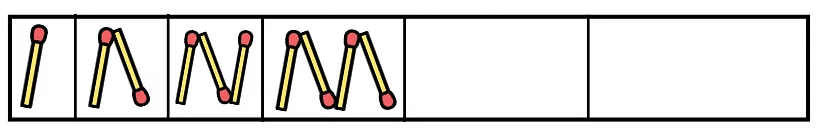Introduction
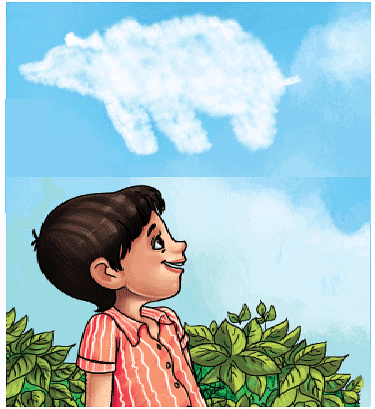
The poem A Show of Clouds is about a kid lying on the ground, looking up at the sky, and imagining different shapes in the clouds. The poet has beautifully described the shapes of the clouds and how they can look like different objects. The poem is a great way to encourage children to use their imagination and creativity.
Detailed Summary
Stanza 1:
As I lie on my back,
Looking up at the sky.
I see a big white bear,
Looking down at me.
Imagine you are lying on the grass, looking up at the sky. The clouds above you start to form different shapes—just like when you see pictures in fluffy cotton candy! In this stanza, the person sees a big white bear in the clouds. It looks like the bear is watching over them, like a kind and gentle giant. This shows how exciting and magical it can be to use our imagination while looking at the sky!
Stanza 2:
As I lie on my back,
Looking up at the sky.
I see a ship sailing,
On a white sea.
Imagine you are lying on the grass, looking up at the big, open sky. The soft, white clouds start to take different shapes. In this stanza, the person sees a cloud shaped like a ship sailing across a sea of white. The sky feels like a huge ocean, and the clouds look like gentle waves. This shows how using our imagination can make the sky feel like a magical place full of adventure!
Stanza 3
As I lie on my back,
Looking up at the sky.
I see an elephant,
Waving its trunk at me.
Imagine you’re lying on the ground, looking up at the sky. The clouds start to look like different shapes. In this poem, the person sees a cloud shaped like an elephant waving its trunk, almost like it’s saying hello!
Stanza 4
As I lie on my back,
Looking up at the sky.
Oh! It’s fun, it’s fun to me,
To see whatever I want to see.
Imagine you’re lying on your back, looking up at the sky. The clouds can turn into anything you imagine—a bear, a ship, or even an elephant! In this poem, the person feels happy and excited because they can see whatever they want in the clouds. It shows how fun it is to use your imagination and make the sky your own picture book!
Try yourself:
What does the person in the poem see when looking up at the sky that resembles an animal waving its trunk?
- A.A bear watching over them.
- B.A ship sailing on a sea of white.
- C.An elephant waving its trunk.
- D.A cloud shaped like a big white bear.
Summary of all the Stanzas:
In this poem, the speaker is lying on their back and gazing at the sky. They imagine shapes in the clouds and describe what they see.
- The speaker is lying on their back and looking at the sky. This means they are lying down and watching the clouds above.
- They see a big white bear in the clouds. This bear seems to be looking back at the speaker.
- Next, the speaker sees a ship that looks like it’s sailing on a sea made of white clouds.
- They also imagine an elephant in the sky, and it looks like the elephant is waving its trunk at them.
- The speaker finds this activity very enjoyable. They can use their imagination to see anything they want in the clouds.
New Words and Meanings
- Gaze: To look at something for a long time, like when you stare at the sky or a beautiful view.
- Imagine: To create pictures or ideas in your mind, even if they are not real.
- Shapes: Different forms or outlines of things, like the shapes of clouds in the sky.
- Sailing: When a boat or ship moves on the water using the wind to push it forward.
- Elephant: A big animal with a long trunk and large ears, often found in some parts of the world.
- Trunk: The long, flexible nose of an elephant.
- Enjoyable: When something is fun or makes you happy.







