestion, running away from predators.
Q11: Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances with the help of one example each. List two changes in habits that people must adopt to dispose non-biodegradable waste, for saving the environment. (CBSE 2015)
Ans: Biodegradable substances:
These can be broken down into simpler substances by nature/ decomposers/bacteria/saprophytes/ saprobionts.
Example: Human Excreta/Vegetable peels, etc.
Non-biodegradable substances:
These can’t be broken down into simpler substances by nature/decomposers.
Example: Plastic/glass (or any other) (Any one)
Habits:
(1) Use of separate dustbins for iodegradable and non-biodegradable waste.
(2) Recycling of waste.
(3) Use of cotton/jute bags for carrying vegetables etc
 Hence, B depends on:
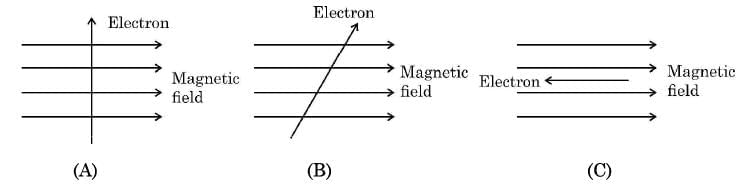
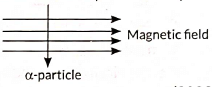
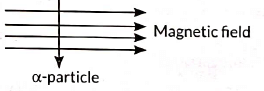
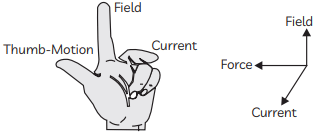
Hence, B depends on: (For a positive charge it would be into the page.)
(For a positive charge it would be into the page.)


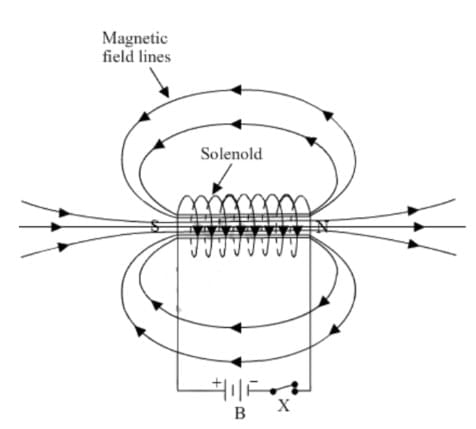


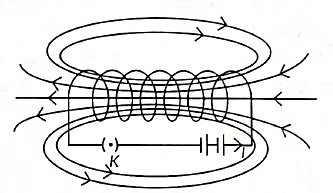
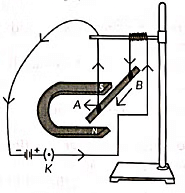
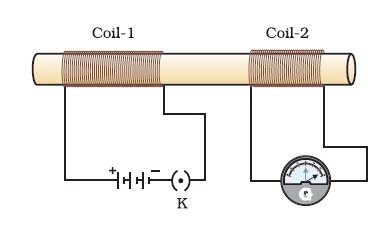
 (b) Permanent magnet / Current carrying solenoid/ Electromagnet is used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material.
(b) Permanent magnet / Current carrying solenoid/ Electromagnet is used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material. 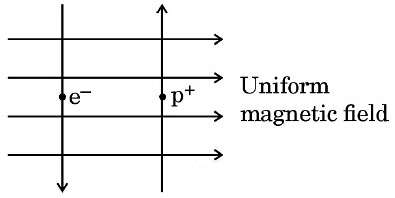



















 Hence, the total equivalent resistance becomes
Hence, the total equivalent resistance becomes












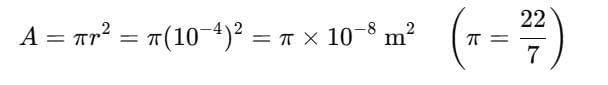
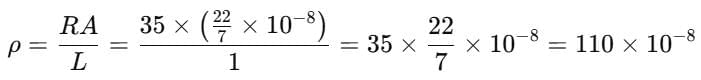
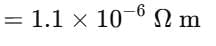



