Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What does the term ‘Second Urbanisation’ refer to?
a) Growth of cities during the British era
b) Rebuilding of Harappan cities
c) Growth of new cities in the 1st millennium BCE
d) Urban development in the Gupta period
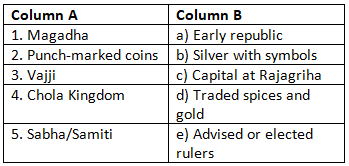
Q2: Which ancient capital was located in the mahajanapada of Magadha?
a) Ujjain
b) Rajagriha
c) Kausambi
d) Pataliputra
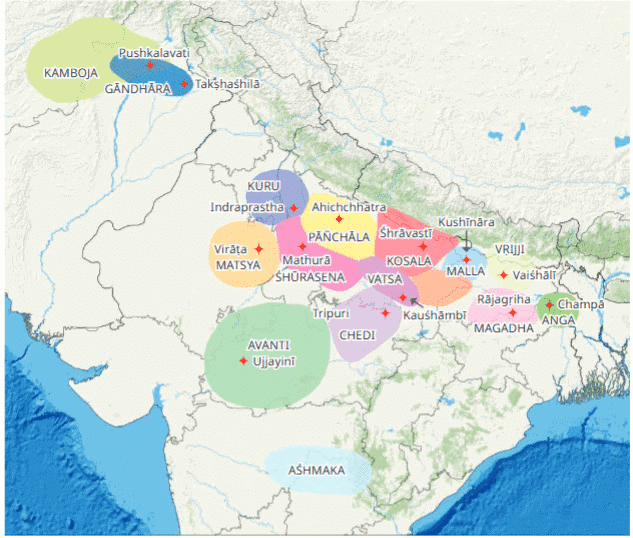
Map of 16 Mahajanpadas
Q3: What was the role of the sabhā or samiti in janapadas?
a) They collected taxes
b) They conducted rituals
c) They advised the raja
d) They built fortifications
Q4: Which of the following was a gana or sangha rather than a monarchy?
a) Magadha
b) Kosala
c) Vajji
d) Avanti
Q5: What helped the mahajanapadas grow in the Ganga plains?
a) Lack of enemies
b) Coastal trade
c) Fertile land and iron tools
d) Influence of Harappan cities
Q6: Which of these was a key innovation in the economic system of the mahajanapadas?
a) Use of bronze coins
b) Stone seals
c) Punch-marked coins
d) Gold jewellery
Q7: Which southern kingdom was known for trade in spices and precious stones?
a) Mauryas
b) Cheras
c) Guptas
d) Kushanas
Q8: What term describes the social group associated with a specific job passed through families?
a) Varna
b) Samiti
c) Jāti
d) Sabha
Q9: Which trade route connected the Ganga plains with south India?
a) Uttarapatha
b) Dakshinapatha
c) Silk Route
d) Spice Route
Q10: Which of the following varnas included traders and farmers?
a) Brahmins
b) Kshatriyas
c) Vaishyas
d) Shudras
Fertile Ganga Plains heped Mahajanpadas to grow
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The term janapada means “where people __________.”
Q2: The __________ was a council of elders that advised the raja.
Q3: Fortified cities often had __________ and narrow gateways for defense.
Q4: The capital of Vatsa mahajanapada was __________.
Q5: __________ coins were early silver coins stamped with symbols.
Q6: In a __________, the raja’s power passed to his son.
Q7: __________ is the term for a job-based group in society.
Q8: The term varna comes from __________ texts.
Q9: The __________ kingdom in south India is mentioned in ancient Tamil texts.
Q10: __________ connected northwest India with the Ganga plains.
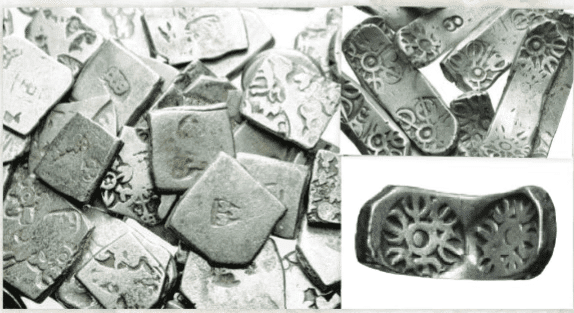
Punch Marked Coins
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What does the word janapada literally mean?
Q2: Name any one mahajanapada with a republican form of government.
Q3: What metal became common for tools and weapons in this period?
Q4: What were early Indian coins called?
Q5: Which ancient capital is now near modern-day Patna?

Samiti
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What were mahajanapadas and why were they important?
Q2: What was the role of sabhā and samiti in governance?
Q3: How did iron tools impact agriculture?
Q4: Describe the social structure based on varnas.
Q5: What was Dakshinapatha and why was it significant?
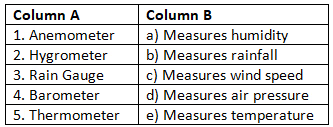
Match the Following
(Match Column A with the correct option in Column B)