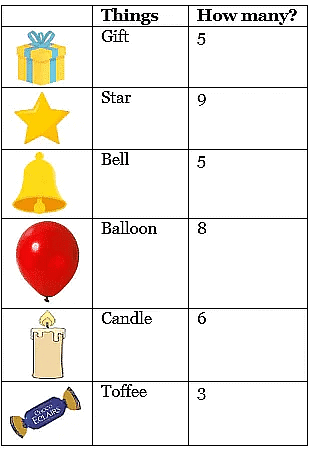







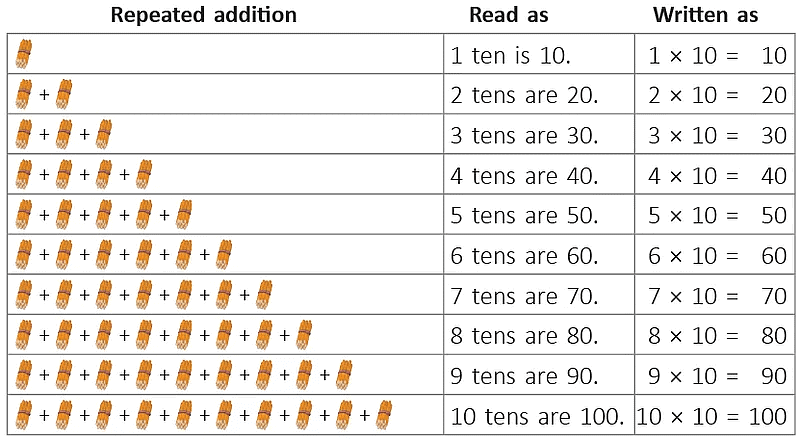
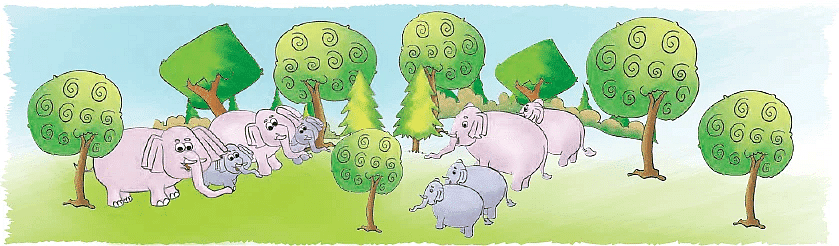 Each family has 4 elephants.We say, there are 4 + 4 = 8 elephants going for a jungle walk.
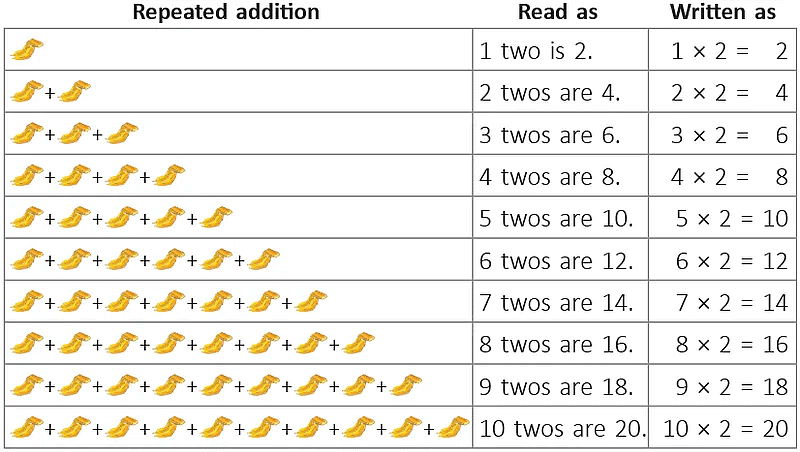
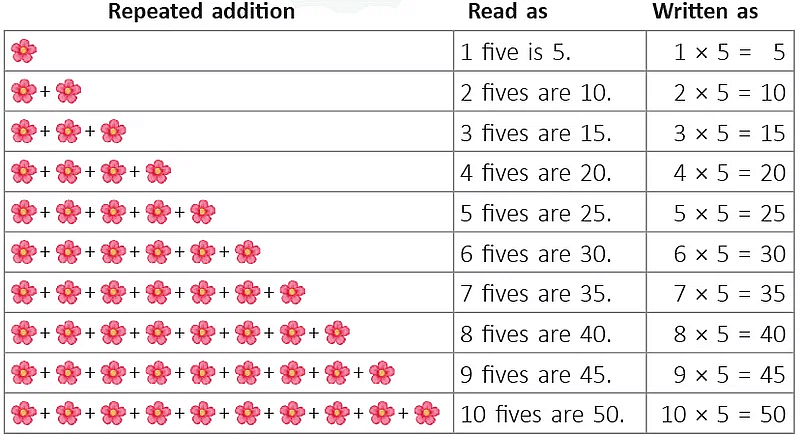
Each family has 4 elephants.We say, there are 4 + 4 = 8 elephants going for a jungle walk.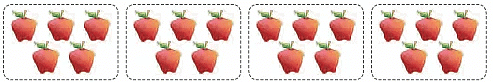 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 20Instead of adding the same number 5 over and over again 4 times, an easier way to get the answer is 4 x 5 = 20.4 x 5 = 20 is read as 4 times 5 is equal to 20.