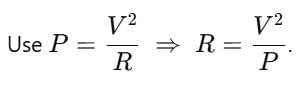











 = 0.04 Ω.
= 0.04 Ω. We can rearrange formula to solve for V:
We can rearrange formula to solve for V: Substitute the values:
Substitute the values: ⇒ The potential difference across the 4 Ω resistor is 20 volts.
⇒ The potential difference across the 4 Ω resistor is 20 volts. (I) Draw a circuit diagram showing the above two resistors X and Y joined in parallel with the same battery and same ammeter and voltmeter. (1 Mark)
(I) Draw a circuit diagram showing the above two resistors X and Y joined in parallel with the same battery and same ammeter and voltmeter. (1 Mark)

























 where:
where: (a) R1 = R2 = R3
(a) R1 = R2 = R3

 = Ω-m
= Ω-m




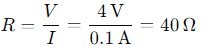








 So the current flowing in the circuit increases.
So the current flowing in the circuit increases.














 Therefore, the minimum resistance that can be made using five resistors, each of 1/5Ω, is 1/25Ω.
Therefore, the minimum resistance that can be made using five resistors, each of 1/5Ω, is 1/25Ω. Glasses Type: Convergent (convex lens)
Glasses Type: Convergent (convex lens)
 (in metres).
(in metres). Compute step by step: f = 1/- 0.5 = -2.0 meters = -200 cm.
Compute step by step: f = 1/- 0.5 = -2.0 meters = -200 cm. N = Near point of a hypermetropic eye
N = Near point of a hypermetropic eye



 ⇒ f = -x
⇒ f = -x




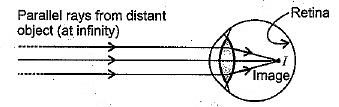
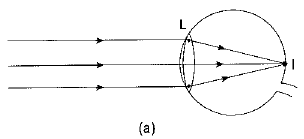
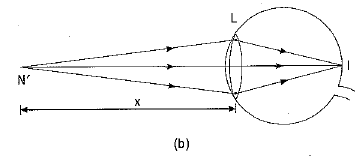
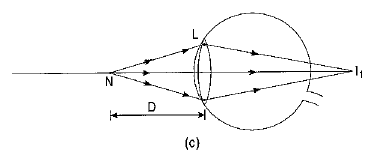
 An important point to be noted here is that a rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the Sun.
An important point to be noted here is that a rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the Sun.

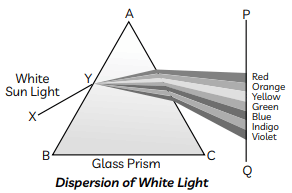




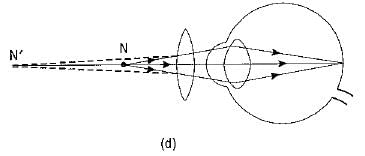
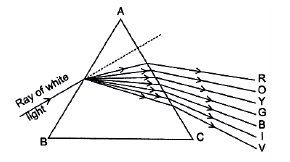
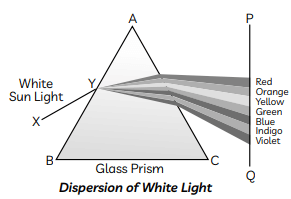
 Cause of Dispersion: When a beam of white light enters a glass prism (or any other dispersive medium), the light ray bends towards the normal one entering into the glass. However, different colours of light bend through different angles concerning the incident ray The red light bends the least while the violet light bends the most. So, rays of different colours emerge along different paths and, thus, become distinct. Hence, dispersion is caused and a spectrum is formed.
Cause of Dispersion: When a beam of white light enters a glass prism (or any other dispersive medium), the light ray bends towards the normal one entering into the glass. However, different colours of light bend through different angles concerning the incident ray The red light bends the least while the violet light bends the most. So, rays of different colours emerge along different paths and, thus, become distinct. Hence, dispersion is caused and a spectrum is formed.

