Previous Year Questions 2025
Q1: An old person is suffering from an eye defect caused by weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens. If the defect of vision is ‘a’ which can be corrected by lens ‘b’, then ‘a’ and ‘b’ respectively are : (1 Mark)
(a) hypermetropia and convex lens
(b) presbyopia and bifocal lens
(c) myopia and concave lens
(d) myopia and bifocal lens
Ans: (b)
With ageing, the ciliary muscles weaken and the flexibility of the eye lens decreases, reducing the power of accommodation. This causes presbyopia, which is corrected using bifocal lenses containing both concave and convex parts for distant and near vision respectively.
Q2: A person has to keep reading material much beyond 25 cm (say at 50 cm) from the eye for comfortable reading. Name the defect of vision he is suffering from. List two causes responsible for arising of this defect. Draw a labelled diagram showing correction of this defect using eye-glasses. Are these glasses convergent or divergent of light? (3 Marks)
Ans:
Defect: Hypermetropia
Causes:
- The focal length of the eye lens becomes too long, or
- The eyeball becomes too small.
Correction:
- Hypermetropia is corrected by using a convex lens (converging lens) of appropriate power.
- The convex lens provides the additional focusing power required to form the image on the retina.
Diagram:  Glasses Type: Convergent (convex lens)
Glasses Type: Convergent (convex lens)
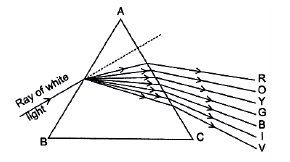
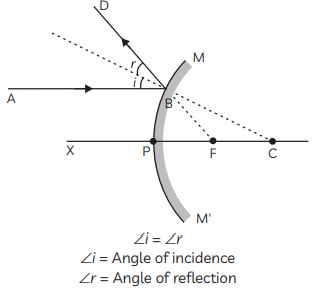
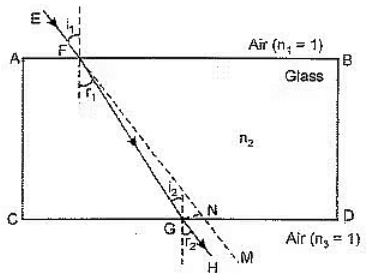
Q3: The students in a class took a thick sheet of cardboard and made a small hole in its centre. Sunlight was allowed to fall on this small hole and they obtained a narrow beam of white light. A glass prism was taken and this white light was allowed to fall on one of its faces. The prism was turned slowly until the light that comes out of the opposite face of the prism appeared on the nearby screen. They studied this beautiful band of light and concluded that it is a spectrum of white light.
(i) Give any one more instance in which this type of spectrum is observed. (1 Mark)
(ii) What happens to white light in the above case? (1 Mark)
(iii) (A) List two conditions necessary to observe a rainbow. (2 Marks)
Ans:
(i) One more instance:
A similar spectrum is observed in a rainbow formed in the sky after a rain shower.
(ii) What happens to white light:
In the prism experiment, white light splits into its seven component colours — Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red (VIBGYOR). This process is called dispersion of light.
(iii) Conditions necessary to observe a rainbow:
- The Sun should be shining in one part of the sky (behind the observer).
- Tiny water droplets must be present in the atmosphere in the direction opposite to the Sun, to refract, disperse and internally reflect sunlight to form the rainbow.
OR
(iii) (B) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a rainbow. Mark on it, points (a), (b) and (c) as given below: (2 Marks)
(a) Where dispersion of light occurs.
(b) Where light gets reflected internally.
(c) Where final refraction occurs.
Hide Answer (iii) (B) Diagram Description: A ray diagram for rainbow formation shows a sunlight ray entering a spherical water droplet. Label:
- (a) Dispersion: At the point where the ray enters the droplet, white light splits into colors due to refraction and varying wavelengths.
- (b) Internal Reflection: Inside the droplet, the dispersed light reflects off the inner surface (total internal reflection).
- (c) Final Refraction: The light exits the droplet, refracting again, forming the spectrum seen as a rainbow.

Q4: The Question consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer the question selecting the appropriate option (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below :
Assertion (A): White light is dispersed by a glass prism into seven colours.
Reason (R): The red light bends the least while the violet the most when a beam of white light passes through a glass prism. (1 Mark)
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans: (a)
A glass prism disperses white light into seven colours because different colours (wavelengths) refract by different amounts in the prism — red bends least and violet bends most — causing the colours to separate.
Q5: The possible way to restore clear vision of those people whose eyeball has elongated is the use of suitable: (1 Mark)
(a) bifocal lens
(b) concave lens
(c) converging lens
(d) convex lens
Ans: (b)
An elongated eyeball causes myopia (near-sightedness), where the image of distant objects forms in front of the retina.
Using a concave (diverging) lens shifts the image back onto the retina, restoring clear distant vision.
Q6: The part of human eye which controls the amount of light entering into it: (1 Mark)
(a) Iris
(b) Cornea
(c) Ciliary muscles
(d) Pupil
Ans: (d)
The pupil regulates and controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Q7: (A) Give reasons:
(i) The sky appears dark to passengers flying at very high altitude.
(ii) ‘Danger’ signal lights are red in colour. (2 Marks)
Ans (A):
(i) The sky appears dark to passengers flying at very high altitude:
At high altitudes, the atmosphere is very thin, and scattering of light is not prominent. Hence, there is no scattering of sunlight, and the sky appears dark instead of blue.
(ii) ‘Danger’ signal lights are red in colour:
Red light has the longest wavelength and is least scattered by fog, smoke, or dust. Therefore, it can be seen clearly from a distance, making it ideal for danger or warning signals.
OR
(b) What is a rainbow ? “We see a rainbow in the sky only after the rainfall.” Why ? (2 Marks)
Ans:
A rainbow is a natural spectrum of sunlight that appears in the sky after a rain shower. It is caused by the dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets present in the atmosphere.
We see a rainbow only after rainfall because water droplets act like small prisms — they refract, disperse, internally reflect, and then refract sunlight again when it emerges, forming the seven colours (VIBGYOR) visible to the observer in the direction opposite to the Sun.
Q8: A person uses lenses of +2.0 D power in his spectacles for the correction of his vision.
(a) Name the defect of vision the person is suffering from.
(b) List two causes of this defect.
(c) Determine the focal length of the lenses used in the spectacles. (3 Marks)
Ans:
(a) Defect: Hypermetropia (far-sightedness).
(b) Two causes:
- The focal length of the eye lens is too long.
- The eyeball has become too small.
(c) Focal length of the lens:
Power P = +2.0D.
Focal length (in metres).
(in metres).
Compute digit by digit: f = 1/2.0 = 0.5 metre = 50 cm.
So the lenses used have focal length 0.5 m (50 cm).
Q9: Most of the refraction for the light rays entering the eye occurs at: (1 Mark)
(a) Iris
(b) Pupil
(c) Crystalline lens
(d) Outer surface of Cornea
Ans: (d)
Most of the refraction of light entering the eye takes place at the outer surface of the cornea, while the crystalline lens provides only finer adjustments of focal length for clear vision.
Q10: The curvature of eye lens of human eye: (1 Mark)
(a) is fixed.
(b) can be increased.
(c) can be decreased.
(d) increases or decreases as the case may be.
Ans: (d)
The curvature of the eye lens is controlled by the ciliary muscles.
It increases to view nearby objects (lens becomes thicker) and decreases to view distant objects (lens becomes thinner).
Q11: A person uses lenses of power -0.5 D in his spectacles for the correction of his vision.
(a) Name the defect of vision the person is suffering from.
(b) List two causes of this defect.
(c) Determine the focal length of the lenses used in the spectacles. (3 Marks)
Ans:
(a) Defect: Myopia (near-sightedness).(b)Two causes:
- Excessive curvature of the eye lens.
- Elongation (increased length) of the eyeball.
(c) Focal length of the lens:
Power
P=−0.5 D.
Focal length  Compute step by step: f = 1/- 0.5 = -2.0 meters = -200 cm.
Compute step by step: f = 1/- 0.5 = -2.0 meters = -200 cm.
So the spectacle lens has focal length −2.0 m (the negative sign shows it is a diverging lens).
Previous Year Questions 2024
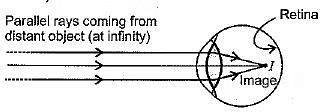
Q1: The lens system of human eye forms an image on a light sensitive screen, which is called as: (2024)
(a) Cornea
(b) Ciliary muscles
(c) Optic nerves
(d) Retina
Ans: (d)
The lens system of the human eye forms an image on a light-sensitive screen called the retina. The retina captures the light and sends the visual information to the brain through the optic nerves, allowing us to see.
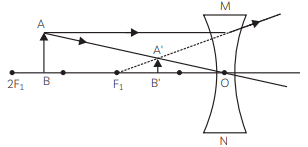
Q2: Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow: (2024)
(i) Name the defect of vision represented in the diagram. Give reason for your answer.
(ii) List two causes of this defect.
(iii) With the help of a diagram show how this defect of vision is corrected.
Ans: (i) Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness.
Reason – Image is formed behind the retina. Near point for the person is farther away from the normal near point (25 cm)
(ii)
- Focal length of the eye lens is too long.
- The eyeball has become too small.
(iii) N = Near point of a hypermetropic eye
N = Near point of a hypermetropic eye
N’= Near point of a normal eye
Q3: Consider the following statements in the context of human eye: (2024)
(A) The diameter of the eye ball is about 2.3 cm.
(B) Iris is a dark muscular diaphragm that controls the size of the pupil.
(C) Most of the refraction for the light rays entering the eye occurs at the crystalline lens.
(D) While focusing on the objects at different distances the distance between the crystalline lens and the retina is adjusted by ciliary muscles.
The correct statements are —
(a) (A) and (B)
(b) (A), (B) and (C)
(c) (B), (C) and (D)
(d) (A), (C) and (D)
Ans: (a)
Adult eyeballs measure around 2.3 cm in diameter. The iris is the dark muscular diaphragm, whereas the ciliary muscle adjusts the focal length to focus images on the retina. The eye’s initial surface, where light transitions from air to the cornea, has the most substantial shift in its index of refraction. The cornea accounts for around 80% of refraction, whereas the inner crystalline lens accounts for 20%.
Q4: Assertion – Reason based questions: (2024)
These questions consist of two statements — Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below :
Assertion (A): Myopic eye cannot see distant objects distinctly.
Reason (R): For the correction of myopia converging lenses of appropriate power are prescribed by eye-surgeons.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Ans: (c)
The assertion (A) states that a myopic eye, or near sighted eye, cannot see distant objects clearly, which is true. However, the reason (R) claims that converging lenses are used to correct myopia, which is false; instead, diverging lenses are prescribed for myopia to help the eye focus on distant objects. Thus, the answer is (c) because (A) is true, but (R) is false.
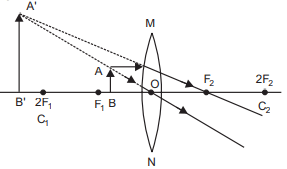
Q5: When do we say that a particular person is suffering from hypermetropia? List two causes of this defect. Name the type of lens used to correct this defect. (CBSE 2024)
Ans: When he cannot see nearby objects distinctly but can see far object clearly.
2 causes:
(i) Focal length of the eye lens is too long.
(ii) Eyeball becomes too small.
lens used to correct this defect is Convex or Converging lens
Q6: (a) Define the term power of accommodation of human eye. Write the name of the part of eye which plays a major role in the process of accommodation and explain what happens when human eye focuses (i) nearby objects and (ii) distant objects.
OR
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a rainbow in the sky. On this diagram mark A — where dispersion of light occurs, B — where internal reflection of light occurs and C — where refraction of light occurs. List two necessary conditions to observe a rainbow. (2024)
Hide Answer Ans: (a)
- The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length, so as to clearly focus rays coming from distant as well as near objects on the retina, is called the power of accommodation of the eye.
- Ciliary muscles play a major role in maintaining power of accommodation.
(i) While focusing on nearby objects ciliary muscles contract, eye lens becomes thick and its focal length decreases.
(ii) While focusing on distant objects ciliary muscles relax, eye lens becomes thin and its focal length increases.
OR
(b)
Two conditions:
(i) The Presence of tiny water droplets in the atmosphere.
(ii) Position of Sun at the back(behind) of the observer.
Q7: Name and explain the phenomenon of light due to which the path of a beam of light becomes visible when it enters a smoke filled room through a small hole. Also state the dependence of colour of the light we receive on the size of the particle of the medium through which the beam of light passes. (CBSE 2024)
Ans: The phenomenon responsible is the Tyndall Effect, where light scatters due to tiny particles in the medium, making the beam visible in a smoke-filled room.
Dependence on Particle Size:
- Small Particles – Scatter shorter wavelengths (blue/violet) more, making the sky appear blue.
- Medium Particles – Scatter all wavelengths almost equally, making the light appear white.
- Large Particles – Scatter all wavelengths equally, giving a white or greyish appearance, like clouds.
Q8: When a beam of white light passes through a region having very fine dust particles, the colour of light mainly scattered in that region is: (2024)
(a) Red
(b) Orange
(c) Blue
(d) Yellow
Ans: (c)
When a beam of white light passes through an area with fine dust particles, the color of light that gets scattered the most is blue. This happens because shorter wavelengths of light, like blue, scatter more easily than longer wavelengths, like red or orange. Therefore, blue light is not visible in such conditions.
Q9: Define the term power of accommodation of human eye. What happens to the image distance in the eye when we increase the distance of an object from the eye ? Name and explain the role of the part of human eye responsible for it in this case. (2024)
Ans:
- Power of Accommodation – The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length to focus objects at different distances on the retina.
- Image Distance – Remains unchanged as the image always forms on the retina.
- Role of Ciliary Muscles:
- For Distant Objects – Ciliary muscles relax, lens becomes thin, focal length increases.
- For Nearby Objects – Ciliary muscles contract, lens becomes thick, focal length decreases.
Q10: (a) Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow: (2024)
(i) Name the defect of vision depicted in this diagram stating the part of the eye responsible for this condition. (ii) List two causes of this defect. (iii) Name the type of lens used to correct this defect and state its role in this case.
OR
(b) What is dispersion of white light? State its cause. Draw a diagram to show dispersion of a beam of white light by a glass prism.
Ans:
(a) Defect of Vision
(i) Name & Responsible Part:
- Hypermetropia (Farsightedness) – Caused by ciliary muscles/eye lens.
(ii) Causes:
- Focal length of the eye lens is too long.
- Eyeball is too small, forming the image behind the retina.
(iii) Correction:
- Convex lens (Converging lens) decreases the focal length, helping focus the image on the retina.
(b) Dispersion of White Light
- Definition: Splitting of white light into seven colours when passing through a prism.
- Cause: Different colours bend at different angles due to varying wavelengths.
Q11: For Q. Nos.11 and 12, two statements are given – One labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below: (2024)
Assertion (A): The rainbow is a natural spectrum of sunlight in the sky.
Reason (R): Rainbow is formed in the sky when the sun is overhead and water droplets are also present in air.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans: (c)
- Assertion (A): True. A rainbow is a natural spectrum formed by the dispersion, refraction, and internal reflection of sunlight by water droplets.
- Reason (R): False. Rainbows form when the sun is behind the observer at a low angle (typically ~42° above the horizon for the primary rainbow), not overhead, and water droplets are present in the atmosphere.
Q12: Assertion (A) and Reason (R), answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below: (CBSE 2024)
Assertion (A): Red light signals are used to stop the vehicles on the road.
Reason (R): Red coloured light is scattered the most so as to be visible from a large distance.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is not correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Ans: (c)
The assertion (A) is true because red light signals are indeed used to indicate that vehicles should stop. However, the reason (R) is false; red light is actually scattered the least among the visible colors due to longer wavelength , which is why it can be seen from a distance without much scattering. Therefore, the correct answer is (c), as (A) is true, but (R) is false.
Previous Year Questions 2023
Q1: Observe the following diagram and answer the questions following it :
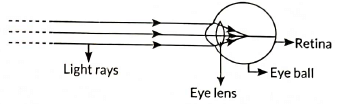
(i) Identify the defect of vision shown.
(ii) List its two causes.
(iii) Name the type of lens used for the correction of this defect. (2023)
Ans:
- Student is suffering from myopia.
- The two possible reasons due to which the defect of vision arises are:
- excessive curvature of the eye-lens
- elongation of the eye-ball
- A student with myopia has the far point nearer than infinity, thus, the image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina.
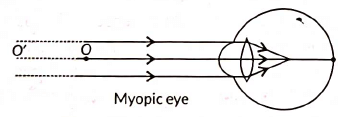
Correction of myopia: This defect can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable power as it brings the image back on to the retina, thus the defect is corrected.