5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 20Instead of adding the same number 5 over and over again 4 times, an easier way to get the answer is 4 x 5 = 20.4 x 5 = 20 is read as 4 times 5 is equal to 20. 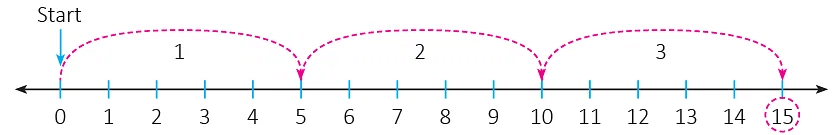 Starting from 0, there are 3 jumps and each jump covers 5 units (steps) on the number line.Or3 times 5 units covered.
Starting from 0, there are 3 jumps and each jump covers 5 units (steps) on the number line.Or3 times 5 units covered.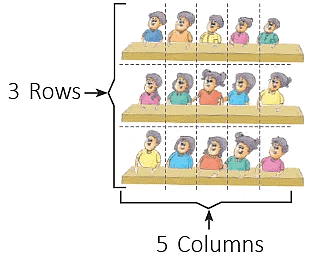 Here, there are 3 equal groups of 5 children.OrThere are 3 x 5 = 15 children in all.
Here, there are 3 equal groups of 5 children.OrThere are 3 x 5 = 15 children in all.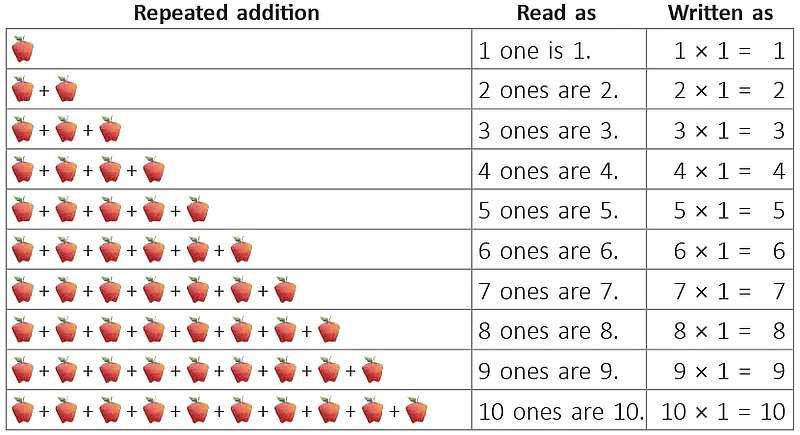
 We wake up in the morning
We wake up in the morning We have lunch in the Afternoon
We have lunch in the Afternoon We play in the Evening
We play in the Evening We sleep at Night
We sleep at Night







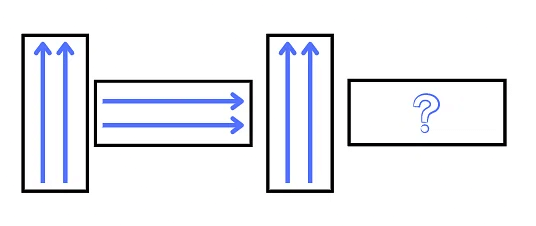

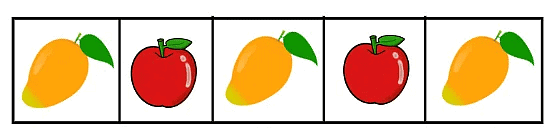
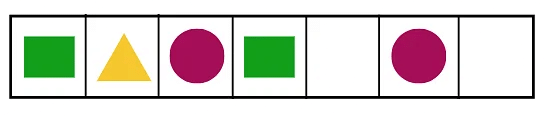 In the first box, we see a rectangle. In the second box, we see a triangle. And in the third box, we see a circle.
