Q1: 250 cm = ? m
(a) 2.5 m
(b) 25 m
(c) 0.25 m
(d) 2500 m
Sol: (a) 2.5 m
1 meter = 100 centimeters
So, 250 ÷ 100 = 2.5 meters
Q2: A rope is 600 cm long. If cut into 10 equal pieces, the length of each piece is:
(a) 60 m
(b) 60 cm
(c) 6 m
(d) 600 m
Sol: (b) 60 cm
Total length = 600 cm
Number of pieces = 10
Each piece = 600 ÷ 10 = 60 cm
Q3: 5 km = ? m
(a) 500
(b) 5000
(c) 50
(d) 50,000
Sol: (b) 5000
1 kilometer = 1000 meters
So, 5 × 1000 = 5000 meters
Q4: A train is 250 m long. What is its length in kilometers?
(a) 0.025 km
(b) 2.5 km
(c) 0.25 km
(d) 25 km
Sol: (c) 0.25 km
1 kilometer = 1000 meters
So, 250 ÷ 1000 = 0.25 kilometers
Q5: A ribbon is 36 m long. If each piece is 4 m long, how many pieces can be cut?
(a) 8
(b) 9
(c) 10
(d) 12
Sol: (b) 9
Total length = 36 meters
Each piece = 4 meters
Number of pieces = 36 ÷ 4 = 9
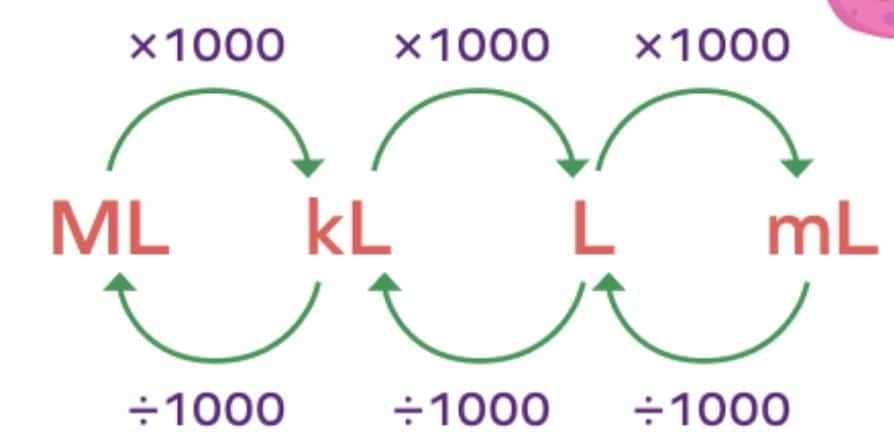
Q6: Convert the following into centimeters.
(i) 66 mm
(ii) 32 dm
(iii) 4 cm 8 mm
(iv) 63 km
(v) 16 m
(vi) 1.5 dm
Sol: We use:
- 1 cm = 10 mm
- 1 dm = 10 cm
- 1 m = 100 cm
- 1 km = 1000 m = 100,000 cm
(i) 66 mm
Since 10 mm = 1 cm
66 mm = 66 ÷ 10 = 6.6 cm
(ii) 32 dm
Since 1 dm = 10 cm
32 dm = 32 × 10 = 320 cm
(iii) 4 cm 8 mm
8 mm = 0.8 cm
So, 4 cm + 0.8 cm = 4.8 cm
(iv) 63 km
1 km = 100,000 cm
63 km = 63 × 100,000 = 6,300,000 cm
(v) 16 m
1 m = 100 cm
16 m = 16 × 100 = 1600 cm
(vi) 1.5 dm
1 dm = 10 cm
1.5 dm = 1.5 × 10 = 15 cm
Q7: Convert the following into kilometers.
(i) 14 m
(ii) 59 hm
(iii) 136 dam
(iv) 207 dam
(v) 5600 cm
(vi) 10000 cm
Sol: We use:
- 1 km = 1000 m
- 1 hm (hectometer) = 100 m
- 1 dam (decameter) = 10 m
- 1 m = 100 cm
(i) 14 m
1 km = 1000 m
14 m = 14 ÷ 1000 = 0.014 km
(ii) 59 hm
1 hm = 100 m
59 hm = 59 × 100 = 5900 m
5900 ÷ 1000 = 5.9 km
(iii) 136 dam
1 dam = 10 m
136 dam = 136 × 10 = 1360 m
1360 ÷ 1000 = 1.36 km
(iv) 207 dam
207 dam = 207 × 10 = 2070 m
2070 ÷ 1000 = 2.07 km
(v) 5600 cm
1 m = 100 cm → 5600 cm = 5600 ÷ 100 = 56 m
Now, 56 ÷ 1000 = 0.056 km
(vi) 10000 cm
10000 ÷ 100 = 100 m
100 ÷ 1000 = 0.1 km
Q8: Compare the following using >, < or = sign:
(i) 702 cm ………. 503 cm
(ii) 2 m ………. 9 m
(iii) 800 cm ………. 80 m
(iv) 702 cm ………. 5 m
(v) 8 km ………. 7000 m
(vi) 625 cm ………. 9 m
(vii) 10 m ………. 4 cm
(viii) 1000 m ………. 1000 km
(ix) 100 cm ………. 100 m
(x) 1 km ………. 1000 m
Sol: (i) 702 cm > 503 cm
So, 702 cm > 503 cm
(ii) 2 m … 9 m
Clearly, 2 m < 9 m
(iii) 800 cm … 80 m
Convert: 800 cm = 8 m.