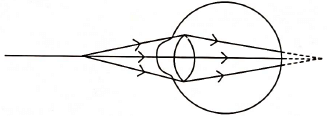
Q2: Observe the following diagram showing an image formation in an eye:
(a) Identify the defect of vision shown in the figure.
(b) List its two causes and suggest a suitable corrective lens to overcome this defect (2023)
Ans: (a) Hypermetropia
(b) Hypermetropia is caused due to following reasons:
(i) Shortening of the eyeball
(ii) Focal length of crystalline lens is too long
It is corrected by using a convex lens which converges and shifts the image to the retina from behind.
Q3: Define the term dispersion of white light. State the colour which bends (i) the most, and (ii) the least while passing through a glass prism. Draw a diagram to show the dispersion of white light. (2023)
Ans:
(i) The phenomenon of the splitting up of the white light into its constituent’s colours is called dispersion of light. Dispersion of light is caused due to different constituents and colours of light after different refractive indices to the material of the prism.
(ii) The formation of a rainbow is caused by the dispersion of the white sunlight into its constituent colours.
(iii) Based on the dispersion of white light into its constituent’s colours, we can conclude that
(a) The white light consists of seven colours.
(b) The violet light suffers maximum deviations and the red light suffers minimum deviation.
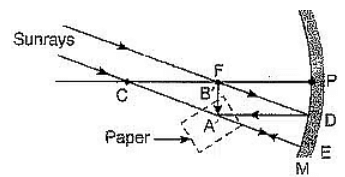
Q4: What is a rainbow? Draw a labelled diagram to show its formation. (2023)
Ans: After a rain-shower, the sunlight gets dispersed by tiny droplets, present in the atmosphere. The water droplets act like small glass prisms. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally, and finally refract it again when it comes out of the raindrop. Due to dispersion or light and internal reflection, different colours reach the observer’s eye, which is called a rainbow.
Q5: The colour of the clear sky from the Earth appears blue but from space, it appears black. Why? (2023)
Ans: As our earth has an atmosphere and space has no atmosphere, the sunlight scatters by the particles in the atmosphere. The amount of scattering of light is inversely proportional to wavelength thus violet, and blue colours scatter more than red and hence the colour of the sky appears blue from the earth.
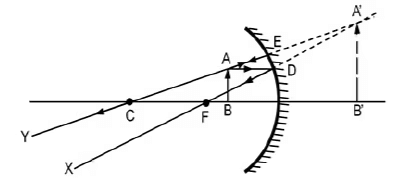
Q6: A narrow beam XY of white light is passing through a glass prism ABC as shown in the diagram:
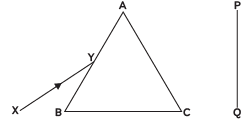
Trace it on your answer sheet and show the path of the emergent beam as observed on the screen PQ. Name the phenomenon observed and state its cause. (CBSE 2023)
Ans:
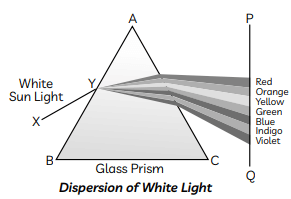
The phenomenon of the splitting up of the white light into its constituent colours is called dispersion of light. Dispersion of light is caused when different constituent colours of light offer different refractive indices to the material of the prism.
Q7: Give reasons for the following.
(A) Danger signals installed at airports and at the top of tall buildings are of red colour.
(B) The sky appears dark to the passengers flying at very high altitudes.
(C) The path of a beam of light passing through a colloidal solution is visible. (CBSE 2023)
Ans: (A) Red danger signals are used because red light has the longest wavelength in the visible spectrum and is scattered the least by atmospheric particles, fog, or smoke. This allows red light to be visible from greater distances, making it effective for warning signals.
(B) At higher altitude either the atmospheric medium is very rare or there are no particles present/no atmosphere, thus the scattering of light taking place is not enough at such heights or no scattering of sunlight takes place. Hence, the sky appears dark to the passengers flying at very high altitude.
(C) Tyndall effect deals with the phenomenon of scattering of light by colloidal particles. When a fine beam of sunlight enters a room, the particles present in the room become visible due to scattering of light by these particles. When sunlight passes through a canopy of a dense forest, tiny water droplets in the mist scatter light.
Q8: It is observed that the power of an eye to see nearby objects as well as far off objects diminishes with age.
(A) Give reason for the above statement.
(B) Name the defect that is likely to arise in the eyes in such a condition.
(C) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the type of corrective lens used for restoring the vision of such an eye. (CBSE 2023)
Ans: (A) We know that the ability of the accommodation factor to alter the focal length declines with ageing. Without corrective spectacles, aged people have difficulty seeing surrounding objects clearly.
(B) The person is suffering from presbyopia.
(C)
 | Get additional INR 200 off today with EDUREV200 coupon. | Avail Offer |
Previous Year Questions 2022
Q1: In the diagram given below. X and Y are the end colours of the spectrum of white light. The colour of ‘Y’ represents the (2022)
(a) Colour of sky as seen from earth during the day
(b) Colour of the sky as seen from the moon
(c) Colour used to paint the danger signals
(d) Colour of sun at the time of noon.
Ans: (c)
Sol: Red colour is used to paint the danger signals. As live know, visible spectrum has violet indigo, blue, green, yellow. orange and red colour and these colours are arranged with red on the top and violet at the bottom (near base of the prism) on the basis of wavelength and frequency, and among these colours red colour has largest wavelength (≈ 750 nm). Thus, here Y will be red.
Previous Year Questions 2021
Q1: Assertion (A): Sky appears blue in the day time. Reason
(R) : White light is composed of seven colours. (2021)
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not correct explanation of A
(c) (A) is true, but R is false.
(d) (A) is false but R is true.
Ans: (b)
Sol: The blue colour of clear sky is due to scattering of sunlight
Q2: Which of the following statements is NOT true for the scattering of light?
(a) Colour of the scattered light depends on the size of particles of the atmosphere.
(b) Red light is least scattered in the atmosphere.
(c) Scattering of light takes place as various colours of white light travel with different speed in air.
(d) The fine particles in the atmospheric air scatter the blue light more strongly than red. So the scattered blue light enters our eyes. (CBSE Term-1 2021)
Ans: (c)
(a) This statement is true. The color of scattered light depends on the size of the particles in the atmosphere. Smaller particles scatter shorter wavelengths (like blue) more than longer wavelengths (like red).
(b) This statement is true. Red light is least scattered in the atmosphere because it has a longer wavelength.
(c) This statement is NOT true. All colors of white light travel at the same speed in air. Scattering occurs due to the interaction of light with particles, not because of a difference in the speed of various colors in air.
(d) This statement is true. Fine particles in the atmosphere scatter blue light more strongly than red light, which is why the sky appears blue to our eyes.
Therefore, the correct answer is (c) Scattering of light takes place as various colours of white light travel with different speed in air.
| Also read: The Human Eye |
Previous Year Questions 2020
Q1: Why is the Tyndall effect shown by colloidal particles? State four instances of observing the Tyndall effect. (2020)
Ans: The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particles gives rise to the Tyndall effect. When a beam of light strikes colloidal particles, the path of the beam becomes visible. This is known as the Tyndall effect. This phenomenon can be observed when
(i) Sunlight passes through a canopy of dense forest when tiny water droplets in the mist scatter light.
(ii) torch light is switched on in a foggy environment, light rays are visible after being scattered by the fog particles in the surrounding air.
(iii) a fine beam of sunlight enters a smoke-filled room through a small hole.
(iv) Shining a flashlight beam into a glass of dilated milk produces a Tyndall effect.
Previous Year Questions 2019
Q1: Define the term power of accommodation. Write the modification in the curvature of the eye which enables us to see the nearby objects. What are the limits of the accommodation power of a healthy normal human eye? (CBSE 2019)
Ans:
- Accommodation power is the property of the eye lens to adjust its focal length to focus objects situated at different distances from the eye on the retina.
- When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thin and its focal length is maximum and equal to the diameter of the eyeball. In this condition, one can see distant objects.
- At the time of looking at nearby objects, the ciliary muscles of the eye contract and the eye lens become thicker. Consequently, the focal length of the eye lens decreases and nearby objects are focussed at the retina.
- There are definite limits to accommodation power for a healthy normal eye. The farthest distance, up to which an eye can see objects clearly, is called the far point of the eye and its value is infinity.
- The minimum distance, up to which an eye can see distinctly, is known as the near point of the eye and its value is 25 cm for a normal eye.
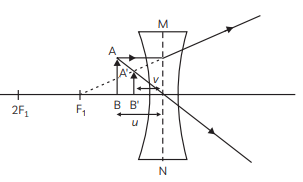
Q2: When do we consider a person to be myopic? List two causes of this defect.
Explain using a ray diagram how can this defect of an eye be corrected. (CBSE 2019)
Ans:
- A person is said to have a myopic vision if he can see objects situated near the eye clearly but cannot see distant objects.
- If a person can see clearly up to a distance x from the eye then it means that the far point of the eye has shifted from infinity to a point O situated at distance V from the eye.
- Light rays coming from a distant object (u = ∞) are focussed in front of the retina of the eye.
- Two possible causes of myopia are :
- Either the power of the eye lens has become more than its normal value due to excessive curvature of the cornea (focal length of eye lens has decreased) or
- Elongation of the eyeball due to some genetic defect.
- To rectify this defect a concave lens of focal length f is used, which may form the virtual image of the distant object at the far point of the defective eye (i.e., u = – ∞ and v = – x) so that now the defective eye may form the image at the retina.
- Obviously, by using the lens formula, we have
 ⇒ f = -x
⇒ f = -x
The ray diagram of the defective eye and its rectification are shown here.
Normal Eye 
Myopic Eye
Correction by concave lens
Q3: Name two defects of vision. Mention their cause and the type of lenses used to correct them. (CBSE 2019)
Ans: Two main defects of vision, their cause and correction are as follows :
(1) Myopia – In myopia or near-sightedness (or short-sightedness), a person can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects distinctly. For a myopic eye, the far point is not at infinity but has shifted nearer to the eye.
Myopia arises due to either (i) excessive curvature of the cornea, or (ii) elongation of the eyeball.
Myopia can be corrected by using a concave lens whose focal length has the same numerical value as the distance of the far point of the defective eye.