 (c) A beam of white light entering the prism ABC undergoes refraction and is dispersed into its constituent seven colours.
(c) A beam of white light entering the prism ABC undergoes refraction and is dispersed into its constituent seven colours. Whenever refraction of light takes place through a prism, the emergent ray bends towards the base of the prism. The angle between the directions of the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation D.
Whenever refraction of light takes place through a prism, the emergent ray bends towards the base of the prism. The angle between the directions of the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation D.

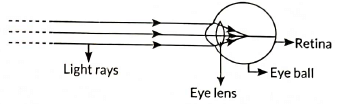
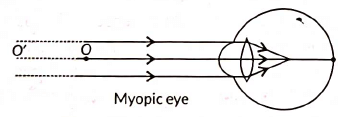
 The fluctuation in the positions of the stars occurs continuously due to the changing amount of light entering the eye. The stars sometimes appear brighter and at some other times, they appear fainter. This causes the twinkling of stars.
The fluctuation in the positions of the stars occurs continuously due to the changing amount of light entering the eye. The stars sometimes appear brighter and at some other times, they appear fainter. This causes the twinkling of stars.








 for a given pair of media and light colour. This constant is the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first (Snell’s law).
for a given pair of media and light colour. This constant is the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first (Snell’s law).

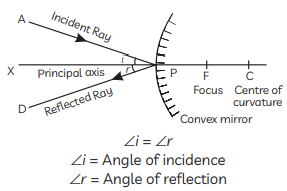
 For a concave mirror take u = -10 cm (object to the left) and f = -15 cm. Substitute:
For a concave mirror take u = -10 cm (object to the left) and f = -15 cm. Substitute: so, v = +30 cm.
so, v = +30 cm.
 Take u = -30 cm (object to the left) and v = -60 cm (real image in front of mirror, same side as object).
Take u = -30 cm (object to the left) and v = -60 cm (real image in front of mirror, same side as object).
 Step 2:
Step 2:  and
and Image distance v =−24 cm indicates image is on the same side as object (virtual image).
Image distance v =−24 cm indicates image is on the same side as object (virtual image).



 (Sign ‘−’ means the object is placed on the incoming-light side; distance = 40 cm.)
(Sign ‘−’ means the object is placed on the incoming-light side; distance = 40 cm.)
 Mirror formula:
Mirror formula:






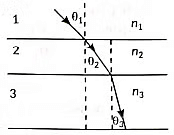
 This means that the speed of light in medium B is less than that in A and C:
This means that the speed of light in medium B is less than that in A and C:




 v = -36 cm
v = -36 cm



 (2) is directed towards its principal focus
(2) is directed towards its principal focus (ii) Given u = –16 cm, f = + 24 cm, h = 4 cm
(ii) Given u = –16 cm, f = + 24 cm, h = 4 cm


 The image is at v=+10cm, virtual and behind the mirror.
The image is at v=+10cm, virtual and behind the mirror. The positive focal length indicates a convex mirror, consistent with the positive magnification.
The positive focal length indicates a convex mirror, consistent with the positive magnification.
 Mirror Formula:
Mirror Formula: 
 The new object distance is 40 cm from the mirror.
The new object distance is 40 cm from the mirror. Magnification:
Magnification: The magnification is +1/3, as required.
The magnification is +1/3, as required.






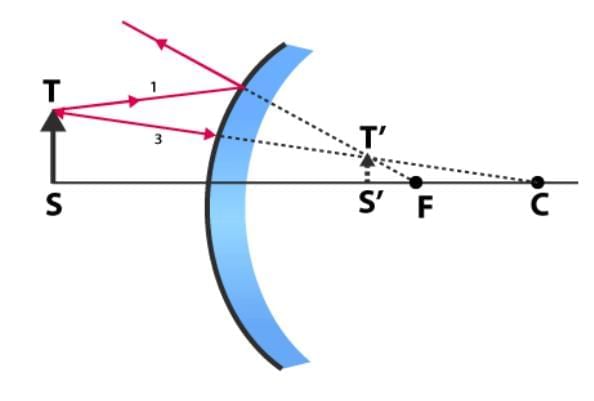
 (B) The image of object obtained in the convex mirror is erect and diminished. This is because a convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image of an object.
(B) The image of object obtained in the convex mirror is erect and diminished. This is because a convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image of an object. 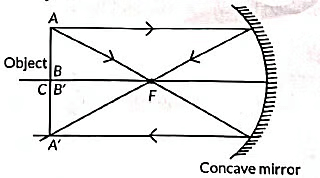
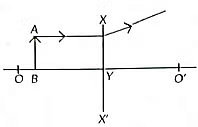

