Q1: What is a partial solar eclipse?
Ans: A partial solar eclipse occurs when the Moon partially blocks the Sun.
Q2: Why is the Moon able to block the Sun during a solar eclipse?
Ans: The Moon is much smaller than the Sun, but it is much closer to the Earth, making it appear to cover the Sun.
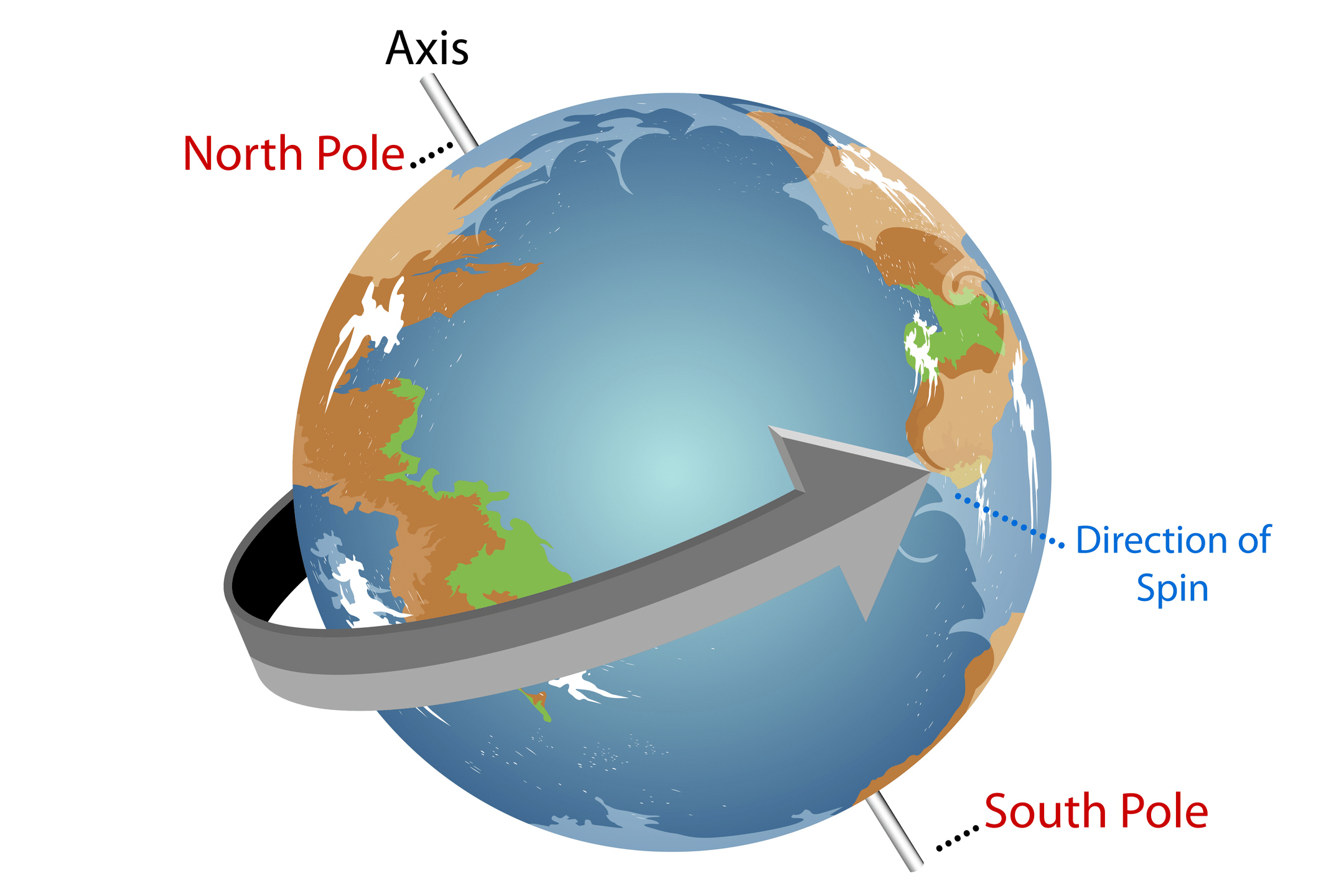
Q3: What is rotation?
Ans: Rotation is the spinning of an object around its own axis.
Q4: What is the Earth’s axis of rotation?
Ans: It is an imaginary line that passes through the North and South poles.
Q5: How long does it take for the Earth to complete one rotation?
Ans: About 24 hours.
Q6: Which direction does the Earth rotate when viewed from the North Pole?
Ans: The Earth rotates in the anti-clockwise direction, from West to East.
Q7: What causes day and night on Earth?