(2) Hypermetropia -In hypermetropia or long-sightedness, a person can see distant objects distinctly but cannot see nearby objects so clearly. For a longsighted eye, the near point is not at 25 cm but has shifted away from the eye.
Hypermetropia arises either because
(i) the focal length of the eye lens is too large, or
(ii) contraction of the eyeball.
Hypermetropia can be corrected by using a suitable convex lens, which forms a virtual image of the object situated at 25 cm at the near point of the defective eye so that the eye lens can focus it on the retina.
Q4: What is a rainbow? Draw a labelled diagram to show the formation of a rainbow. (CBSE 2019)
Or
Describe the formation of the rainbow in the sky with the help of a diagram.
Ans: A rainbow is a natural spectrum appearing in the sky after a rain shower. A Rainbow is caused by the dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets hanging in the atmosphere after a rain shower. The water droplets act like small prisms. As shown in the figure, the water droplets refract and disperse the incident sunlight. These rays are then reflected internally and finally refracted again and come out of raindrops. Due to the dispersion and internal reflection of light different colours reach the observer’s eye and a rainbow is seen. An important point to be noted here is that a rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the Sun.
An important point to be noted here is that a rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the Sun.
Q5: What is atmospheric refraction? Briefly explain. Why does the apparent position of a star appear different from its true position? (CBSE 2019)
Ans: The atmospheric air layer just near the earth’s surface is comparatively denser and the upper layers of the atmosphere are successively rarer and more rarer. Hence, a light ray passing through atmospheric air undergoes refraction. Since the physical conditions of air are not stationary, the apparent position of the distant object, as seen through the air, fluctuates. It is known as an effect of atmospheric refraction.
Light coming from a distant star entering into the earth’s atmosphere gradually bends towards the normal on account of atmospheric refraction. Hence, the star appears slightly higher than its actual position when viewed near the horizon.
Q6: The stars appear higher from the horizon than they are. Explain why it is so. (CBSE 2019)
Ans: As we go up and up in earth’s atmosphere, it goes on becoming rarer and more rarer. As a result, the atmospheric layer near the earth’s surface has a maximum refractive index and the refractive index gradually decreases with an increase in height.
When a light ray from a star enters into earth’s atmosphere, it travels from a rarer to denser medium and hence continues to bend towards the normal. As a result, an observer on Earth considers the apparent position of a star to be at a higher altitude.
Q7: What happens to the image distance in the normal human eye when we decrease the distance of an object, say 10 m to 1 m? Justify your answer. (Delhi 2019)
Ans: There is no change in the image distance in the eye. The eye lens can adjust its focal length called accommodation. When object distance decreases, ciliary muscles contract and lens becomes thick and its focal length decreases. It facilitates near vision.
Q8: Due to the gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens a certain defect of vision arises. Write the name of this defect. Name the type of lens required by such persons to improve their vision. Explain the structure and function of such a lens. (Delhi 2019)
Ans:
- The defect of vision is Presbyopia.
- A bifocal lens is required by such persons to improve their vision.
Structure and function of Bifocal lens
- To view far-off objects, the upper part of the bifocal lens is a Concave or Diverging lens.
- To facilitate or view nearby objects, the Lower part of the bifocal lens is Convex or Converging lens.
Q9: (A) State the role of ciliary muscles present in our eye.
(B) Identify the defect of vision in each of the given cases and suggest its corrective measure.
(i) The eye lens has become milky and cloudy.
(ii) The eye lens has excessive curvature.
(iii) The eye lens has large focal length (longer than normal).
(iv) Ciliary muscles have weakened.
Ans: (A) Ciliary muscles relax and contract to adjust/modify the focal length of eye lens.
(B) Eye defects and corrective measures:
Q10: (A) With the help of diagram explain Isaac Newton’s experiment that led to the idea that the sunlight is made up of seven colours.
(B) What is atmospheric refraction? List two natural phenomena based on atmospheric refraction.
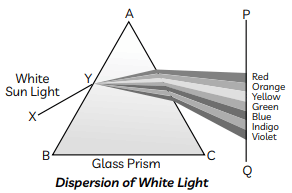
Ans: (A) Issac Newton was the first to use a glass prism to obtain the spectrum of white light. He tried to split various colours of the spectrum of white light by using another similar prism, but he could not get any more colours. Thus he proved that sunlight is made of seven colours.
(B) Atmospheric Refraction: It is the refraction of light by the earth’s atmospheric layers having varying refractive indices.
Two natural phenomena:
(1) Twinkling of stars,
(2) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset.
Previous Year Questions 2018
Q1: (a) Write the function of each of the following parts of the human eye :
(i) Cornea
(ii) Iris
(iii) Crystalline lens
(iv) Ciliary muscles.
(b) Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning? Will this phenomenon be observed by an astronaut on the Moon? Give a reason to justify your answer. (CBSE 2018)
Ans: (a) The function of the given parts is stated below:
(i) The cornea is the outer bulged-out thin transparent layer of the eye and provides most of the refraction for the light entering into the eye.
(ii) The iris controls the size of the pupil of the eye.
(iii) The crystalline lens provides the finer adjustment of the focal length required to focus objects situated at different distances in front of the eye on the retina.
(iv) The ciliary muscles help in controlling the curvature of the crystalline lens and thus can change the power of the crystalline lens.
(b) In the early morning, the Sun is situated near the horizon. Light from the Sun passes through thicker layers of air and covers a larger distance in the Earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes. While passing through atmosphere blue light is mostly scattered away and the Sun appear reddish as shown in Fig.
The phenomenon is not observed by an observer on the Moon because the Moon has no atmosphere of its own and hence no scattering of light is possible.
Q2: (a) What is meant by the term power of accommodation? Name the component of the eye that is responsible for the power of accommodation.
(b) A student sitting at the back bench in a class has difficulty in reading. What could be his defect of vision? Draw a ray diagram to illustrate the image formation of the blackboard when he is seated at the (i) back seat and (ii) front seat. State two possible causes of this defect. Explain the method of correcting this defect with the help of a ray diagram. (CBSE 2018)
Ans: (a) Power of accommodation: The ability of an eye lens to adjust its focal length to form a sharp image of the object at varying distances on the retina is called the power of accommodation. The ciliary muscles of the eye are responsible for changing the focal length of the eye lens.
(b)
- The student is suffering from myopia shortsightedness or nearsightedness.
- When a student is seated in the back seat.
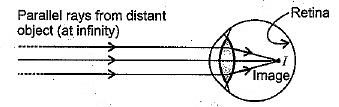
In this case, the student is suffering from myopia and has a short focal length of the eye lens.
(ii) When a student is seated in the front seat.
Causes:
(i) Excessive curvature of the eye lens
(ii) Elongation of eyeball.
The defect is corrected by using a concave lens of suitable power placed in front of the eye as shown below. It diverges the rays and forms a virtual image of a distant object at the far point of the myopic eye. These diverged rays enter the eye and form the image on the retina. Thus, the concave lens shifts the image back onto the retina instead of in front of it and the defect is corrected.
Q3: (a) What is presbyopia? State its cause. How is it corrected?
(b) Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning? Explain with the help of a labelled diagram. (CBSE 2018C)
Ans: (a) (i) Presbyopia
- Presbyopia is a condition that occurs as a part of normal ageing.
Due to loss of power of accommodation of the eye, with age, objects at a normal near working distance will appear blurry. The near point gradually recedes away. This defect of the eye is called Presbyopia. - Sometimes, a person may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia.
(ii) Presbyopia is caused due to
- weakening of ciliary muscles, and
- eye lens becomes less flexible and elastic, i.e. reducing the ability of the eye lens to change its curvature with the help of ciliary muscles.
(iii) A bifocal lens will be required to see nearby as well as distant objects. For myopic defects, the upper part of the bifocal lens consists of a concave lens used for distant vision and to correct hypermetropia, the lower part of the bifocal lens consists of a convex lens. It facilitates near vision.
(b) At the time of sunrise/sunset, the sun is near the horizon, so the sun’s rays have to travel through a larger atmospheric distance. The fine particles of the atmosphere scatter away the blue component and other shorter wavelengths of the sunlight. As λb < λr, only red colour having a longer wavelength and is least scattered, reaches our eyes. Hence, the sun appears red at sunrise or sunset.
Previous Year Questions 2017
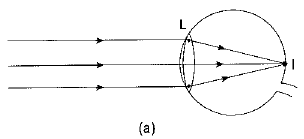
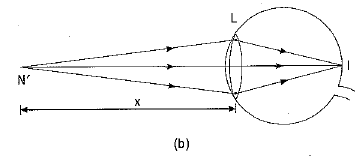
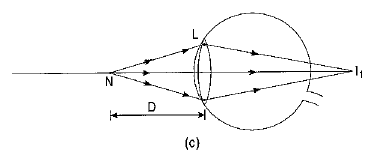
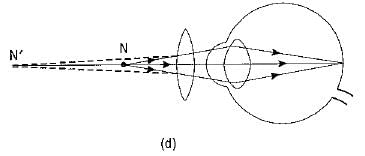
Q1: What eye defect is hypermetropia? What are its two possible causes? Describe with a ray diagram how this defect of vision can be corrected by using an appropriate lens. (CBSE 2017)
Ans: Hypermetropia or long-sightedness is that defect of vision in which the defective eye can see distant objects distinctly but is unable to see distinctly an object placed near his eye. For a nearby object, the image is formed behind the retina.
Two possible causes of this defect of vision are :
(i) The power of the eye lens is less (or the focal length of the eye lens is more) due to less curvature of the cornea.
(ii) The size of the eyeball is shortened.
The hypermetropia defect can be corrected by using a converging (convex) lens of appropriate power.
Ray diagrams showing the defect and its correction are
Q2: What is dispersion of white light? Draw a neat diagram to show the dispersion of white light by a glass prism. What is the cause of dispersion? (CBSE 2017)
Ans: When a beam of white light passes through a glass prism it splits up into its constituent seven colours. The splitting of white light into its constituent colours when light passes through a dispersive medium is called “dispersion of light”. The seven colours, usually expressed as ‘VTBGYOR’ constitute the spectrum of white light.