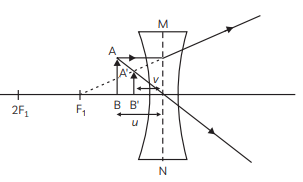
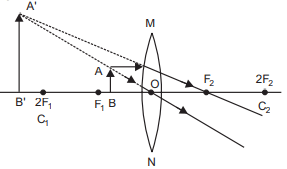
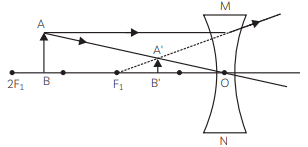
 The image formed is real, inverted and of the same size.
The image formed is real, inverted and of the same size.



 So, the object is placed at u=−25.
So, the object is placed at u=−25. The positive focal length indicates the lens is convex with a focal length of 12.5 cm.
The positive focal length indicates the lens is convex with a focal length of 12.5 cm. The negative sign indicates the image is formed on the same side as the object.Negative v′ means a virtual image on the object side.Object position: u=−25 cm (25 cm in front of lens).Focal length: f=+12.5 cm, convex lens.New image position: v′=−50 cm (50 cm on same side as object).
The negative sign indicates the image is formed on the same side as the object.Negative v′ means a virtual image on the object side.Object position: u=−25 cm (25 cm in front of lens).Focal length: f=+12.5 cm, convex lens.New image position: v′=−50 cm (50 cm on same side as object).

 (c) The four characteristics of the image formed by the convex mirror are virtual, erect, diminished and laterally inverted.
(c) The four characteristics of the image formed by the convex mirror are virtual, erect, diminished and laterally inverted.
















 Hence, when RRyy (round, green) is crossed with rrYY (wrinkled, yellow), all F₁ offspring have the genotype RrYy, expressing the dominant traits — round and yellow seeds.
Hence, when RRyy (round, green) is crossed with rrYY (wrinkled, yellow), all F₁ offspring have the genotype RrYy, expressing the dominant traits — round and yellow seeds.
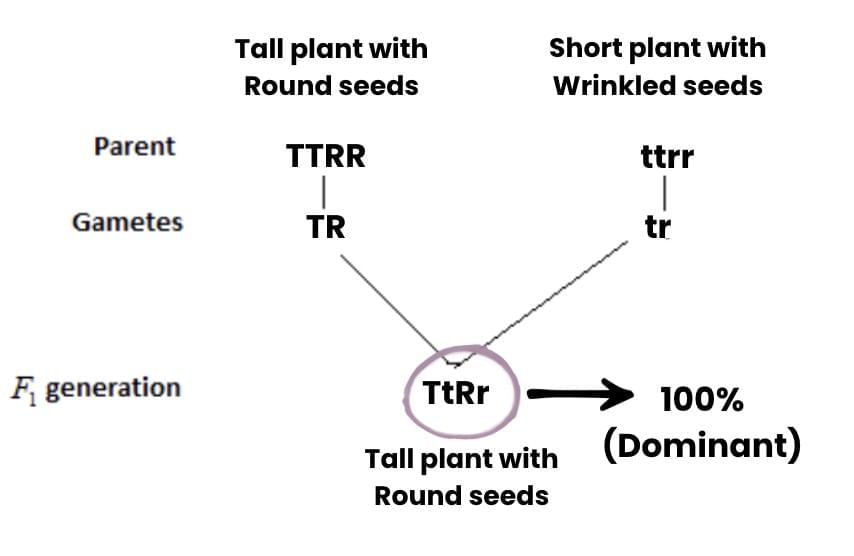
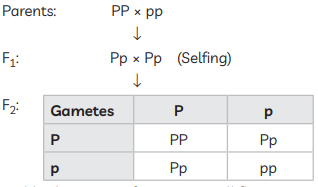
 When TT is crossed with tt, all offspring have the genotype Tt, which expresses the dominant tall trait.
When TT is crossed with tt, all offspring have the genotype Tt, which expresses the dominant tall trait. 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt
1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt
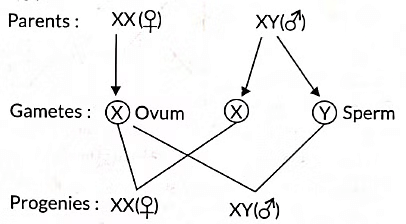
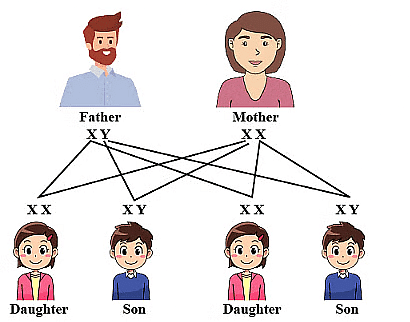
 During fertilisation, the male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote, restoring the diploid number of chromosomes. This ensures the stability of DNA content and the chromosome number in each new generation.
During fertilisation, the male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote, restoring the diploid number of chromosomes. This ensures the stability of DNA content and the chromosome number in each new generation.