Ans: The Earth’s rotation causes day and night.
Q8: What happens during the rotation of the Earth on its axis?
Ans: Half of the Earth faces the Sun and experiences daytime, while the other half experiences nighttime.
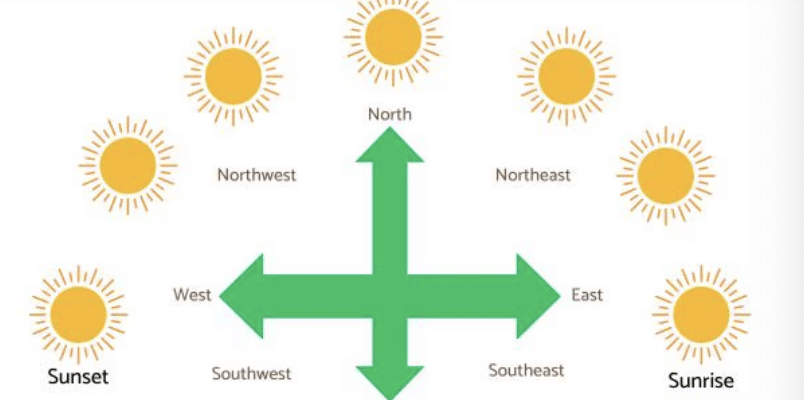
Q9: What direction does the Sun appear to move in the sky?
Ans: The Sun appears to rise in the East and set in the West.
Q10: What causes the stars to appear to move in the sky?
Ans: The Earth’s rotation causes the apparent movement of stars.
Q11: What is revolution?
Ans: Revolution is the movement of the Earth around the Sun along its orbit.
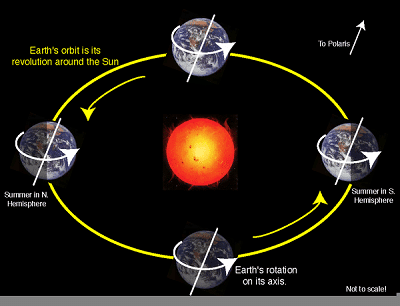
Q12: How long does the Earth take to complete one revolution around the Sun?
Ans: About 365 days and 6 hours.
Q13: Why do the stars in the night sky change over the course of a year?
Ans: The changing position of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun causes different stars to be visible at different times.
Q14: What causes the seasons on Earth?
Ans: The tilt of the Earth’s axis and its orbit around the Sun causes the seasons.
Q15: When does the Northern Hemisphere experience summer?
Ans: In June, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun.
Q16: When does the Northern Hemisphere experience winter?
Ans: In December, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun.
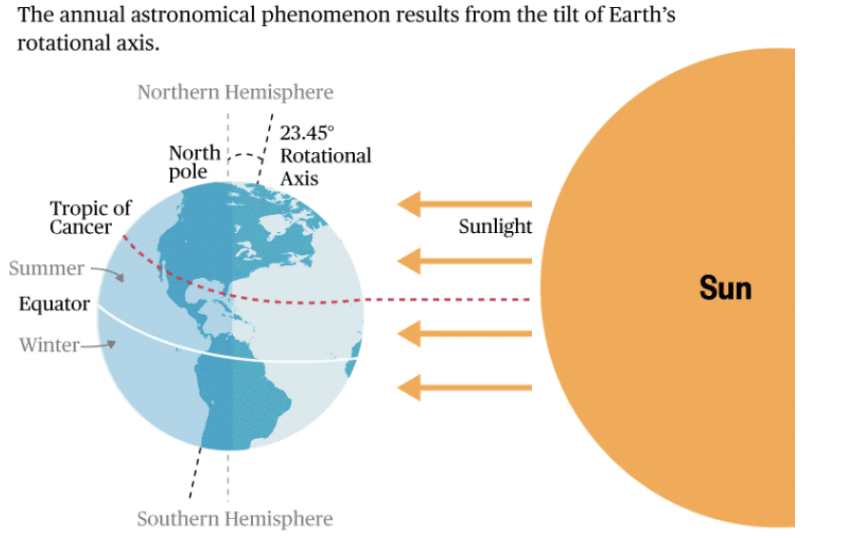
Q17: What is the
Ans: The longest day in the Northern Hemisphere, occurring around 21 June.
Q18: What happens during a solar eclipse?
Ans: The Moon blocks the Sun’s light from reaching the Earth.
Q19: What is a lunar eclipse?
Ans: A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth blocks the Sun’s light from reaching the Moon.
Q20: Why should we not look directly at a solar eclipse?
Ans: Directly viewing a solar eclipse can damage the eyes and cause blindness.