The ray diagram showing dispersion is given here Cause of Dispersion: When a beam of white light enters a glass prism (or any other dispersive medium), the light ray bends towards the normal one entering into the glass. However, different colours of light bend through different angles concerning the incident ray The red light bends the least while the violet light bends the most. So, rays of different colours emerge along different paths and, thus, become distinct. Hence, dispersion is caused and a spectrum is formed.
Cause of Dispersion: When a beam of white light enters a glass prism (or any other dispersive medium), the light ray bends towards the normal one entering into the glass. However, different colours of light bend through different angles concerning the incident ray The red light bends the least while the violet light bends the most. So, rays of different colours emerge along different paths and, thus, become distinct. Hence, dispersion is caused and a spectrum is formed.
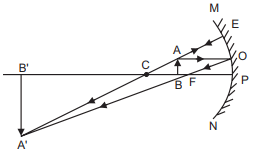
Q3: State the cause of dispersion of white light by a glass prism. How did Newton, using two identical glass prisms, show that white light is made of seven colours? Draw a ray diagram to show the path of a narrow beam of white light, through a combination of two identical prisms arranged together in an inverted position concerning each other, when it is allowed to fall obliquely on one of the faces of the first prism of the combination. (AI 2017)
Ans: Cause of dispersion: From Snell’s law of refraction, the angle of refraction of light in a prism depends on the refractive index of the prism material. Moreover, the refractive index of the material varies inversely with the speed of light and also varies inversely with the wavelength of light. Hence, different colours of white light bend through different angles concerning the incident light, as they pass through the glass prism.
Newton Experiment: Consider a prism A. When a beam of white light falls obliquely on one of the faces of this prism, it splits up into seven constituent colours. The violet colour deviates the most and the red colour deviates the least.
If another identical prism B is placed in an inverted position concerning the first prism A, the constituent coloured rays that emerge out of prism A will be made to merge to come out as a beam of white light, as shown below.
Q4: Name the type of defect of vision a person is suffering from, if he uses convex lenses in his spectacles for the correction of his vision. If the power of the lenses is +0.5 D, find the focal length of the lenses. (AI2017C)
Ans: The defect of vision is hypermetropia.
Focal length of lenses,
Q5: A student traces the path of a ray of light through a glass prism for different angles of incidence. He analyses each diagram and draws the following conclusion:
(I) On entering prism, the light ray bends towards its base.
(II) Light ray suffers refraction at the point of incidence and point of emergence while passing through the prism.
(III) Emergent ray bends at certain angle to the direction of the incident ray.
(IV)While emerging from the prism, the light ray bends towards the vertex of the prism.
Out of the given inferences, the correct ones are:
(a) (I), (II) and (III)
(b) (I), (III) and (IV )
(c) (II), (III) and (IV )
(d) (I) and (IV ) (CBSE 2017)
Ans: (a)
(I) On entering the prism, the light ray bends towards its base: This is correct. When light enters a denser medium (the prism) at an angle, it bends towards the base of the prism due to refraction.
(II) The light ray suffers refraction at the point of incidence and point of emergence while passing through the prism: This is correct. The ray undergoes refraction at both the surfaces of the prism — first when it enters the prism and again when it exits.
(III) The emergent ray bends at a certain angle to the direction of the incident ray: This is correct. The emergent ray is deviated from the original path of the incident ray, resulting in a measurable angle of deviation.
(IV) While emerging from the prism, the light ray bends towards the vertex of the prism: This is incorrect. When the ray emerges from the prism, it actually bends away from the normal (towards the base of the prism) as it moves from a denser to a rarer medium.
Thus, the correct inferences are (I), (II), and (III), making the correct answer (a) (I), (II) and (III).
Q6: What is scattering of light? Why is the colour of the clear sky blue? Explain. (CBSE 2017)
Ans: Scattering of light is the phenomenon of change in the direction of light on striking an obstacle like an atom, a molecule, dust particle, water droplet, etc. The blue colour of the sky is due to the scattering of sunlight by a large number of molecules such as fine dust particles, gases, water vapour, etc. present in Earth’s atmosphere. Due to the very small size of the scatterer as compared to the wavelength of light, light of smaller wavelength, such as blue, is scattered the most as compared to light of longer wavelength.
Q7: Due to gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens a certain defect of vision arises. Write the name of this defect. Name the type of lens required by such persons to improve the vision. Explain the structure and function of such a lens. (CBSE 2017)
Ans: The defect of vision that arises due to gradual weakening of ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens is presbyopia. Most people find it difficult to see nearby objects comfortably and clearly without using corrective lenses. This is corrected by using convex lens of appropriate power. However, sometimes people may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia. This can be corrected by using a bifocal lens. A bifocal lens consists of two parts – the upper part is concave lens and lower part is convex lens. The upper part is for viewing distant objects and the lower part facilitates near vision.
Q8: Varun instead of copying from the black board used to copy regularly from the notebook of his friend, Sudhir with whom he sat on the same desk. Sudhir told the teacher about it. The teacher asked Varun to get his eyes checked by a doctor and explained to the whole class the reason why Varun copied from Sudhir’s notebook.
(A) What in your view, is wrong with Varun’s eyes and how can it be corrected?
(B) If the doctor prescribes Varun to use lenses of power – 0.5 D, what is the type of the lenses?
(C) Write the values displayed by Sudhir and his teacher.
Ans: (A) Varun is suffering from the defect of vision called myopia. Myopia can be corrected by using concave lens of appropriate power.
(B) Power of lens = – 0.5 D. This means it is a concave lens.
(C) Values displayed by Sudhir: Concerned, helpful, compassionate
Values displayed by teacher: Concerned, Knowledgeable.
Q9: Curvature of eye lens of human eye can be modified by ciliary muscles to some extent so that its focal length is changed as per requirement. How will the curvature and focal length of eye lens change when:
(A) a distant object is to be seen, and,
(B) a nearby object is to be seen clearly? Write the reason why a normal eye is not able to see clearly, the objects placed closer than 25 cm, without any strain on the eye.
Ans: (A) When we see a distant object, the muscles relax and the lens become thin and its focal length increases.
(B) When we see a nearby object, the ciliary muscles contract, this increases the curvature of the eye lens and it becomes thicker. Consequently the focal length of the eye lens decreases. A normal eye is unable to clearly see the objects placed closer than 25 cm because the ciliary muscles of eyes are unable to contract beyond a certain limit.
Previous Year Questions 2016
Q1: Describe an activity to show that the colours of white light split by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Also, draw a ray diagram to show the recombination of the spectrum of white light. (AI 2016)
Ans: Recombination of Colours: The colours of white light split by a glass prism can be recombined to get white light by another identical glass prism. Newton; demonstrated this phenomenon of recombination of the coloured rays of a spectrum to get back white light.
(а) A triangular prism ABC is placed on its base BC.
(b) A similar prism A ‘B ‘C ‘ is placed alongside its refracting surface in the opposite direction, i.e. in an inverted position concerning the first prism as shown in the figure. (c) A beam of white light entering the prism ABC undergoes refraction and is dispersed into its constituent seven colours.
(c) A beam of white light entering the prism ABC undergoes refraction and is dispersed into its constituent seven colours.
(d) These constituent seven coloured rays are incident on the second inverted prism A’B’C’ and get further refracted.
(e) The second prism recombines them into a beam of white light that emerges from the other side of the second prism and falls on the screen.
(f) This is because the refraction or bending produced by the second inverted prism is equal and opposite to the refraction or bending produced by the first prism. This causes the seven colours to recombine.
(g) A white patch of light is formed on the screen placed beyond the second prism. This proves the phenomenon of recombination of the spectrum of white light.
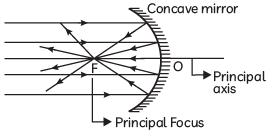
Q2: What is the function of the retina in the human eye? (CBSE 2016)
Ans. The retina behaves like a light-sensitive screen, on which real and inverted image of any object situated in front of the eye is formed.
Q3: What is the function of the crystalline lens of the eye? (CBSE 2016)
Ans: It provides the fine adjustment of the focal length of the eye lens system to focus images of objects situated at different distances on the retina.
Q4: Write the function of the iris in the human eye. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: Iris controls the size of the pupil
Q5: State the role of ciliary muscles in the accommodation of the eye. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: Adjust/modify the shape (curvature) of the eye lens so that its focal length can be increased or decreased.
Q6: What are the values of (i) near point and (ii) far point of vision of a normal adult person? (CBSE 2016)
Ans: (i ) 25 cm, (ii ) infinity.
Q7: Name two possible causes of myopia. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: (i) Excessive curvature of the eye lens.
(ii) Elongation of the eyeball.
Q8: An old person is unable to see nearby objects as well as distant objects. What defect of vision he is suffering from? (CBSE 2016)
Ans: The old person is suffering from presbyopia.
Q9: Priya prefers to sit in the front row as she finds it difficult to read the blackboard from the last desk in her classroom. State the defect of vision she is suffering from. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: Priya is suffering from myopia (near-sightedness).
Q10: Name the component of white light that deviates (i) the least and (ii ) the most while passing through a glass prism. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: (e) Red light is deviated the least and Violet light is deviated the most.
Q11: What will be the colour of the sky when it is observed from a place in the absence of any atmosphere? (CBSE 2016)
Ans: Black (dark).
Q12: Why is the red colour selected for danger signal lights? (CBSE 2016)
Ans: Red light is least scattered by fog or smoke and can be easily seen from a distance.