 (b) On self-pollinating the F₁ plants (RrYy × RrYy), the F₂ generation shows four possible trait combinations of seeds in the ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 —
(b) On self-pollinating the F₁ plants (RrYy × RrYy), the F₂ generation shows four possible trait combinations of seeds in the ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 —



 (iii) (A) Self-pollination / Self-fertilisation / Selfing of F1 plants
(iii) (A) Self-pollination / Self-fertilisation / Selfing of F1 plants
 75% yellow seeds
75% yellow seeds OR
OR





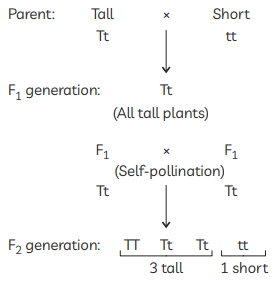
 So, the plants of F1 generation will be all tall plants and after self pollinating the ratio of tall and dwarf plants that Mendel obtained in F2 generation plants is 3 : 1.
So, the plants of F1 generation will be all tall plants and after self pollinating the ratio of tall and dwarf plants that Mendel obtained in F2 generation plants is 3 : 1.

 Skeleton of forelimbs of (a) Human (b) Dog (c) Bird (d) Whale showing homologous features.
Skeleton of forelimbs of (a) Human (b) Dog (c) Bird (d) Whale showing homologous features. (ii) Analogous organs: Such organs which perform similar functions but are structurally different are called analogous organs. For example, wings of a bird and wing of an insect. Presence of such organs show that these organisms have different origin.
(ii) Analogous organs: Such organs which perform similar functions but are structurally different are called analogous organs. For example, wings of a bird and wing of an insect. Presence of such organs show that these organisms have different origin.



 Independent inheritance of two separate traits, shape and colour of seeds(i) Traits may be dominant or recessive:
Independent inheritance of two separate traits, shape and colour of seeds(i) Traits may be dominant or recessive:
 Hence, genotype Tt with a recessive gene is expressed as phenotype of Tall. This shows that only dominant gene is expressed as the trait (T) while ‘t’ is not expressed.
Hence, genotype Tt with a recessive gene is expressed as phenotype of Tall. This shows that only dominant gene is expressed as the trait (T) while ‘t’ is not expressed.
 (a) All flowers in F1 progeny will be blue in colour.
(a) All flowers in F1 progeny will be blue in colour.