So, 8 m < 80 m
→ 800 cm < 80 m
(iv) 702 cm … 5 m
Convert: 702 cm = 7 m 2 cm = 7.02 m.
So, 7.02 m > 5 m
→ 702 cm > 5 m
(v) 8 km … 7000 m
Convert: 8 km = 8000 m.
So, 8000 m > 7000 m
→ 8 km > 7000 m
(vi) 625 cm … 9 m
Convert: 625 cm = 6 m 25 cm = 6.25 m.
So, 6.25 m < 9 m
→ 625 cm < 9 m
(vii) 10 m … 4 cm
Convert: 10 m = 1000 cm.
So, 1000 cm > 4 cm
→ 10 m > 4 cm
(viii) 1000 m … 1000 km
Convert: 1000 m = 1 km.
So, 1 km < 1000 km
→ 1000 m < 1000 km
(ix) 100 cm … 100 m
Convert: 100 cm = 1 m.
So, 1 m < 100 m
→ 100 cm < 100 m
(x) 1 km … 1000 m
Convert: 1 km = 1000 m.
So, 1 km = 1000 m
Q9: A road between two villages is 8 km 250 m long. Out of this, workers have repaired 5 km 750 m. How much road is still left to repair?
Sol: Total length of road = 8 km 250 m
Repaired length = 5 km 750 m
First, convert both into metres:
- 8 km 250 m = 8000 + 250 = 8250 m
- 5 km 750 m = 5000 + 750 = 5750 m
Length left to repair = 8250 – 5750 = 2500 m
Now convert back into km and m:
2500 m = 2 km 500 m
2 km 500 m of road is still left to repair.
Q10: A cloth merchant bought a roll of cloth 45 m long. He sold 12 m 40 cm to one customer and 18 m 60 cm to another. How much cloth is left with him?
Sol: Total length of cloth = 45 m
Sold cloth:
- To first customer = 12 m 40 cm = 12.40 m
- To second customer = 18 m 60 cm = 18.60 m
Total cloth sold = 12.40 m + 18.60 m = 31.00 m
Cloth left = 45.00 m – 31.00 m = 14.00 m
14 m cloth is left with the merchant.
Q11: The distance from a school to the railway station is 4 km 300 m. The bus travels this distance in the morning and returns in the afternoon. What is the total distance covered by the bus in a day?
Sol: Distance from school to railway station = 4 km 300 m
Since the bus goes in the morning and comes back in the afternoon, the distance is covered two times.
Convert into metres first:
4 km 300 m = 4000 + 300 = 4300 m
Total distance = 2 × 4300 = 8600 m
Now convert back into km and m:
8600 m = 8 km 600 m
The bus covers 8 km 600 m in a day.
Q12: A ribbon is 96 m long. It is cut into 12 equal pieces. What is the length of each piece?
Sol: Total length of ribbon = 96 m
Number of equal pieces = 12
Length of each piece = 96 ÷ 12 = 8 m
Each piece is 8 m long.
Q13: A man walks 3 km every day. How many kilometers will he walk in 15 days?
Sol: Distance walked in 1 day = 3 km
Number of days = 15
Total distance = 3 × 15 = 45 km
The man will walk 45 km in 15 days.
Q14: A train travels 125 km in 1 hour. How much distance will it cover in 8 hours?
Sol: Distance covered in 1 hour = 125 km
Time = 8 hours
Total distance = 125 × 8 = 1000 km
The train will cover 1000 km in 8 hours.
Q15: A road is 420 m long. It is divided into 7 equal sections. What is the length of each section?
Sol: Total length of road = 420 m
Number of equal sections = 7
Length of each section = 420 ÷ 7 = 60 m
Each section is 60 m long.

 Ans:
Ans:
 Ans:
Ans:


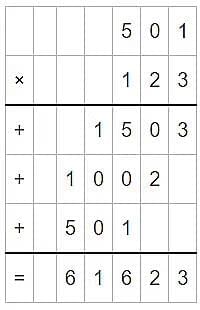 = 501 x 123 = 61623
= 501 x 123 = 61623