Q13: (a) What is the function of the iris and pupil of the eye?
(b) How does the focal length of the eye lens change as per the distance of the object in front of the eye? (CBSE 2016)
Ans: (a) The iris controls the size of the pupil. It adjusts in size, and therefore, helps in regulating the amount of light entering the eye through a variable aperture ‘pupil’. When the fight is very bright, the pupil becomes very small. However, in dim fight, it opens up completely through the relaxation of the iris.
(b) The crystalline eye lens consists of a fibrous, jelly-like material. Its curvature can be modified to some extent by the ciliary muscles. The change in the curvature of the eye lens can change its focal length. When the muscles are relaxed, the lens is thin and its focal length is more (about 2.5 cm). When the ciliary muscles contract the eye lens becomes thicker. Consequently, the focal length of the eye lens decreases.
Q14: What is a prism? Draw a neat diagram to show the refraction of a light ray through a triangular glass prism. Define the angle of deviation. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: An optical prism has two triangular bases and three rectangular lateral surfaces, which are inclined to each other. The angle between its two lateral faces is called the angle of the prism.
The labelled diagram has been shown in Fig in which
∠PEN = ∠i = angle of incidence, ∠N’EF = ∠r = angle of refraction and ∠MFR = ∠e = angle of emergence Whenever refraction of light takes place through a prism, the emergent ray bends towards the base of the prism. The angle between the directions of the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation D.
Whenever refraction of light takes place through a prism, the emergent ray bends towards the base of the prism. The angle between the directions of the incident ray and the emergent ray is called the angle of deviation D.
Q15: Explain why the planets do not twinkle but the stars twinkle. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: Stars are very far away from the earth and behave as almost a point object. The atmosphere is made of several layers and their refractive indices keep on changing continuously. So the light rays coming from the star keep on changing their paths continuously. As a consequence, the number of rays (or the light energy) entering the pupil of the eye changes with time and the stars appear twinkling.
A planet is comparatively nearer to the Earth and subtends a larger angle at the eye. So, it may be considered a collection of a large number of point-sized objects. Due to atmospheric refraction, the quantity of light coming from any one point-sized object changes with time but the total light entering the observer’s eye due to all these point objects remains almost the same. As a result, the planet does not twinkle.
Q16: Explain with the help of a diagram, how we are able to observe the sunrise about two minutes before the sun gets above the horizon. Hence, explain why does apparent duration of a day from sunrise to sunset is 4 minutes more than its actual duration. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: The air becomes rarer as its height above the earth increases. Its refractive index decreases. A ray of light from the Sun when it enters the atmosphere at the horizon gets refracted from a rarer to a denser medium. The rays, therefore gradually bend towards the normal and the Sun appears to be raised.
As a result, the Sun is visible to an observer nearly two minutes before actual sunrise at the horizon. Similarly, even after actual sunset, the Sun is seen by us for about 2 minutes. Thus, in effect, the Sun is seen for 4 minutes more. It means that the apparent duration of the day (from sunrise to sunset) has increased by 4 minutes more than its actual duration.
Q17: (a) What is the dispersion of white light? State its cause.
(b) “Rainbow is an example of dispersion of sunlight” Justify this statement by explaining, with the help of a labelled diagram, the formation of a rainbow in the sky. List two essential conditions for observing a rainbow. (Foreign 2016)
Ans: (a) Dispersion: The splitting up of white light into its component colours is called dispersion.
Cause of dispersion: From Snell’s law of refraction, the angle of refraction of light in a prism depends on the refractive index of the prism material. Moreover, the refractive index of the material varies with the speed of light. The different constituent colours of white light have different speeds in the transparent material of the prism. Hence for each colour/wavelength, the refractive index of prism material is different. Therefore, each colour bends (refracted) through a different angle concerning incident rays, as they pass through the prism. The red colour has maximum speed in the glass prism, so it is least deviated, while the violet colour has minimum speed so its deviation is maximum. Thus, the ray of each colour emerges along different paths and becomes distinct.
(b) Rainbow: It is an optical natural spectrum, produced by nature in the sky, in the form of a multicoloured arc. The rainbow is formed due to the dispersion of sunlight by water droplets suspended in the atmosphere after rainfall. These water droplets act like small prisms. The Sunlight enters the water droplets. At the point of incidence, it refracts and disperses then gets reflected internally and finally gets refracted again at the point of emergence as it comes out of the rain-drop.
Therefore, due to refraction, dispersion and internal reflection of the sunlight, different colours reach the observer’s eye along different paths and become distinct. It creates a rainbow in the sky.
Hence “Rainbow is an example of dispersion of sunlight.”
Necessary conditions for the formation of a rainbow.
(i) The presence of water droplets in the atmosphere, and
(ii) The sun must be at the back of the observer, i.e. the observer must stand with his back towards the sun.
Q18: What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events.
(a) Twinkling of stars
(b) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset.
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answers. (AI 2016)
Ans: Atmospheric Refraction: The refraction of light caused by the earth’s atmosphere due to gradual change in the refractive indices of its different layers by the varying conditions of it, is called atmospheric refraction.
(a) Twinkling of stars
The hot layers (low densities) of air at a high altitude, behave as an optically rarer medium for the light rays, whereas the cold dense layers (high densities) of air near the earth’s surface, behave as an optically denser medium for the light rays. So, when the light rays (starlight) pass through the various layers of the atmosphere, they will deviate and bend toward the normal. As a result, the apparent position of the star is slightly different from its actual position. Thus, the stars appear slightly higher (above) than their actual positions in the sky. The fluctuation in the positions of the stars occurs continuously due to the changing amount of light entering the eye. The stars sometimes appear brighter and at some other times, they appear fainter. This causes the twinkling of stars.
The fluctuation in the positions of the stars occurs continuously due to the changing amount of light entering the eye. The stars sometimes appear brighter and at some other times, they appear fainter. This causes the twinkling of stars.
(b) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset: The sun is visible 2 minutes before sunrise and 2 minutes after sunset because of atmospheric refraction. This can be explained below.
The figure shows the actual position of the sun S at the time of sunrise or sunset, just below the horizon while the apparent position S’ above the horizon appears to us.
When the sun is slightly below the horizon, the light rays move through the different layers of varying refractive indices of air and get bent towards the normal. These rays appear to come from S’ which is the apparent position of the sun. That is why, the sun is visible to us when it has been actually below the horizon or before the actual crossing of the horizon by the sun at the time of sunrise or sunset. So, due to the atmospheric refraction, the phenomenon of advanced advance sunrise and delayed sunset is observed.
Q19: In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a triangular glass prism, a student would observe that the emergent ray:
(a) is parallel to the incident ray.
(b) is along the same direction of incident ray.
(c) gets deviated and bends towards the thinner part of the prism.
(d) gets deviated and bends towards the thicker part (base) of the prism. (CBSE 2016)
Ans: (d)
In a triangular glass prism, when a ray of light passes through, it first bends towards the normal upon entering the prism (due to refraction into a denser medium). As it exits the prism into a less dense medium (air), the emergent ray bends away from the normal. This causes the emergent ray to deviate from its original path, and it generally bends towards the thicker part (base) of the prism.
Thus, the correct answer is (d) gets deviated and bends towards the thicker part (base) of the prism.
| Also read: The Human Eye |
Previous Year Questions 2015
Q1: What is a pupil? (CBSE 2005,2013,2015)
Ans: The pupil is a small circular transparent aperture whose size is controlled by the iris.
Q2: Name the condition resulting due to the eye lens becoming cloudy. (CBSE 2012,2013,2015)
Ans: Cataract
Q3: What is the dispersion of light? (CBSE 2012,2015)
Ans: Dispersion of light is the splitting of light into its component colours on passing through a dispersive medium e.g., a prism.
Q4: List the factors on which the scattering of light depends. (CBSE 2012,2015)
Ans: The scattering of light depends on the size of the scattering particle and the wavelength of light.
Previous Year Questions 2014
Q1: What is myopia? List two causes for the development of this defect. How can this defect be corrected using a lens? Draw ray diagrams to show the image formation in case of (i) defective eye and (ii) corrected eye. OR
A student is unable to see the words written on the blackboard placed at a distance of approximately 4 m from him. Name the defect of vision the boy is suffering from. Explain the method of correcting this defect. Draw a ray diagram for the:
(i) defect of vision and also
(ii) for its correction. OR
What is myopia? State the two causes of myopia.
With the help of a labelled ray diagram show (a) the eye defect and (b) the correction of myopia. (DoE) (Foreign 2014)
Ans:
Myopia (Nearsightedness):
Myopia is a defect of vision in which a person can see nearby objects clearly but cannot see distant objects distinctly. The image of a distant object is formed in front of the retina instead of on it.
Causes:
- Excessive curvature of the eye lens.
- Elongation of the eyeball.
Correction:
- Concave lens (Diverging lens) is used to correct myopia.
- It diverges the incoming light rays so that the eye lens forms the image on the retina instead of in front of it.
Ray Diagrams:
(i) Defective Eye – Image of a distant object forms in front of the retina.
(ii) Corrected Eye – Concave lens diverges light rays, shifting the image onto the retina.