In the first box, we see a rectangle. In the second box, we see a triangle. And in the third box, we see a circle. 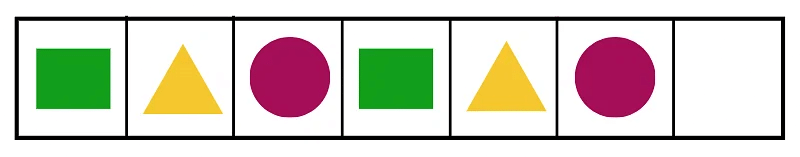
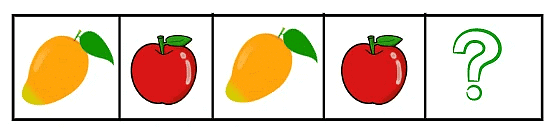
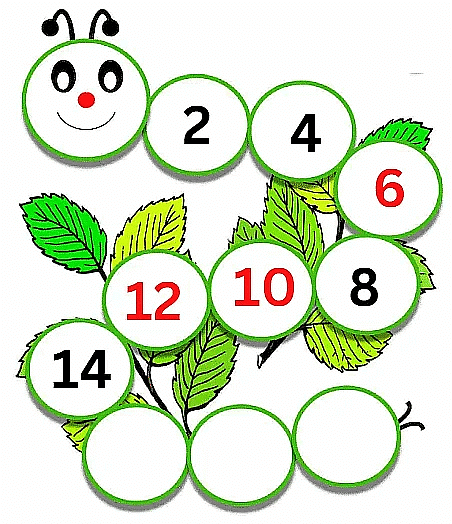
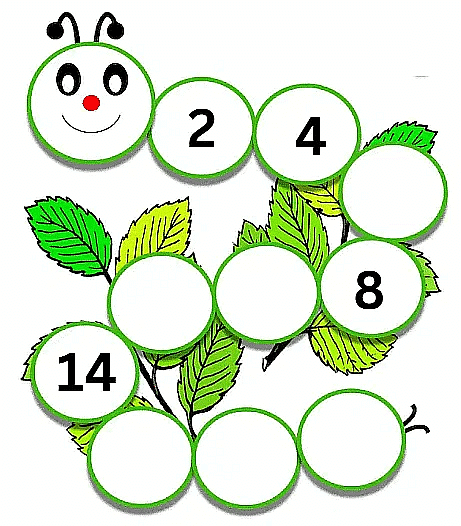 So by looking at the numbers we see that 2 is followed by 4, then there is a missing number which is followed by 8. So what do we get to know about this sequence? We see that 2+2 = 4, 4+2 = 6, 6+2 = 8. So we can see that the missing number is 6. That’s where the missing number went!
So by looking at the numbers we see that 2 is followed by 4, then there is a missing number which is followed by 8. So what do we get to know about this sequence? We see that 2+2 = 4, 4+2 = 6, 6+2 = 8. So we can see that the missing number is 6. That’s where the missing number went!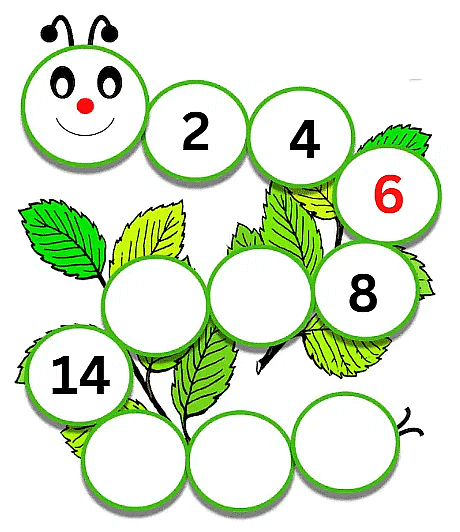
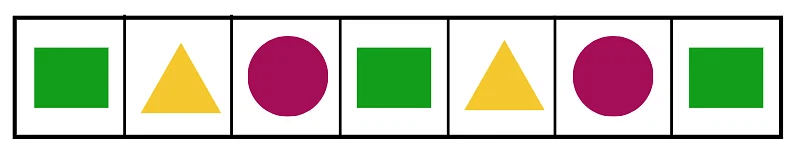
 Traffic Lights
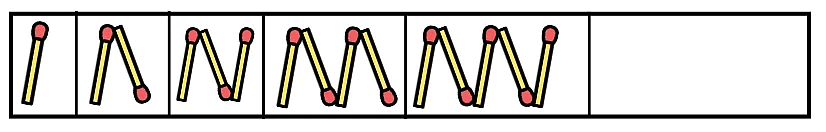
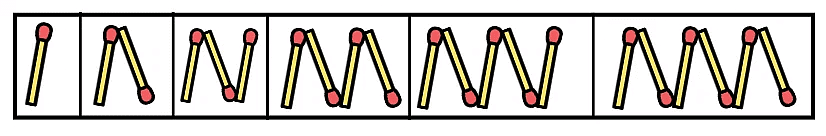
Traffic Lights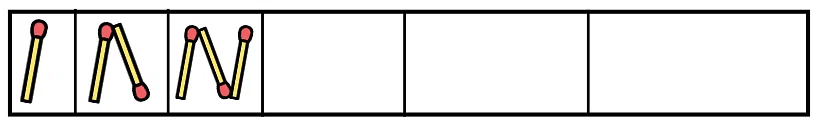 Now, we need to complete the pattern for the next three empty boxes.
Now, we need to complete the pattern for the next three empty boxes.