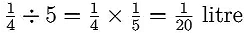Q.1. True/False
(i) Digestion of starch starts in the stomach.
False
(ii) The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva.
True
(iii) The gall bladder temporarily stores bile.
True
(iv) The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for some time.
True
(v) We chew the food with the teeth and break it down mechanically into small pieces.
True
(vi) Large intestine receives digested and absorbed food.
False
Q.2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) The main steps of nutrition in humans are ____, ____, ____, ____ and ____.
ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion.
(ii) The largest gland in the human body is ____.
liver
(iii) The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and ____ juices which act on food.
digestive
(iv) The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger-like outgrowths called ____.
villi
(v) Amoeba digests its food in the food ____.
vacuole
(vi) We chew the food with the ____ and break it down mechanically into small pieces.
teeth
Answer the following Questions
Q.3. Where are fats digested in the body?
Fats are primarily digested in the small intestine.
Q.4. What kills bacteria that enter along with the juices to act?
The acid kills many bacteria that enter along with the juices to act. This process helps to maintain a safe environment for digestion and prevents the growth of harmful bacteria.
Q.5. Where are faeces formed in the human body?
Faeces are formed in the human body in large intestine.
Q.6. Where food is absorbed in our body?
Absorption of food takes place in small intestine.
Q.7. Where faeces are stored?
Faeces are stored in rectum.
Q.8. What does saliva do to food in our mouth?
The saliva breaks down the starch into sugars.
Q.9. What is rumen?
Rumen is a large, sac-like structure found in ruminants, such as cattle and deer.
Q.10. What does animal nutrition include?
Animal nutrition includes nutrient requirement, mode of intake of food and its utilisation in the body.
Q.11. What are the different modes of feeding in animals?
Different modes of feeding in animals include:
- Scraping – removing food from surfaces.
- Chewing – breaking down food into smaller pieces.
- Sucking – drawing in liquids, like nectar.
- Capturing and swallowing – catching prey whole.
- Filtering – sifting tiny food particles from water.
Q.12. What are ruminant animals?
The grazing animals like cows, buffaloes and deer are known as ruminants.
Q.13. What do pancreatic juices digest?
The pancreatic juice plays a crucial role in digestion by acting on:
- Carbohydrates – breaking them down into simpler sugars.
- Fats – converting them into fatty acids and glycerol.
- Proteins – transforming them into amino acids.
Overall, pancreatic juice helps in simplifying these food components for better absorption in the body.
Q.14. What do you mean by rumination?
Rumination is a process that occurs in certain animals, known as ruminants. It involves the following steps:
- Animals quickly swallow their food, which is often grass.
- The food is stored in a part of the stomach called the rumen.
- Later, the partially digested food, known as cud, returns to the mouth.
- The animal then chews the cud thoroughly before swallowing it again.
This process helps in the digestion of tough plant materials, particularly cellulose, which many animals, including humans, cannot digest effectively
Q.15. What are the main steps involved in the process of respiration in animals?
The main steps of respiration in animals include inhalation, where oxygen is taken into the body; gas exchange in the lungs or tissues, where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide; and exhalation, where carbon dioxide is expelled from the body. This process is crucial for supplying oxygen to cells and removing waste gases.













 View Answer
View Answer