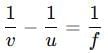







 for a given pair of media and light colour. This constant is the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first (Snell’s law).
for a given pair of media and light colour. This constant is the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first (Snell’s law).

 For a concave mirror take u = -10 cm (object to the left) and f = -15 cm. Substitute:
For a concave mirror take u = -10 cm (object to the left) and f = -15 cm. Substitute: so, v = +30 cm.
so, v = +30 cm.
 Take u = -30 cm (object to the left) and v = -60 cm (real image in front of mirror, same side as object).
Take u = -30 cm (object to the left) and v = -60 cm (real image in front of mirror, same side as object).
 Step 2:
Step 2:  and
and Image distance v =−24 cm indicates image is on the same side as object (virtual image).
Image distance v =−24 cm indicates image is on the same side as object (virtual image).


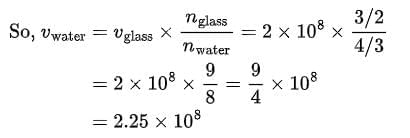

 (Sign ‘−’ means the object is placed on the incoming-light side; distance = 40 cm.)
(Sign ‘−’ means the object is placed on the incoming-light side; distance = 40 cm.)
 Mirror formula:
Mirror formula:






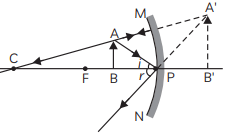
 This means that the speed of light in medium B is less than that in A and C:
This means that the speed of light in medium B is less than that in A and C:




 v = -36 cm
v = -36 cm



 (2) is directed towards its principal focus
(2) is directed towards its principal focus (ii) Given u = –16 cm, f = + 24 cm, h = 4 cm
(ii) Given u = –16 cm, f = + 24 cm, h = 4 cm


 The image is at v=+10cm, virtual and behind the mirror.
The image is at v=+10cm, virtual and behind the mirror. The positive focal length indicates a convex mirror, consistent with the positive magnification.
The positive focal length indicates a convex mirror, consistent with the positive magnification.
 Mirror Formula:
Mirror Formula: 
 The new object distance is 40 cm from the mirror.
The new object distance is 40 cm from the mirror. Magnification:
Magnification: The magnification is +1/3, as required.
The magnification is +1/3, as required.






 (B) The image of object obtained in the convex mirror is erect and diminished. This is because a convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image of an object.
(B) The image of object obtained in the convex mirror is erect and diminished. This is because a convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image of an object. 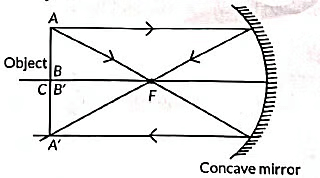

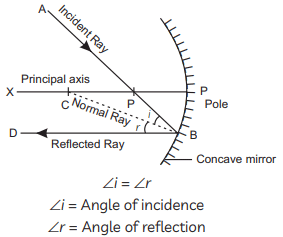
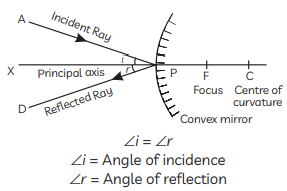
 The image formed is real, inverted and of the same size.
The image formed is real, inverted and of the same size.



 So, the object is placed at u=−25.
So, the object is placed at u=−25. The positive focal length indicates the lens is convex with a focal length of 12.5 cm.
The positive focal length indicates the lens is convex with a focal length of 12.5 cm. The negative sign indicates the image is formed on the same side as the object.Negative v′ means a virtual image on the object side.Object position: u=−25 cm (25 cm in front of lens).Focal length: f=+12.5 cm, convex lens.New image position: v′=−50 cm (50 cm on same side as object).
The negative sign indicates the image is formed on the same side as the object.Negative v′ means a virtual image on the object side.Object position: u=−25 cm (25 cm in front of lens).Focal length: f=+12.5 cm, convex lens.New image position: v′=−50 cm (50 cm on same side as object).

 (c) The four characteristics of the image formed by the convex mirror are virtual, erect, diminished and laterally inverted.
(c) The four characteristics of the image formed by the convex mirror are virtual, erect, diminished and laterally inverted.
















 Hence, when RRyy (round, green) is crossed with rrYY (wrinkled, yellow), all F₁ offspring have the genotype RrYy, expressing the dominant traits — round and yellow seeds.
Hence, when RRyy (round, green) is crossed with rrYY (wrinkled, yellow), all F₁ offspring have the genotype RrYy, expressing the dominant traits — round and yellow seeds.
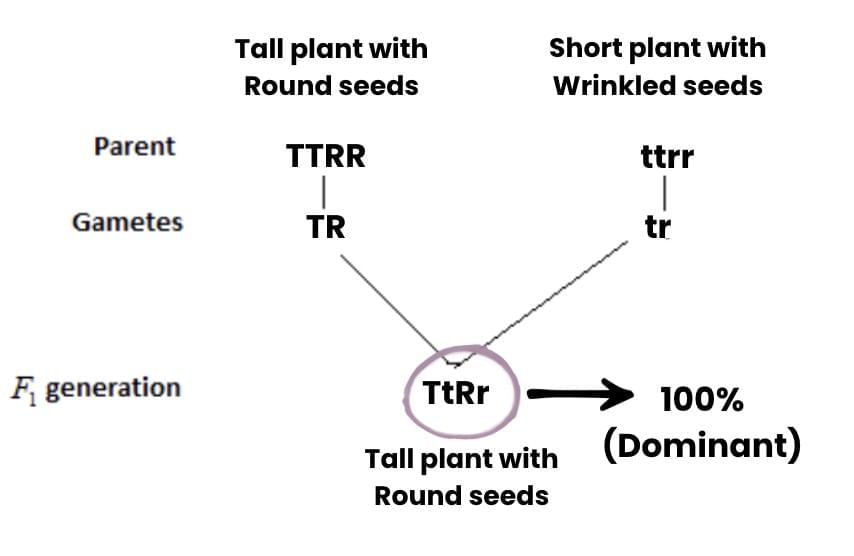
 When TT is crossed with tt, all offspring have the genotype Tt, which expresses the dominant tall trait.
When TT is crossed with tt, all offspring have the genotype Tt, which expresses the dominant tall trait. 1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt
1 TT : 2 Tt : 1 tt
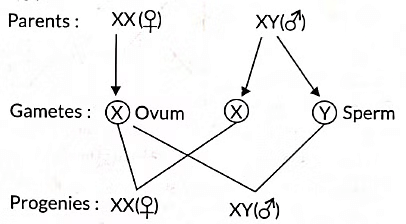
 During fertilisation, the male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote, restoring the diploid number of chromosomes. This ensures the stability of DNA content and the chromosome number in each new generation.
During fertilisation, the male and female gametes fuse to form a zygote, restoring the diploid number of chromosomes. This ensures the stability of DNA content and the chromosome number in each new generation.



 (b) On self-pollinating the F₁ plants (RrYy × RrYy), the F₂ generation shows four possible trait combinations of seeds in the ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 —
(b) On self-pollinating the F₁ plants (RrYy × RrYy), the F₂ generation shows four possible trait combinations of seeds in the ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 —



 (iii) (A) Self-pollination / Self-fertilisation / Selfing of F1 plants
(iii) (A) Self-pollination / Self-fertilisation / Selfing of F1 plants
 75% yellow seeds
75% yellow seeds OR
OR





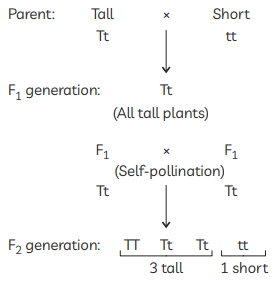
 So, the plants of F1 generation will be all tall plants and after self pollinating the ratio of tall and dwarf plants that Mendel obtained in F2 generation plants is 3 : 1.
So, the plants of F1 generation will be all tall plants and after self pollinating the ratio of tall and dwarf plants that Mendel obtained in F2 generation plants is 3 : 1.