 (ii) Yellowish Structures: Pollen grains
(ii) Yellowish Structures: Pollen grains


 (b) Petals, they dry and fall off.
(b) Petals, they dry and fall off. 
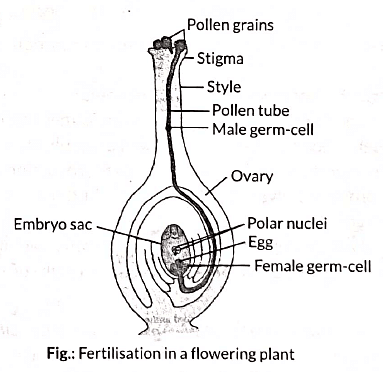
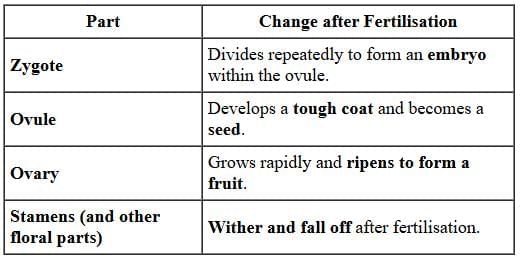
 Fertilisation, in plants, occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grain fuses with the female gamete (or egg) present in ovule. When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, it bursts open and grows a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary. Male gametes move down the pollen tube. The pollen tube enters the ovule in the ovary. The tip of pollen tube bursts and male gametes comes out of pollen tube. In ovary, the male gamete of pollen combines with the female gamete or egg present in ovule to form a fertilised egg. After fertilisation,(i) ovule develops into seed
Fertilisation, in plants, occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grain fuses with the female gamete (or egg) present in ovule. When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, it bursts open and grows a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary. Male gametes move down the pollen tube. The pollen tube enters the ovule in the ovary. The tip of pollen tube bursts and male gametes comes out of pollen tube. In ovary, the male gamete of pollen combines with the female gamete or egg present in ovule to form a fertilised egg. After fertilisation,(i) ovule develops into seed
 (b) Gonorrhoea and syphilis are two bacterial diseases which are transmitted sexually.
(b) Gonorrhoea and syphilis are two bacterial diseases which are transmitted sexually. The species reproducing sexually will have better chances of survival because genetic variation is created during sexual reproduction; in case of an adverse environmental change, atleast some variants will survive and continue the race.
The species reproducing sexually will have better chances of survival because genetic variation is created during sexual reproduction; in case of an adverse environmental change, atleast some variants will survive and continue the race.



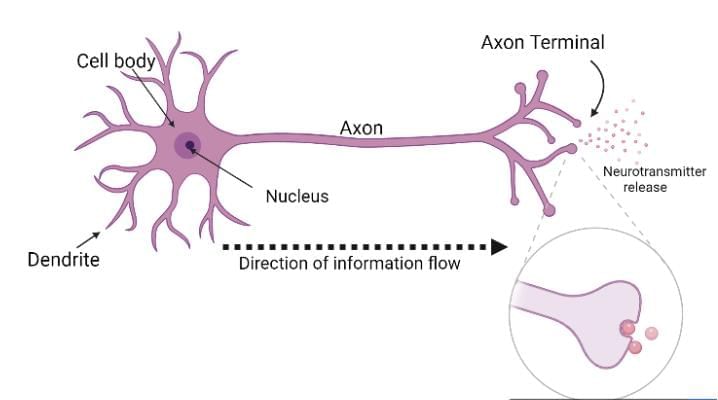


 (ii)A reflex action is a quick, automatic, and involuntary response to a stimulus. It is controlled by the spinal cord and helps protect the body from sudden harmful changes in the environment.
(ii)A reflex action is a quick, automatic, and involuntary response to a stimulus. It is controlled by the spinal cord and helps protect the body from sudden harmful changes in the environment.

 OR
OR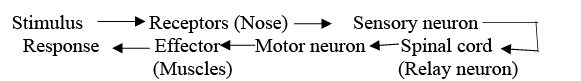


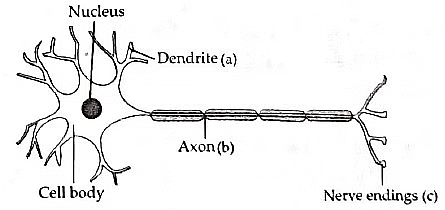

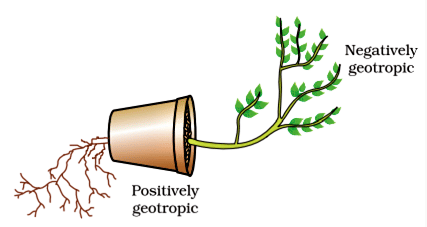



 Sequence of events when we touch a hot object are:
Sequence of events when we touch a hot object are:






 (ii) During inhalation, the ribs move upward and outward, and the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, increasing the space in the chest cavity. This creates low pressure, allowing air to enter the lungs.
(ii) During inhalation, the ribs move upward and outward, and the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, increasing the space in the chest cavity. This creates low pressure, allowing air to enter the lungs.

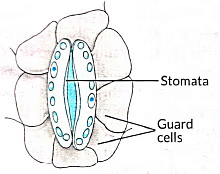
 (a) Evaporation : maintains water contents in leaf cells.
(a) Evaporation : maintains water contents in leaf cells. (ii) The separation of the heart into right and left sides is beneficial because:
(ii) The separation of the heart into right and left sides is beneficial because:
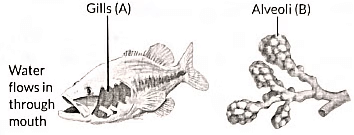









 Excretory System of Human Beings
Excretory System of Human Beings


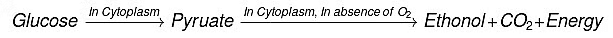









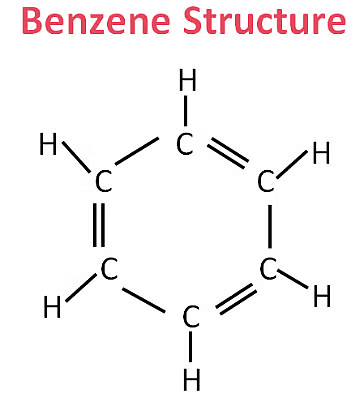



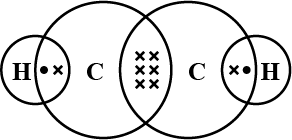
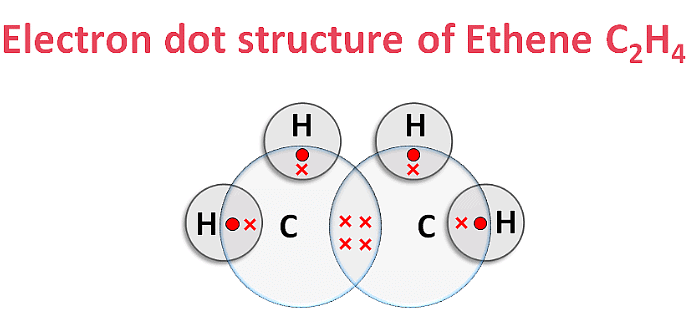
 Electron dot structure of Methane
Electron dot structure of Methane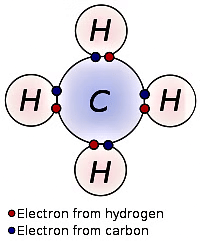
 Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane







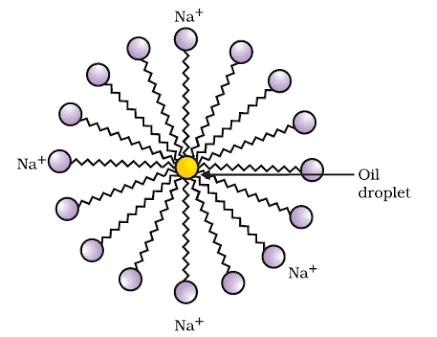
 When a soap is dissolved in water, the molecules associate together as clusters called micelles in which, water molecules being polar in nature, surround the ions and the hydrocarbon part of the molecule attracts grease, oil and dirt.Hard water has Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions when they react with soap to form insoluble compound and soap goes waste.
When a soap is dissolved in water, the molecules associate together as clusters called micelles in which, water molecules being polar in nature, surround the ions and the hydrocarbon part of the molecule attracts grease, oil and dirt.Hard water has Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions when they react with soap to form insoluble compound and soap goes waste.