 Skeleton of forelimbs of (a) Human (b) Dog (c) Bird (d) Whale showing homologous features.
Skeleton of forelimbs of (a) Human (b) Dog (c) Bird (d) Whale showing homologous features. (ii) Analogous organs: Such organs which perform similar functions but are structurally different are called analogous organs. For example, wings of a bird and wing of an insect. Presence of such organs show that these organisms have different origin.
(ii) Analogous organs: Such organs which perform similar functions but are structurally different are called analogous organs. For example, wings of a bird and wing of an insect. Presence of such organs show that these organisms have different origin.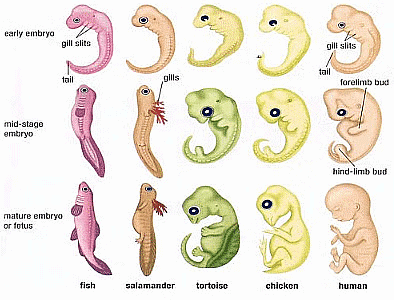



 Independent inheritance of two separate traits, shape and colour of seeds(i) Traits may be dominant or recessive:
Independent inheritance of two separate traits, shape and colour of seeds(i) Traits may be dominant or recessive:
 Hence, genotype Tt with a recessive gene is expressed as phenotype of Tall. This shows that only dominant gene is expressed as the trait (T) while ‘t’ is not expressed.
Hence, genotype Tt with a recessive gene is expressed as phenotype of Tall. This shows that only dominant gene is expressed as the trait (T) while ‘t’ is not expressed.
 (a) All flowers in F1 progeny will be blue in colour.
(a) All flowers in F1 progeny will be blue in colour.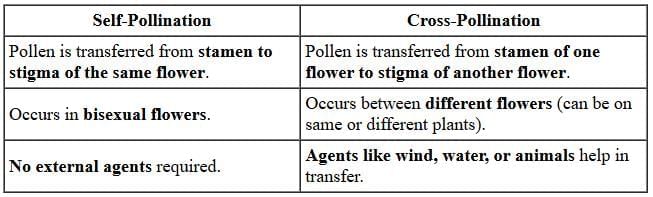






 (ii) Yellowish Structures: Pollen grains
(ii) Yellowish Structures: Pollen grains
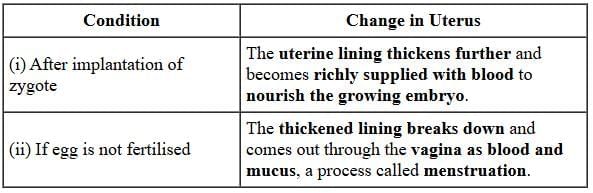


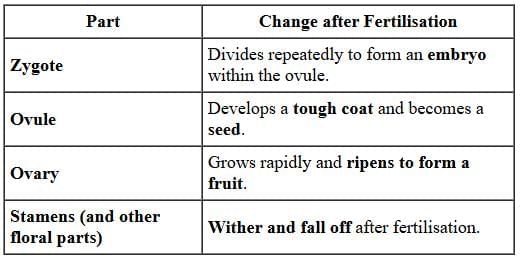
 (b) Petals, they dry and fall off.
(b) Petals, they dry and fall off. 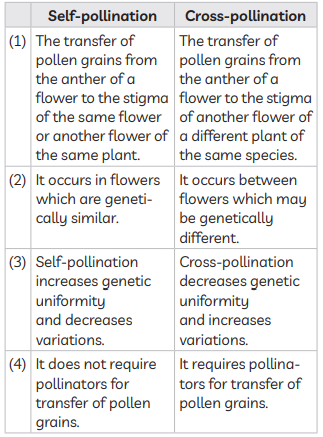
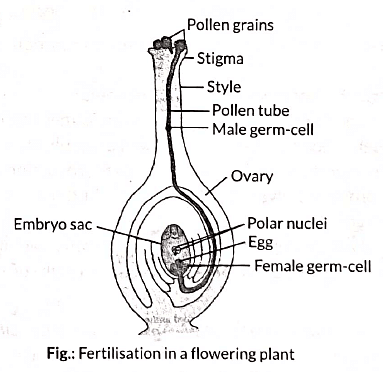
 Fertilisation, in plants, occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grain fuses with the female gamete (or egg) present in ovule. When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, it bursts open and grows a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary. Male gametes move down the pollen tube. The pollen tube enters the ovule in the ovary. The tip of pollen tube bursts and male gametes comes out of pollen tube. In ovary, the male gamete of pollen combines with the female gamete or egg present in ovule to form a fertilised egg. After fertilisation,(i) ovule develops into seed
Fertilisation, in plants, occurs when the male gamete present in pollen grain fuses with the female gamete (or egg) present in ovule. When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, it bursts open and grows a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary. Male gametes move down the pollen tube. The pollen tube enters the ovule in the ovary. The tip of pollen tube bursts and male gametes comes out of pollen tube. In ovary, the male gamete of pollen combines with the female gamete or egg present in ovule to form a fertilised egg. After fertilisation,(i) ovule develops into seed
 (b) Gonorrhoea and syphilis are two bacterial diseases which are transmitted sexually.
(b) Gonorrhoea and syphilis are two bacterial diseases which are transmitted sexually. The species reproducing sexually will have better chances of survival because genetic variation is created during sexual reproduction; in case of an adverse environmental change, atleast some variants will survive and continue the race.
The species reproducing sexually will have better chances of survival because genetic variation is created during sexual reproduction; in case of an adverse environmental change, atleast some variants will survive and continue the race.



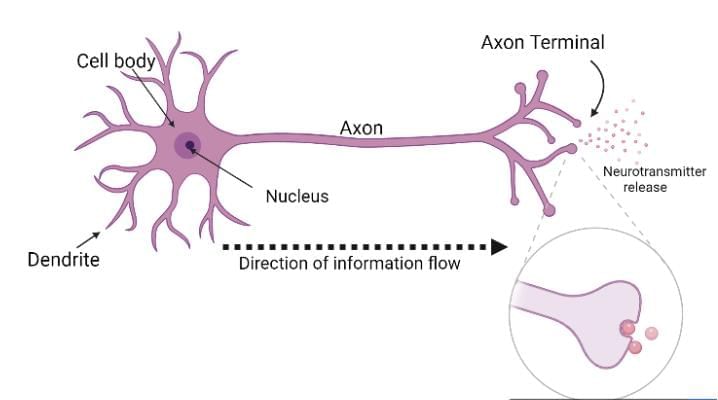


 (ii)A reflex action is a quick, automatic, and involuntary response to a stimulus. It is controlled by the spinal cord and helps protect the body from sudden harmful changes in the environment.
(ii)A reflex action is a quick, automatic, and involuntary response to a stimulus. It is controlled by the spinal cord and helps protect the body from sudden harmful changes in the environment.

 OR
OR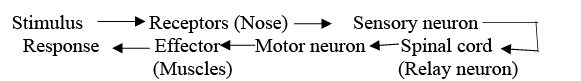






 Sequence of events when we touch a hot object are:
Sequence of events when we touch a hot object are:






 (ii) During inhalation, the ribs move upward and outward, and the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, increasing the space in the chest cavity. This creates low pressure, allowing air to enter the lungs.
(ii) During inhalation, the ribs move upward and outward, and the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, increasing the space in the chest cavity. This creates low pressure, allowing air to enter the lungs.

 (a) Evaporation : maintains water contents in leaf cells.
(a) Evaporation : maintains water contents in leaf cells. (ii) The separation of the heart into right and left sides is beneficial because:
(ii) The separation of the heart into right and left sides is beneficial because:









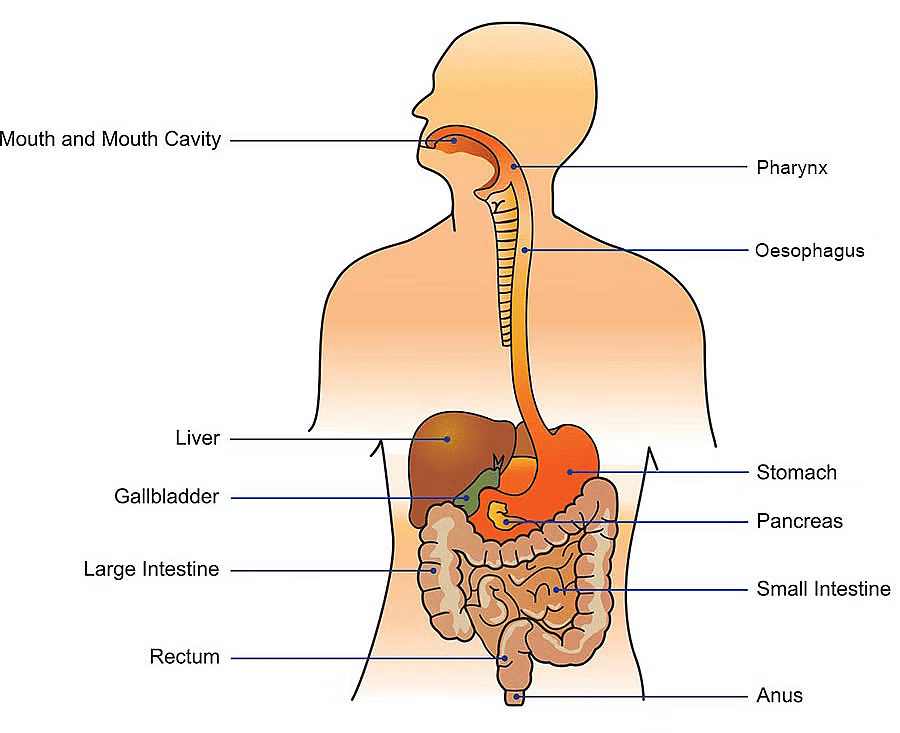
 Excretory System of Human Beings
Excretory System of Human Beings














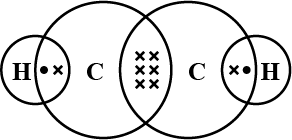
 Electron dot structure of Methane
Electron dot structure of Methane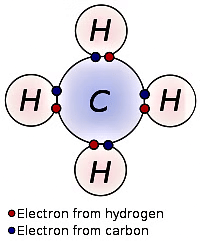
 Cyclohexane
Cyclohexane
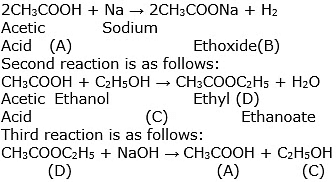







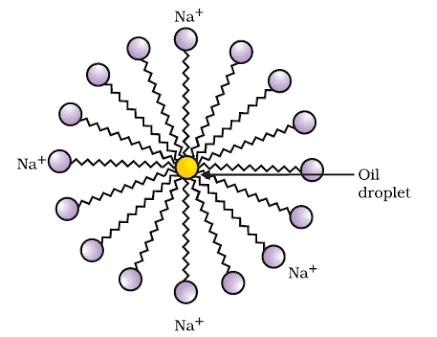
 When a soap is dissolved in water, the molecules associate together as clusters called micelles in which, water molecules being polar in nature, surround the ions and the hydrocarbon part of the molecule attracts grease, oil and dirt.Hard water has Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions when they react with soap to form insoluble compound and soap goes waste.
When a soap is dissolved in water, the molecules associate together as clusters called micelles in which, water molecules being polar in nature, surround the ions and the hydrocarbon part of the molecule attracts grease, oil and dirt.Hard water has Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions when they react with soap to form insoluble compound and soap goes waste.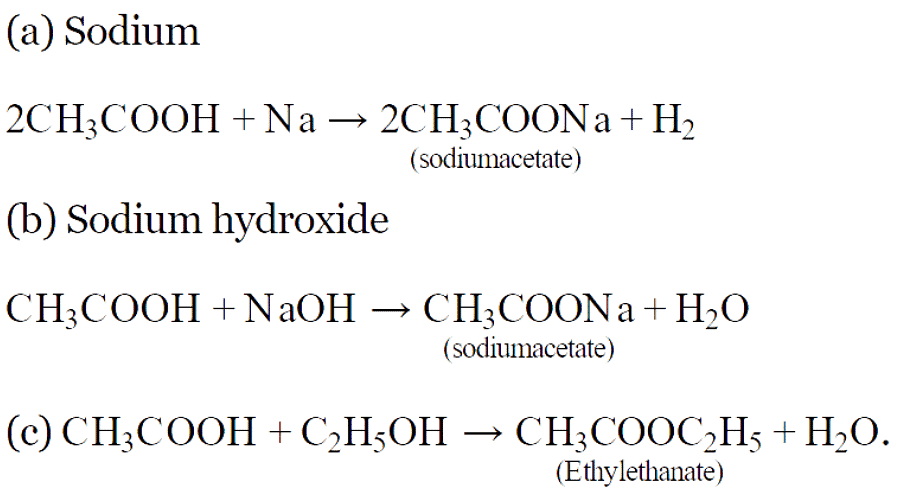
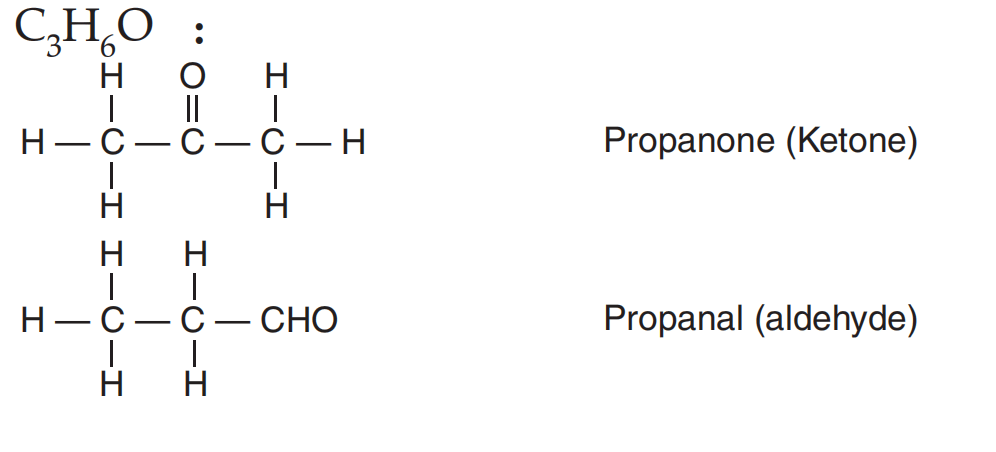



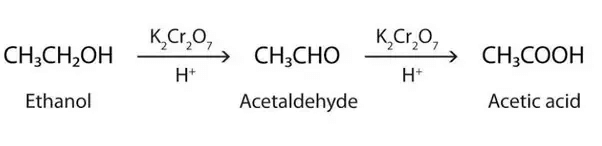

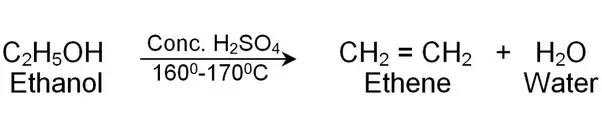
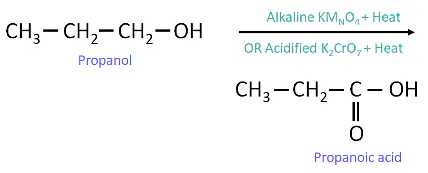

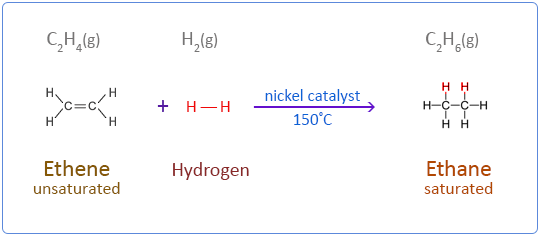

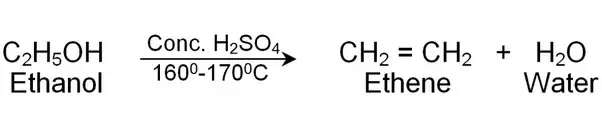






 (iv) Electron Dot Structure of B (CH₃COOH):
(iv) Electron Dot Structure of B (CH₃COOH):








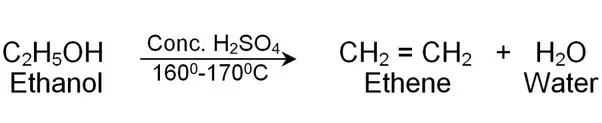
 Reaction between the alcohol and the acid in presence of an acid (esterification)
Reaction between the alcohol and the acid in presence of an acid (esterification) (Ester formed: ethyl ethanoate, a sweet-smelling compound used in perfumes and flavoring.)
(Ester formed: ethyl ethanoate, a sweet-smelling compound used in perfumes and flavoring.) (c) (A) NH₃ Formation:
(c) (A) NH₃ Formation: OR
OR 




 OR
OR













 Due to small size, the nucleus of carbon atom can hold its shared pairs of electrons strongly. As a result, the bonds that carbon forms with most of the other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc. are very strong there by making these compounds exceptionally stable.
Due to small size, the nucleus of carbon atom can hold its shared pairs of electrons strongly. As a result, the bonds that carbon forms with most of the other elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc. are very strong there by making these compounds exceptionally stable.








 (C) Compound C is ethane. When it undergoes combustion, it forms CO2 and water.
(C) Compound C is ethane. When it undergoes combustion, it forms CO2 and water. (D) Hydrogenation reactions are used in the production of saturated vegetable ghee from unsaturated vegetable oils.
(D) Hydrogenation reactions are used in the production of saturated vegetable ghee from unsaturated vegetable oils. 







 (b) The compound ‘X’ is likely an unsaturated compound (such as an alkene or alkyne) that burns in air, producing a yellow, sooty flame with significant smoke.
(b) The compound ‘X’ is likely an unsaturated compound (such as an alkene or alkyne) that burns in air, producing a yellow, sooty flame with significant smoke.
















 So, the gas is hydrogen that is evolved during the reaction.
So, the gas is hydrogen that is evolved during the reaction.


 In this reaction, sodium displaces hydrogen from ethanol, resulting in the formation of sodium ethoxide and the release of hydrogen gas.
In this reaction, sodium displaces hydrogen from ethanol, resulting in the formation of sodium ethoxide and the release of hydrogen gas.










 There are total 7 covalent bonds. Six C — H covalent bonds and one C — C covalent bond.
There are total 7 covalent bonds. Six C — H covalent bonds and one C — C covalent bond.


 OR
OR






 (B) Metal oxides are categorised as amphoteric oxides that react with both acids as well as bases to create salts and water. Amphoteric oxides, among many others, include lead oxide and zinc oxide. These oxides are oxygen compounds that show both acidic and basic characteristics. These undergo a neutralisation reaction to form water and salt.
(B) Metal oxides are categorised as amphoteric oxides that react with both acids as well as bases to create salts and water. Amphoteric oxides, among many others, include lead oxide and zinc oxide. These oxides are oxygen compounds that show both acidic and basic characteristics. These undergo a neutralisation reaction to form water and salt.


 Thus, the “milkiness” arises from the formation of solid calcium carbonate.OR
Thus, the “milkiness” arises from the formation of solid calcium carbonate.OR










 (b) The metals in the middle of the reactivity series are obtained from their ores by chemical reduction with a suitable reducing agent, e.g.
(b) The metals in the middle of the reactivity series are obtained from their ores by chemical reduction with a suitable reducing agent, e.g.


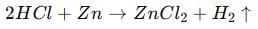
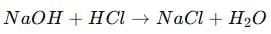
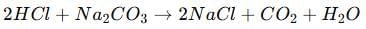

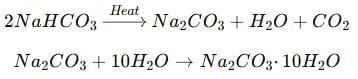

 (ii) Sodium chloride is neutral in nature because it is formed from a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH), giving a salt with pH 7.
(ii) Sodium chloride is neutral in nature because it is formed from a strong acid (HCl) and a strong base (NaOH), giving a salt with pH 7.



 (B) The differences between baking soda and baking powder are:
(B) The differences between baking soda and baking powder are:
 X: NaOH (Sodium hydroxide)
X: NaOH (Sodium hydroxide)

 Baking soda on heating gives sodium carbonate which on crystallisation from aqueous solution gives washing soda, e.g.
Baking soda on heating gives sodium carbonate which on crystallisation from aqueous solution gives washing soda, e.g.